Direct Characterization of Quantum Dynamics: General Theory
... and comprehensive comparison of the required physical resources in different QPT schemes see Ref. [3]. ...
... and comprehensive comparison of the required physical resources in different QPT schemes see Ref. [3]. ...
Multiply Excited Intra
... the basis of symmetry and therefore independent of the model describing the dynamics of the system. Hence, the resulting classification schemes are very general and useful in connection with the so-called symmetric rotor model presented in chapters 3 and 4. The classification follows the ideas prese ...
... the basis of symmetry and therefore independent of the model describing the dynamics of the system. Hence, the resulting classification schemes are very general and useful in connection with the so-called symmetric rotor model presented in chapters 3 and 4. The classification follows the ideas prese ...
Quantum Computing - Department of Computing
... Quantum mechanics is a very accurate description of nature as it predicts quantum effects up to an astonishing precision of 14 decimal places. But we do not know why nature works like that and why quantum mechanics gives such a good description of nature. In other words, quantum mechanics tells us h ...
... Quantum mechanics is a very accurate description of nature as it predicts quantum effects up to an astonishing precision of 14 decimal places. But we do not know why nature works like that and why quantum mechanics gives such a good description of nature. In other words, quantum mechanics tells us h ...
How the Laws of Physics Lie
... finally, ‘a physical explanation in terms of electron theory’ given by Lorentz, which is ‘essentially the theory we accept today’. Everitt distinguishes Airy's phenomenological law from the later theoretical treatment of Lorentz, not because Lorentz employs the unobservable electron, but rather beca ...
... finally, ‘a physical explanation in terms of electron theory’ given by Lorentz, which is ‘essentially the theory we accept today’. Everitt distinguishes Airy's phenomenological law from the later theoretical treatment of Lorentz, not because Lorentz employs the unobservable electron, but rather beca ...
Tensor Product Methods and Entanglement
... (TTNS) approach.[98–100] The QC-TTNS combines a number of favorable features that suggest it might represent a novel, flexible approach in quantum chemistry: the more general concept of data-sparsity inherent in the TNS representation allows for the efficient representation of a much bigger class of ...
... (TTNS) approach.[98–100] The QC-TTNS combines a number of favorable features that suggest it might represent a novel, flexible approach in quantum chemistry: the more general concept of data-sparsity inherent in the TNS representation allows for the efficient representation of a much bigger class of ...
Quantum Computing
... Deutsch developed a notion of a quantum mechanical Turing machine. Bernstein, Vazirani, and Yao showed that quantum computers can do anything a classical computer can do with at most a small (logarithmic) slow down. The early 1990s saw the first truly quantum algorithms, algorithms with no classica ...
... Deutsch developed a notion of a quantum mechanical Turing machine. Bernstein, Vazirani, and Yao showed that quantum computers can do anything a classical computer can do with at most a small (logarithmic) slow down. The early 1990s saw the first truly quantum algorithms, algorithms with no classica ...
Experimental one-way quantum computing
... single-particle measurements carried out from the left side of the cluster to the right side, where the final readout takes place. The important feature of the quantum circuits is that the output of one circuit can be fed into the input of a subsequent one if their cluster states are bonded together ...
... single-particle measurements carried out from the left side of the cluster to the right side, where the final readout takes place. The important feature of the quantum circuits is that the output of one circuit can be fed into the input of a subsequent one if their cluster states are bonded together ...
Graphene and Relativistic Quantum Physics
... the Berry’s phase induced by the pseudo spin rotation. In particular, for complete backscattering, Eq. (5) yields R(2π) = eiπ , indicating that rotation in κ by 2π leads to a change of the phase of the wave function |κi by π. This non-trivial Berry’s phase may lead to non-trivial quantum corrections ...
... the Berry’s phase induced by the pseudo spin rotation. In particular, for complete backscattering, Eq. (5) yields R(2π) = eiπ , indicating that rotation in κ by 2π leads to a change of the phase of the wave function |κi by π. This non-trivial Berry’s phase may lead to non-trivial quantum corrections ...
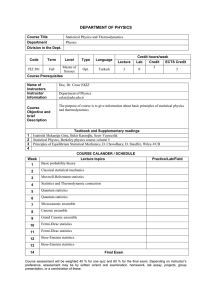
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Course Title Statistical Physics and
... A Brief Summary of Special Relativity ...
... A Brief Summary of Special Relativity ...