Zeeman effect – Studying magnetic fields in star
... beam squint = small offset of the beam in L and R circular polarization in the presence of vgradients in the cloud, this produce a pseudoZeeman splitting the polarization leakage between L and R circularly polarized receiver channels See more from Heiles and Crutcher 2005, Cosmic magnetic fields, Le ...
... beam squint = small offset of the beam in L and R circular polarization in the presence of vgradients in the cloud, this produce a pseudoZeeman splitting the polarization leakage between L and R circularly polarized receiver channels See more from Heiles and Crutcher 2005, Cosmic magnetic fields, Le ...
AP2 Unit 5 BW3
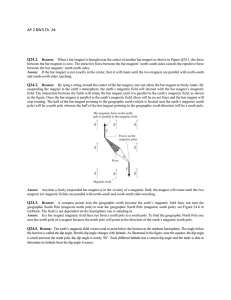
... will be stronger than the magnetic force felt on the right side (furthest from the straight wire) of the square loop. The current on the left side of the square loop is opposite from the current in the wire, therefore, the wires will repel each other. There will be an attractive force from the righ ...
... will be stronger than the magnetic force felt on the right side (furthest from the straight wire) of the square loop. The current on the left side of the square loop is opposite from the current in the wire, therefore, the wires will repel each other. There will be an attractive force from the righ ...
Chapter 4 Powerpoint
... 1.) Emission Spectrum: All wavelengths of light emitted by an atom. 2.) Absorption Spectrum: All wavelengths of light that are not absorbed by an atom. This is a continuous spectrum with wavelengths removed that are absorbed by the atom. These are shown as black lines for absorbed light. Continu ...
... 1.) Emission Spectrum: All wavelengths of light emitted by an atom. 2.) Absorption Spectrum: All wavelengths of light that are not absorbed by an atom. This is a continuous spectrum with wavelengths removed that are absorbed by the atom. These are shown as black lines for absorbed light. Continu ...
Advanced electronic bonding and how these affect molecular shapes
... levels around the atom. • These energy levels are called shells. • Electrons jump to higher energy levels when provided with energy, but will automatically drop back down to the lowest energy level possible. • These energy levels are named 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and so on. (So far the heaviest eleme ...
... levels around the atom. • These energy levels are called shells. • Electrons jump to higher energy levels when provided with energy, but will automatically drop back down to the lowest energy level possible. • These energy levels are named 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and so on. (So far the heaviest eleme ...
Lewis
... Elements of 2. period can build not more than 4 bonds, because there are only 4 orbitals available → octett rule. Consider ground states (Pauli, Hund), exited states. * Number of electrons in bonds ...
... Elements of 2. period can build not more than 4 bonds, because there are only 4 orbitals available → octett rule. Consider ground states (Pauli, Hund), exited states. * Number of electrons in bonds ...
Set 9 - STEMwomen.org
... (d) Calculate the average z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum for this ground state. (e) Does Lz commute with the hamiltonian for a hydrogen-like atom ? Show whether the z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum in this hydrogen-like atom is a constant of the motion. ...
... (d) Calculate the average z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum for this ground state. (e) Does Lz commute with the hamiltonian for a hydrogen-like atom ? Show whether the z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum in this hydrogen-like atom is a constant of the motion. ...
A quantum phase transition seen from 0 to 600 K
... quantum critical point at xc= 0.25. So that property is due to the addition of rhenium to the cubic crystal structure, and not to quantum antiferromagnetic fluctuations from chromium as has been suspected in the past. Our low temperature measurements established the precise position of the quantum c ...
... quantum critical point at xc= 0.25. So that property is due to the addition of rhenium to the cubic crystal structure, and not to quantum antiferromagnetic fluctuations from chromium as has been suspected in the past. Our low temperature measurements established the precise position of the quantum c ...
Mn6 1 Many-particle Systems, 6 Fermion gas at low temperature At
... informative as expressing PF in macroscopic units—i.e., converting eV to J and nm to m. When this is done we find PF = 2x1010 N/m2. As 1 atm = 105 N/m2, we see that PF = 2x105 atm! No wonder solids are hard. You can’t squeeze the electrons (very much). (Recall Mn3, p3.) Example: What is PF for a neu ...
... informative as expressing PF in macroscopic units—i.e., converting eV to J and nm to m. When this is done we find PF = 2x1010 N/m2. As 1 atm = 105 N/m2, we see that PF = 2x105 atm! No wonder solids are hard. You can’t squeeze the electrons (very much). (Recall Mn3, p3.) Example: What is PF for a neu ...
Document
... [26] Peripheral nerve stimulation properties of an asymmetric head-only gradient coil compatible with a high-channel-count receiver array S.-K. Lee, J.-B Mathieu, D. Graziani, J. Piel, E. Budesheim, E. Fiveland, C. J. Hardy, E. T. Tan, B. Amm, T. K.-F. Foo, M. A. Bernstein, J. Huston III, Y. Shu, J. ...
... [26] Peripheral nerve stimulation properties of an asymmetric head-only gradient coil compatible with a high-channel-count receiver array S.-K. Lee, J.-B Mathieu, D. Graziani, J. Piel, E. Budesheim, E. Fiveland, C. J. Hardy, E. T. Tan, B. Amm, T. K.-F. Foo, M. A. Bernstein, J. Huston III, Y. Shu, J. ...
Evolution of Rising Magnetic Cavities and UHECR acceleration
... We seek solutions that take into account the plasma pressure and have no surface currents ...
... We seek solutions that take into account the plasma pressure and have no surface currents ...
FABRICATION AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF
... nanowires, and the magnetic properties of GaAs/Fe core/shell nanowires. As a part of this study, I explore the growth mechanisms behind the formation of eutectic nanoparticles which are used as a catalyst to fabricate nanowires by molecular beam epitaxy. The morphology of nanowires grown by molecula ...
... nanowires, and the magnetic properties of GaAs/Fe core/shell nanowires. As a part of this study, I explore the growth mechanisms behind the formation of eutectic nanoparticles which are used as a catalyst to fabricate nanowires by molecular beam epitaxy. The morphology of nanowires grown by molecula ...
quantum mechanical model
... Big Picture The quantum mechanical model is now the modern and accepted model of the atom. Unlike previous models, the quantum mechanical model of the atom does not predict the path that an electron takes around the nucleus. Due to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the position of an electron ca ...
... Big Picture The quantum mechanical model is now the modern and accepted model of the atom. Unlike previous models, the quantum mechanical model of the atom does not predict the path that an electron takes around the nucleus. Due to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the position of an electron ca ...
How to make an electromagnet
... How to make an electromagnet Electromagnets are created using electricity and a magnetic material such as iron, an iron nail is perfect for this example. When electricity passes through a copper wire it creates a magnetic field around the wire. By winding a coil of wire around an iron core you can i ...
... How to make an electromagnet Electromagnets are created using electricity and a magnetic material such as iron, an iron nail is perfect for this example. When electricity passes through a copper wire it creates a magnetic field around the wire. By winding a coil of wire around an iron core you can i ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... accomplished by the use of a simple Atwood’s machine. A string looped over the large pulley groove of the rotary motion sensor suspends the magnet. The weight of the magnet is balanced by a mass of equal weight on the other end of the string. Setup DataStudio to accept measurements from a Voltage S ...
... accomplished by the use of a simple Atwood’s machine. A string looped over the large pulley groove of the rotary motion sensor suspends the magnet. The weight of the magnet is balanced by a mass of equal weight on the other end of the string. Setup DataStudio to accept measurements from a Voltage S ...
Ripplon-induced tunneling transverse to the magnetic field P. M. Platzman
... weak, and therefore the crossover from the tunneling without ripplons to the ripplon-induced one occurs for a very close to 1. The dependence of the exponent R on the magnetic field is comparatively weak for a ;1, in contrast to the extremely steep dependence of the tunneling rate without ripplons, ...
... weak, and therefore the crossover from the tunneling without ripplons to the ripplon-induced one occurs for a very close to 1. The dependence of the exponent R on the magnetic field is comparatively weak for a ;1, in contrast to the extremely steep dependence of the tunneling rate without ripplons, ...
chem 1411- chapter 7
... States that no two electrons in an atom can have the entire four quantum numbers same. The principle follows that an orbital cannot accommodate more than two electrons. 2.Hund’s rule The rule states that pairing of electrons any orbital of the atom is not possible until all the available orbital of ...
... States that no two electrons in an atom can have the entire four quantum numbers same. The principle follows that an orbital cannot accommodate more than two electrons. 2.Hund’s rule The rule states that pairing of electrons any orbital of the atom is not possible until all the available orbital of ...
File
... electrons – each of the 3 orbitals can hold 2 electrons • d orbitals can hold 10 electrons – each of the 5 orbitals can hold 2 electrons • f orbitals can hold 14 electrons – each of the 7 orbitals can hold 2 electrons ...
... electrons – each of the 3 orbitals can hold 2 electrons • d orbitals can hold 10 electrons – each of the 5 orbitals can hold 2 electrons • f orbitals can hold 14 electrons – each of the 7 orbitals can hold 2 electrons ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.