Aufbau Diagram Directions
... To figure out the electron configuration In doing so, we demonstrate the 3 main principles: Aufbau: Electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first Pauli Exclusion: an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons (each electron will have a different spin) Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbita ...
... To figure out the electron configuration In doing so, we demonstrate the 3 main principles: Aufbau: Electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first Pauli Exclusion: an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons (each electron will have a different spin) Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbita ...
Physical Science
... Matter – Anything that has mass and takes up space Mass – the amount of matter something contains Solid – matter that has a definite shape and takes up a definite amount of space Liquid – matter that takes the shape of its container and takes up a definite amount of space ...
... Matter – Anything that has mass and takes up space Mass – the amount of matter something contains Solid – matter that has a definite shape and takes up a definite amount of space Liquid – matter that takes the shape of its container and takes up a definite amount of space ...
Unit 2 Review KEY
... Quantum – minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. Photon – particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. Heisenberg uncertainty principle – it is impossible to determine at the same time both the position and the velocity of an ele ...
... Quantum – minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. Photon – particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. Heisenberg uncertainty principle – it is impossible to determine at the same time both the position and the velocity of an ele ...
Degeneracy of Hydrogen atom
... Degeneracy of Hydrogen atom In quantum mechanics, an energy level is said to be degenerate if it corresponds to two or more different measurable states of a quantum system. Conversely, two or more different states of a quantum mechanical system are said to be degenerate if they give the same value o ...
... Degeneracy of Hydrogen atom In quantum mechanics, an energy level is said to be degenerate if it corresponds to two or more different measurable states of a quantum system. Conversely, two or more different states of a quantum mechanical system are said to be degenerate if they give the same value o ...
Chapter 30
... Some examples are given in the table at right The magnetic moment of a proton or neutron is much smaller than that of an electron and can usually be neglected ...
... Some examples are given in the table at right The magnetic moment of a proton or neutron is much smaller than that of an electron and can usually be neglected ...
Magnetic properties of Materials
... magnetization is zero when the field is removed. In the presence of a field, there is now a partial alignment of the atomic magnetic moments in the direction of the field, resulting in a net positive magnetization and positive susceptibility. ...
... magnetization is zero when the field is removed. In the presence of a field, there is now a partial alignment of the atomic magnetic moments in the direction of the field, resulting in a net positive magnetization and positive susceptibility. ...
ELECTRON BEAM IN A MAGNETIC FIELD
... A charged body moving relative to a magnetic field experiences a force which is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and to the magnetic field. This phenomenon is exploited in modern technology in electric motors, generators, meters, sensors, cathode ray tubes (CRTs - used in visual di ...
... A charged body moving relative to a magnetic field experiences a force which is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and to the magnetic field. This phenomenon is exploited in modern technology in electric motors, generators, meters, sensors, cathode ray tubes (CRTs - used in visual di ...
Voltage-tunable ferromagnetism in semimagnetic quantum dots with
... material systems.4 This ability to externally control the properties of magnetic crystals with means other than the external magnetic field may have important device applications. An important feature of modern nanotechnology is the ability to shape semiconductor crystals, designing their quantum pr ...
... material systems.4 This ability to externally control the properties of magnetic crystals with means other than the external magnetic field may have important device applications. An important feature of modern nanotechnology is the ability to shape semiconductor crystals, designing their quantum pr ...
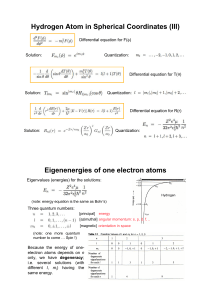
Hydrogen Atom in Spherical Coordinates (III) Eigenenergies of one
... [principal] energy [azimuthal] angular momentum: s, p, d, f, .. [magnetic] orientation in space (note: one more quantum number to come … Spin !) ...
... [principal] energy [azimuthal] angular momentum: s, p, d, f, .. [magnetic] orientation in space (note: one more quantum number to come … Spin !) ...
Magnetic Fields - HCC Learning Web
... Suppose that a proton, injected by source S at the center of the cyclotron in Fig. 28-13, initially moves toward a negatively charged dee. It will accelerate toward this dee and enter it. Once inside, it is shielded from electric fields by the copper walls of the dee; that is, the electric field doe ...
... Suppose that a proton, injected by source S at the center of the cyclotron in Fig. 28-13, initially moves toward a negatively charged dee. It will accelerate toward this dee and enter it. Once inside, it is shielded from electric fields by the copper walls of the dee; that is, the electric field doe ...
CHAPTER 10: Molecules and Solids
... Most solids are in a polycrystalline form. They are made up of many smaller crystals. Solids lacking any significant lattice structure are called amorphous and are referred to as “glasses.” Why do solids form as they do? When the material changes from the liquid to the solid state, the atoms can eac ...
... Most solids are in a polycrystalline form. They are made up of many smaller crystals. Solids lacking any significant lattice structure are called amorphous and are referred to as “glasses.” Why do solids form as they do? When the material changes from the liquid to the solid state, the atoms can eac ...
What are we measuring? Basis of the BOLD signal in fMRI
... RF pulse causes them to spin, in phase, in x,y plane ...
... RF pulse causes them to spin, in phase, in x,y plane ...
EARTH`S MAGNETIC FIELD
... T⋅m/A = 0.4π µT⋅m/A. Moreover, magnetic fields add vectorially, and this must be accounted for in any measurement of magnetic field. In this experiment, we will orient a coil such that its field is perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic field. If we measure the angle of the total magnetic field ...
... T⋅m/A = 0.4π µT⋅m/A. Moreover, magnetic fields add vectorially, and this must be accounted for in any measurement of magnetic field. In this experiment, we will orient a coil such that its field is perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic field. If we measure the angle of the total magnetic field ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.