Chapter 4: Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... 3. The Q.T. describes the wave properties of electrons. 4. By solving the Schrodinger Equation, the probability of finding an electron at a given place around the nucleus is found. These probabilities are used to form atomic orbitals. 5. An Atomic Orbital is a three dimensional region around the nuc ...
... 3. The Q.T. describes the wave properties of electrons. 4. By solving the Schrodinger Equation, the probability of finding an electron at a given place around the nucleus is found. These probabilities are used to form atomic orbitals. 5. An Atomic Orbital is a three dimensional region around the nuc ...
Lecture notes in Solid State 3 Eytan Grosfeld Introduction to Localization
... surprisingly, all the states in 2D are localized as well. In contrast, 3D is special: necessarily there is some intermediate point for which β(g) = 0, defining gc . This is an unstable fixed point between a conducting state and an insulating state, known as the metal-insulator transition. What happe ...
... surprisingly, all the states in 2D are localized as well. In contrast, 3D is special: necessarily there is some intermediate point for which β(g) = 0, defining gc . This is an unstable fixed point between a conducting state and an insulating state, known as the metal-insulator transition. What happe ...
The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two fermions
... The Pauli exclusion principle explains a wide variety of physical phenomena. One particularly important consequence of the principle is the elaborate electron-shell structure of atoms and the way atoms share electrons. It explains the variety of chemical elements and their ...
... The Pauli exclusion principle explains a wide variety of physical phenomena. One particularly important consequence of the principle is the elaborate electron-shell structure of atoms and the way atoms share electrons. It explains the variety of chemical elements and their ...
Chapter 5: Introduction to Machinery Principles
... The direction of the force is given by the right hand rule. If the index finger of the right hand points in the direction of the vector l and the middle finger points in the direction of flux density vector B, then the thumb points in the direction of the resultant force on wire. The magnitude of t ...
... The direction of the force is given by the right hand rule. If the index finger of the right hand points in the direction of the vector l and the middle finger points in the direction of flux density vector B, then the thumb points in the direction of the resultant force on wire. The magnitude of t ...
PHYSICS – Motor and Generators Section I
... Electromagnetic braking involves using eddy currents to slow the motion of a wheel made from a conducting metal (e.g. aluminium). The figure to the right shows a simplified diagram of an electromagnetic braking system. Magnets are brought close to the rotating metal, and the relative motion ...
... Electromagnetic braking involves using eddy currents to slow the motion of a wheel made from a conducting metal (e.g. aluminium). The figure to the right shows a simplified diagram of an electromagnetic braking system. Magnets are brought close to the rotating metal, and the relative motion ...
Ch. 5 Electrons in Atoms
... 2.The electrons absorb a photon of just the right amount of energy 3.The just right amount of energy is called a quantum 4.The electron is on an energy level called its ground state 5.It absorbs the photon containing a quantum of energy, then jumps to its excited state 6.The electron is now energize ...
... 2.The electrons absorb a photon of just the right amount of energy 3.The just right amount of energy is called a quantum 4.The electron is on an energy level called its ground state 5.It absorbs the photon containing a quantum of energy, then jumps to its excited state 6.The electron is now energize ...
Chapter 6 and 7 Reading Guide Electronic Structure of Atoms and
... What is the effect of the spin difference between two electrons in the same orbital? ...
... What is the effect of the spin difference between two electrons in the same orbital? ...
CH 4 SEC 2: Book Notes
... w Values of the principle quantum number are positive integers only—1, 2, 3, and so on. (principle quantum number is referred as n) w As n increases, the electron’s energy and its average distance from the nucleus increase. (see Figure 12) w more than one electron can have the same n value. These ...
... w Values of the principle quantum number are positive integers only—1, 2, 3, and so on. (principle quantum number is referred as n) w As n increases, the electron’s energy and its average distance from the nucleus increase. (see Figure 12) w more than one electron can have the same n value. These ...
PHY 104: Modern Physics - Physlab
... pigments have the colors that they do, why are some materials hard and others soft, why do metals, for example, conduct electricity and heat easily, while glass doesn’t. Quantum physics also forms the basis of our understanding of the chemical world, materials science, as well as electronic devices ...
... pigments have the colors that they do, why are some materials hard and others soft, why do metals, for example, conduct electricity and heat easily, while glass doesn’t. Quantum physics also forms the basis of our understanding of the chemical world, materials science, as well as electronic devices ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... A bombarding electron collides with an electron in the target metal that is in an inner shell If there is sufficient energy, the electron is removed from the target atom The vacancy created by the lost electron is filled by an electron electron falling to the vacancy from a higher energy level The t ...
... A bombarding electron collides with an electron in the target metal that is in an inner shell If there is sufficient energy, the electron is removed from the target atom The vacancy created by the lost electron is filled by an electron electron falling to the vacancy from a higher energy level The t ...
Document
... obtained here extend greatly the earlier results in this field. They can be of interest for research in electron optics, as well as tor the heretofore little-investigated connection between the focusing properties of electric o r magnetic fields and their internal symmetries, the existence of additi ...
... obtained here extend greatly the earlier results in this field. They can be of interest for research in electron optics, as well as tor the heretofore little-investigated connection between the focusing properties of electric o r magnetic fields and their internal symmetries, the existence of additi ...
Slide 1
... Production of Alpha Particles They come from heavy elements of mass greater than 106 atomic mass units. In classical physics, the strong force balances the electromagnetic force, so the alpha does not have the energy to get out. In quantum physics, there is a small chance that the alpha can get out ...
... Production of Alpha Particles They come from heavy elements of mass greater than 106 atomic mass units. In classical physics, the strong force balances the electromagnetic force, so the alpha does not have the energy to get out. In quantum physics, there is a small chance that the alpha can get out ...
PROGRAM ON PHYSICS MECHANICS Kinematics. Mechanical
... Electrostatics. Electrization bodies. The Electric charge. Interaction of charges. An elementary electric charge. The law of preservation of an electric charge. The Coulomb law. Electric field. Intensity of electric field. Electric field of a dot charge. Potentiality of an electrostatic field. A pot ...
... Electrostatics. Electrization bodies. The Electric charge. Interaction of charges. An elementary electric charge. The law of preservation of an electric charge. The Coulomb law. Electric field. Intensity of electric field. Electric field of a dot charge. Potentiality of an electrostatic field. A pot ...
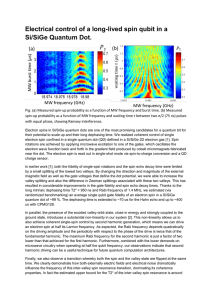
Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a
... Electron spins in Si/SiGe quantum dots are one of the most promising candidates for a quantum bit for their potential to scale up and their long dephasing time. We realized coherent control of single electron spin confined in a single quantum dot (QD) defined in a Si/SiGe 2D electron gas [1]. Spin r ...
... Electron spins in Si/SiGe quantum dots are one of the most promising candidates for a quantum bit for their potential to scale up and their long dephasing time. We realized coherent control of single electron spin confined in a single quantum dot (QD) defined in a Si/SiGe 2D electron gas [1]. Spin r ...
quantum numbers - Cloudfront.net
... Shape of Electron Cloud (l) Also known as sublevel or subshell Indicates the shape of the orbital within a shell Only integer values between 0 and n-1 are allowed Affects orbital energies (bigger l = higher energy) All electrons in an atom with the same value of l are said to belong to the same subs ...
... Shape of Electron Cloud (l) Also known as sublevel or subshell Indicates the shape of the orbital within a shell Only integer values between 0 and n-1 are allowed Affects orbital energies (bigger l = higher energy) All electrons in an atom with the same value of l are said to belong to the same subs ...
SCHRODINGER`S QUANTUM MECHANICS
... e.g. For n = 2, there are two types of sublevels (two “l” values ) Î s, p Since there are three “p” orbitals; we have a total of 4 orbitals (22 = 4) Since each orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, we would have a total of 8 electrons in the second shell (2 * 22 = 8) 4. Spin Quantum Number (s) ...
... e.g. For n = 2, there are two types of sublevels (two “l” values ) Î s, p Since there are three “p” orbitals; we have a total of 4 orbitals (22 = 4) Since each orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, we would have a total of 8 electrons in the second shell (2 * 22 = 8) 4. Spin Quantum Number (s) ...
MAGNETISM
... 12.- Magnets with a weak force can reverse their polarity thruogh the action of a strong magnetic field. ...
... 12.- Magnets with a weak force can reverse their polarity thruogh the action of a strong magnetic field. ...
Satval-Monte-Carlo computer code for windows
... experimental and theoretical studies on heavy-fermion superconductivity have continued to be at the very forefront of modern condensed matter physics. This is due to the special character of the superconducting state, which cannot be described in terms of the conventional theory of superconductivity ...
... experimental and theoretical studies on heavy-fermion superconductivity have continued to be at the very forefront of modern condensed matter physics. This is due to the special character of the superconducting state, which cannot be described in terms of the conventional theory of superconductivity ...
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF A DRUM
... manganese ore, as is shown in Fig. 4. The separator was praised by its users for such advantages as good separation results, no water consumption, less maintenance and low energy consumption. Its application will certainly simplify the process flowsheet achieving good economic results. A spiral conc ...
... manganese ore, as is shown in Fig. 4. The separator was praised by its users for such advantages as good separation results, no water consumption, less maintenance and low energy consumption. Its application will certainly simplify the process flowsheet achieving good economic results. A spiral conc ...
August 15, 1996 Part I
... 7. A mass m is dropped from rest at a height H above a point p on the ground. Assume that Coriolis effects are negligible. Estimate the minimum mean horizontal distance between the ground strike point and p which arises from quantum effects. ...
... 7. A mass m is dropped from rest at a height H above a point p on the ground. Assume that Coriolis effects are negligible. Estimate the minimum mean horizontal distance between the ground strike point and p which arises from quantum effects. ...
Electromagnetic Frequencies and Direct Current Transmission
... Q. What do health and scientific agencies say about static fields and human health? A. Multiple agencies including the International Agency for Research on Cancer; the Advisory Group on NonIonizing Radiation, an independent advisory group reporting to Public Health England; and the World Health Org ...
... Q. What do health and scientific agencies say about static fields and human health? A. Multiple agencies including the International Agency for Research on Cancer; the Advisory Group on NonIonizing Radiation, an independent advisory group reporting to Public Health England; and the World Health Org ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.