First Reading Assignment
... ‘‘an electron came through the double-slit,’’ we really mean that an extended singly excited field came through the double-slit. This field cannot be an electromagnetic field because a similar pattern appears with all beams of matter, even uncharged neutron beams, atomic beams, and C60 !buckeyball" ...
... ‘‘an electron came through the double-slit,’’ we really mean that an extended singly excited field came through the double-slit. This field cannot be an electromagnetic field because a similar pattern appears with all beams of matter, even uncharged neutron beams, atomic beams, and C60 !buckeyball" ...
Inverse magnetic catalysis in QCD and holography
... catalysis effects and the temperature dependence of the deconfinement temperature. Although these computations are still not confirmed by experiments, they are generally regarded as reliable, since they make no additional assumptions other than the QCD Lagrangian. The other method, the one we will b ...
... catalysis effects and the temperature dependence of the deconfinement temperature. Although these computations are still not confirmed by experiments, they are generally regarded as reliable, since they make no additional assumptions other than the QCD Lagrangian. The other method, the one we will b ...
Scientific Evaluation of Aulterra`s cell phone neutralizer
... superimposed fields. The first report of such an interaction demonstrated that a secondary crossbeam of visible light could neutralize the biological effects (induction of glutamate-pyruvate-transaminase activity by pretreatment of the substrate alanine) produced by a primary beam of visible light ...
... superimposed fields. The first report of such an interaction demonstrated that a secondary crossbeam of visible light could neutralize the biological effects (induction of glutamate-pyruvate-transaminase activity by pretreatment of the substrate alanine) produced by a primary beam of visible light ...
Syllabus of B.Sc. Physics
... charged particle in a uniform magnetic field, applications: velocity selector and mass spectrometer, magnetic force on a current carrying wire, torque on a current loop, Biot and Savart’s law, Magnetic field due to a finite straight wire, Force between two parallel wires, Ampere law, Field inside an ...
... charged particle in a uniform magnetic field, applications: velocity selector and mass spectrometer, magnetic force on a current carrying wire, torque on a current loop, Biot and Savart’s law, Magnetic field due to a finite straight wire, Force between two parallel wires, Ampere law, Field inside an ...
Chapter 8: Magnetism - Farmingdale State College
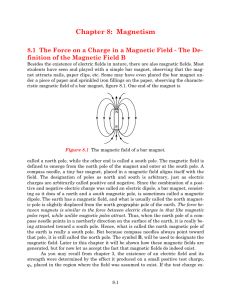
... called a north pole, while the other end is called a south pole. The magnetic field is defined to emerge from the north pole of the magnet and enter at the south pole. A compass needle, a tiny bar magnet, placed in a magnetic field aligns itself with the field. The designation of poles as north and ...
... called a north pole, while the other end is called a south pole. The magnetic field is defined to emerge from the north pole of the magnet and enter at the south pole. A compass needle, a tiny bar magnet, placed in a magnetic field aligns itself with the field. The designation of poles as north and ...
Electrons as field quanta: A better way to teach quantum physics in introductory general physics courses
... ‘‘an electron came through the double-slit,’’ we really mean that an extended singly excited field came through the double-slit. This field cannot be an electromagnetic field because a similar pattern appears with all beams of matter, even uncharged neutron beams, atomic beams, and C60 共buckeyball兲 ...
... ‘‘an electron came through the double-slit,’’ we really mean that an extended singly excited field came through the double-slit. This field cannot be an electromagnetic field because a similar pattern appears with all beams of matter, even uncharged neutron beams, atomic beams, and C60 共buckeyball兲 ...
Electrons as field quanta: A better way to teach quantum physicsin introductory general physics courses
... ‘‘an electron came through the double-slit,’’ we really mean that an extended singly excited field came through the double-slit. This field cannot be an electromagnetic field because a similar pattern appears with all beams of matter, even uncharged neutron beams, atomic beams, and C60 共buckeyball兲 ...
... ‘‘an electron came through the double-slit,’’ we really mean that an extended singly excited field came through the double-slit. This field cannot be an electromagnetic field because a similar pattern appears with all beams of matter, even uncharged neutron beams, atomic beams, and C60 共buckeyball兲 ...
Weak antilocalization and spin relaxation in integrable quantum dots O Z
... During the last years research on the effects of spin-orbit (SO) interactions on transport has again received increasing attention. The reason for the revival of such studies, both experimentally and theoretically, lies in an important role SO interactions play in spin electronics and spin-based qua ...
... During the last years research on the effects of spin-orbit (SO) interactions on transport has again received increasing attention. The reason for the revival of such studies, both experimentally and theoretically, lies in an important role SO interactions play in spin electronics and spin-based qua ...
Reduced absorption coefficient (RAC)
... wing of the first resonant line. X-B transition has a difference potential curve with one maximum and contribute to the “blue” wing and “blue” satellite band. ...
... wing of the first resonant line. X-B transition has a difference potential curve with one maximum and contribute to the “blue” wing and “blue” satellite band. ...
III. Spin and orbital angular momentum
... The Stern-Gerlach experiment therefore points to another source of magnetic momentum, quite different from what arises from the orbital angular momentum. From this and other experiments it has been concluded that each elementary particle has intrinsic ~ Spin is a new degree angular momentum which is ...
... The Stern-Gerlach experiment therefore points to another source of magnetic momentum, quite different from what arises from the orbital angular momentum. From this and other experiments it has been concluded that each elementary particle has intrinsic ~ Spin is a new degree angular momentum which is ...
LITHIUM, SODIUM, AND POTASSIUM RESONANCE LINES
... wing of the first resonant line. X-B transition has a difference potential curve with one maximum and contribute to the “blue” wing and “blue” satellite band. ...
... wing of the first resonant line. X-B transition has a difference potential curve with one maximum and contribute to the “blue” wing and “blue” satellite band. ...
Two-orbital SU(N) magnetism with ultracold alkaline-earth
... the resulting SU (N ) spin symmetry (where N = 2I + 1 can be as large as 10) together with the possibility of combining (nuclear) spin physics with (electronic) orbital physics opens up a wide field of rich many-body systems with alkaline-earth atoms. In what follows, we derive the two-orbital SU (N ...
... the resulting SU (N ) spin symmetry (where N = 2I + 1 can be as large as 10) together with the possibility of combining (nuclear) spin physics with (electronic) orbital physics opens up a wide field of rich many-body systems with alkaline-earth atoms. In what follows, we derive the two-orbital SU (N ...
che-20028 QC lecture 2 - Rob Jackson`s Website
... (Extra slide 2): Demonstration of ZPE: helium at low temperatures • Experimental measurement of zero point energy is difficult(!) but its consequences can be seen: – As temperature is lowered to absolute zero, helium remains a liquid, rather than freezing to a solid, because of its zero-point energ ...
... (Extra slide 2): Demonstration of ZPE: helium at low temperatures • Experimental measurement of zero point energy is difficult(!) but its consequences can be seen: – As temperature is lowered to absolute zero, helium remains a liquid, rather than freezing to a solid, because of its zero-point energ ...
Fiber Bundles and Quantum Theory
... 90-degree rotation of the neutron spin vector. The half-angle relation continues. When the physical spin vector has rotated 180 degrees, it points down. The spin-down probability amplitude is +1 and the spin-up probability is 0. The corresponding point in the neutron-state space is 90 degrees from t ...
... 90-degree rotation of the neutron spin vector. The half-angle relation continues. When the physical spin vector has rotated 180 degrees, it points down. The spin-down probability amplitude is +1 and the spin-up probability is 0. The corresponding point in the neutron-state space is 90 degrees from t ...
p-type and n-type semiconductors
... characterizes a PV cell. This is done a number of different ways, depending on the characteristics of the material; for example, amorphous silicon’s unique structure makes an intrinsic layer (or i layer) necessary. This undoped layer of amorphous silicon fits between the n-type and p-type layers to ...
... characterizes a PV cell. This is done a number of different ways, depending on the characteristics of the material; for example, amorphous silicon’s unique structure makes an intrinsic layer (or i layer) necessary. This undoped layer of amorphous silicon fits between the n-type and p-type layers to ...
Living in a Quantum World
... For quantum electrons, however, the situation is astonish- behave classically. The difficulty of preserving entanglement is a ingly different. You can set up the particles to have a total spin major challenge for those of us seeking to exploit these novel efof zero even when you have not specified w ...
... For quantum electrons, however, the situation is astonish- behave classically. The difficulty of preserving entanglement is a ingly different. You can set up the particles to have a total spin major challenge for those of us seeking to exploit these novel efof zero even when you have not specified w ...
Topological Insulators
... tube (the dirac string) comes up the negative z axis, smuggling in the entire flux. ...
... tube (the dirac string) comes up the negative z axis, smuggling in the entire flux. ...
Two types of proton-electron atoms in a vacuum and an
... neutron, was suggested by Rutherford in 1920 [1]. The existence of the neutron was confirmed in 1932 by Chadwick, however the proton-electron model of the neutron was left because of its contradictions with quantum mechanics [2]. (a) According to quantum mechanics, the total angular momentum of the ...
... neutron, was suggested by Rutherford in 1920 [1]. The existence of the neutron was confirmed in 1932 by Chadwick, however the proton-electron model of the neutron was left because of its contradictions with quantum mechanics [2]. (a) According to quantum mechanics, the total angular momentum of the ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.