1 Slinking round Learning Objectives: 1. Explore the Earthss
... How does the magnetic field measurements differ if you measure through one end of the slinky compared to the other end of the slinky? Why? ...
... How does the magnetic field measurements differ if you measure through one end of the slinky compared to the other end of the slinky? Why? ...
74. Leakage field of the transformer
... be zero. Since the dissipation in an iron core is rather high, in technical transformers the distance between the primary and the secondary coil is made as short as possible. Origin: In the common discussion of the working principle of the transformer one does not argue with the magnetic field stren ...
... be zero. Since the dissipation in an iron core is rather high, in technical transformers the distance between the primary and the secondary coil is made as short as possible. Origin: In the common discussion of the working principle of the transformer one does not argue with the magnetic field stren ...
chapter-27-1-with
... electrons out of atoms. • Light must provide energy to overcome electrical attraction of electron to nucleus – This amount of energy is called the work function (W0) of the metal. ...
... electrons out of atoms. • Light must provide energy to overcome electrical attraction of electron to nucleus – This amount of energy is called the work function (W0) of the metal. ...
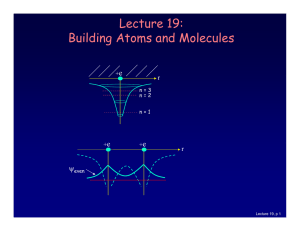
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... Just like electrons, the proton in the H atom also has a spin, which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
... Just like electrons, the proton in the H atom also has a spin, which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
Question bank of magnetism - Kendriya Vidyalaya SAC, Vastrapur
... and B respectively. For what values of the electron speed the beam will remain undeflected? 2. Write any three characteristics of Ferro magnetic substance should possesses if it is to be used to make a permanent magnet.. Give an example of such a material. 3. If χ stands for the magnetic susceptibil ...
... and B respectively. For what values of the electron speed the beam will remain undeflected? 2. Write any three characteristics of Ferro magnetic substance should possesses if it is to be used to make a permanent magnet.. Give an example of such a material. 3. If χ stands for the magnetic susceptibil ...
magnetic-properties
... induction of the magnetic material. This effect of retardation by material is called hysteresis. The magnetic field strength needed to bring the induced magnetization to zero is termed as coercivity, Hc. This must be applied anti-parallel to the original field. A further increase in the field in ...
... induction of the magnetic material. This effect of retardation by material is called hysteresis. The magnetic field strength needed to bring the induced magnetization to zero is termed as coercivity, Hc. This must be applied anti-parallel to the original field. A further increase in the field in ...
The Hall Effect - The Ohio State University
... of zero during calibration as the variable field magnet did not go to zero, so it is possible that as long as a current is flowing through it, even if it is not exposed to a magnetic field, some Hall voltage will be measured, resulting in a pseudo-magnetic field. The earth’s magnetic field may have ...
... of zero during calibration as the variable field magnet did not go to zero, so it is possible that as long as a current is flowing through it, even if it is not exposed to a magnetic field, some Hall voltage will be measured, resulting in a pseudo-magnetic field. The earth’s magnetic field may have ...
Small Current-Loops [ [ ].
... Since the divergence of B is also zero φm satisfies Laplace’s equation which means that many results derived for electrostatics can be reused for magnetostatics. Things are not entirely straightforward as φm is often not single valued and getting boundary conditions right can be tricky. A simple exa ...
... Since the divergence of B is also zero φm satisfies Laplace’s equation which means that many results derived for electrostatics can be reused for magnetostatics. Things are not entirely straightforward as φm is often not single valued and getting boundary conditions right can be tricky. A simple exa ...
THE SOCIETY FOR ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PHYSICAL
... "The Detection of Photochemically-formed Radicals by Magnetic Resonance." By D. J. E. Ingram, M.A., D.Phil. The technique of electron resonance has been employed for some time now not only to observe the state and presence of normal paramagnetic atoms but also to study organic free radicals. Until r ...
... "The Detection of Photochemically-formed Radicals by Magnetic Resonance." By D. J. E. Ingram, M.A., D.Phil. The technique of electron resonance has been employed for some time now not only to observe the state and presence of normal paramagnetic atoms but also to study organic free radicals. Until r ...
I Magnetism in Nature
... magnetic moments, free to rotate. In the absence of any external field and at a finite temperature, they will orient themselves in all directions randomly due to thermal fluctuations: ...
... magnetic moments, free to rotate. In the absence of any external field and at a finite temperature, they will orient themselves in all directions randomly due to thermal fluctuations: ...
Magnon collapse near the Lifshitz point and Leon Balents, KITP, UCSB
... seen at 9 K is an experimental artifact. It was notmagnetic susceptibility χ shown in Fig. 1(a) in a wide The easy to extract a magnetic contribution Cm from the ...
... seen at 9 K is an experimental artifact. It was notmagnetic susceptibility χ shown in Fig. 1(a) in a wide The easy to extract a magnetic contribution Cm from the ...
Variability and Stability in Blazar Jets on Time
... FRI/FRII-type AGN using 85cm telescope at San Pedro Martir 100N/year over a period of (at least) 3 years ...
... FRI/FRII-type AGN using 85cm telescope at San Pedro Martir 100N/year over a period of (at least) 3 years ...
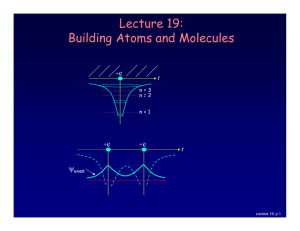
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... Just like electrons, the proton in the H atom also has a spin, which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
... Just like electrons, the proton in the H atom also has a spin, which is described by an additional quantum number, mp, and therefore also a magnetic moment. However, it is several orders of magnitude smaller than that of the electron. ...
Development of electrostatically controlled quantum Hall
... Search for non-Abelian excitations is motivated by both scientific curiosity and a practical desire to alleviate decoherence problems of conventional qubits[1, 2]. While current efforts are primarily focused on the discovery of Majorana fermions, it is understood that braiding of Majoranas is not s ...
... Search for non-Abelian excitations is motivated by both scientific curiosity and a practical desire to alleviate decoherence problems of conventional qubits[1, 2]. While current efforts are primarily focused on the discovery of Majorana fermions, it is understood that braiding of Majoranas is not s ...
Document
... A cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable is shown. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, which is surrounded by an outer conductor, which is surrounded by another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is 1.00 A out of the page and the current ...
... A cross-sectional view of a coaxial cable is shown. The center conductor is surrounded by a rubber layer, which is surrounded by an outer conductor, which is surrounded by another rubber layer. In a particular application, the current in the inner conductor is 1.00 A out of the page and the current ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.






![Small Current-Loops [ [ ].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001674646_1-cf546715d7619106aabfdbe7ffe448eb-300x300.png)