Motors and Generators
... is created by relative motion between coils and the magnetic field from the magnets. The armature is an iron frame around which the rotor coils are wound and is mounted on the axle, which rotates in the magnetic field. The coils usually consist of many turns of copper wire wound on the armature. Tor ...
... is created by relative motion between coils and the magnetic field from the magnets. The armature is an iron frame around which the rotor coils are wound and is mounted on the axle, which rotates in the magnetic field. The coils usually consist of many turns of copper wire wound on the armature. Tor ...
Answers to Critical Thinking Questions 4
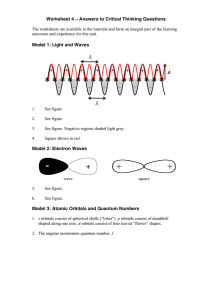
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
... rather than doubly occupying the state already occupied. This could be favored by the exchange effect. In this case, we predict that the Kondo effect with the first electron state will be interrupted each time an additional electron is introduced onto the dot. However, as the gate voltage is further ...
Protons and Neutrons - The Physics of Bruce Harvey
... of its length which is not totally unfeasible and probably a lot more feasible than any of the alternative theories. The most interesting thing which emerges is that the DUion force obeys an inverse square law if the ratio of a : r remains constant. Let us consider the effect of a scaling by a facto ...
... of its length which is not totally unfeasible and probably a lot more feasible than any of the alternative theories. The most interesting thing which emerges is that the DUion force obeys an inverse square law if the ratio of a : r remains constant. Let us consider the effect of a scaling by a facto ...
Properties of interstellar filaments observed with Herschel and 3D
... - pairs of angles (filament + background) defining the 3D structure of the field Fixed parameters (derived from Planck observations): - maximum polarization degree (p0) - position angle of the filament in the plane of the sky Fitting the observations - Spanning all the pairs of angles describing ...
... - pairs of angles (filament + background) defining the 3D structure of the field Fixed parameters (derived from Planck observations): - maximum polarization degree (p0) - position angle of the filament in the plane of the sky Fitting the observations - Spanning all the pairs of angles describing ...
wave function - Purdue Physics
... • The experiment also shows aspects of particle-like behavior since the electrons arrive one at a time at the screen, and also don’t just go in straight lines. • In principle, you can slowly build up an interference pattern over time even if only one electron (or photon) per second arrives at the sc ...
... • The experiment also shows aspects of particle-like behavior since the electrons arrive one at a time at the screen, and also don’t just go in straight lines. • In principle, you can slowly build up an interference pattern over time even if only one electron (or photon) per second arrives at the sc ...
2014-15 Archived Abstracts
... In this talk I will present results on the preparation and highresolution imaging of Rydberg manybody systems and the observation of spontaneous emergence of selforganized ordering. In a first series of experiments we investigate the ordering in the postselected highexcitationdensity component ...
... In this talk I will present results on the preparation and highresolution imaging of Rydberg manybody systems and the observation of spontaneous emergence of selforganized ordering. In a first series of experiments we investigate the ordering in the postselected highexcitationdensity component ...
Lecture 5 Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field
... In general, term linear in B defines magnetic dipole moment µ: ĤM = −µ · B. Result above shows that orbital degrees of freedom of the electron lead to a magnetic moment, µ=− ...
... In general, term linear in B defines magnetic dipole moment µ: ĤM = −µ · B. Result above shows that orbital degrees of freedom of the electron lead to a magnetic moment, µ=− ...
Lecture 20: Polyelectronic Atoms
... • For polyelectronic (i.e. real) atoms, a direct solution of the Schrodinger Equation is not possible. (Can’t solve the 3 body motion problem; Z12.61) • When we construct polyelectronic atoms, we use the hydrogen-atom orbital nomenclature to discuss in which orbitals the electrons reside. • This is ...
... • For polyelectronic (i.e. real) atoms, a direct solution of the Schrodinger Equation is not possible. (Can’t solve the 3 body motion problem; Z12.61) • When we construct polyelectronic atoms, we use the hydrogen-atom orbital nomenclature to discuss in which orbitals the electrons reside. • This is ...
Chapter 6 * Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Now for a couple rules: Aufbau Principle: add electrons from lowest energy to highest energy (you pretty much already do this when you use the proper filling order) Pauli Exclusion Principle: There is a maximum of two electrons for each line (or orbital) Hund’s Rule: Electrons fill in each orbital ...
... Now for a couple rules: Aufbau Principle: add electrons from lowest energy to highest energy (you pretty much already do this when you use the proper filling order) Pauli Exclusion Principle: There is a maximum of two electrons for each line (or orbital) Hund’s Rule: Electrons fill in each orbital ...
Conduction and Semiconductors
... Electron band diagrams are a way to visualize what happens at a p-n junction, using the following rules: 1. The Fermi level must be at the same level on both sides of the junction when there is no applied field 2. Far from the junctions, the materials inherent electrical structure exists 3. He band ...
... Electron band diagrams are a way to visualize what happens at a p-n junction, using the following rules: 1. The Fermi level must be at the same level on both sides of the junction when there is no applied field 2. Far from the junctions, the materials inherent electrical structure exists 3. He band ...
Three-Dimensional Electron Realm in Crystalline Solids Revealed
... Revealed with Soft-X-Rays at the Swiss Light Source The wave nature of electrons enables them to propagate by the atoms in the periodic crystal lattice without scattering on them. Dependence of energy of the electrons E on their wavevector k adopted to the periodic media forms their band structure E ...
... Revealed with Soft-X-Rays at the Swiss Light Source The wave nature of electrons enables them to propagate by the atoms in the periodic crystal lattice without scattering on them. Dependence of energy of the electrons E on their wavevector k adopted to the periodic media forms their band structure E ...
Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 126401
... The effective model and the exact data agree very well for all interdot couplings, as seen in Fig. 2. At zero magnetic field, only the first and the last term in Eq. (15) survive. This is the result of Ref. [20], where primed operators were used to refer to the fact that the Hamiltonian Hex refers t ...
... The effective model and the exact data agree very well for all interdot couplings, as seen in Fig. 2. At zero magnetic field, only the first and the last term in Eq. (15) survive. This is the result of Ref. [20], where primed operators were used to refer to the fact that the Hamiltonian Hex refers t ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • produced by two kinds of electron motion – electron spin • main contributor to magnetism • pair of electrons spinning in same direction creates a stronger magnet • pair of electrons spinning in opposite direction cancels magnetic field of the other ...
... • produced by two kinds of electron motion – electron spin • main contributor to magnetism • pair of electrons spinning in same direction creates a stronger magnet • pair of electrons spinning in opposite direction cancels magnetic field of the other ...
1E6 Electrical Engineering Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 21
... The housing is usually made of cast iron for heavy duty applications and is often bolted to a larger frame, but may be of steel or aluminium for light portable devices. The ends of the housing can be detached from the body and contain bearings to support the rotating parts at each end. The main hous ...
... The housing is usually made of cast iron for heavy duty applications and is often bolted to a larger frame, but may be of steel or aluminium for light portable devices. The ends of the housing can be detached from the body and contain bearings to support the rotating parts at each end. The main hous ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.