9 Quantum Phases and Phase Transitions of Mott
... experiments. The purpose of this article is to review recent theoretical work towards achieving this goal. We will focus mainly on the case of two spatial dimensions (d), but our methods and results often have simple generalizations to d = 3. One useful vantage point for opening this discussion is t ...
... experiments. The purpose of this article is to review recent theoretical work towards achieving this goal. We will focus mainly on the case of two spatial dimensions (d), but our methods and results often have simple generalizations to d = 3. One useful vantage point for opening this discussion is t ...
Chapter 3 – Physico-Chemical Characteristics of
... colloids may be stabilized by adsorption of a wide variety of compounds such as proteins or polymers but also by interaction with other compounds such as thiols that form a compact, self-assembled monolayer on their surface. In describing the structure of colloids, it must be stressed that the synth ...
... colloids may be stabilized by adsorption of a wide variety of compounds such as proteins or polymers but also by interaction with other compounds such as thiols that form a compact, self-assembled monolayer on their surface. In describing the structure of colloids, it must be stressed that the synth ...
Preprint
... The possibility of creating optical fields with many photons in a single mode of a resonator was realized with the creation of the laser in 1960. The possibility of creating a matter-wave field with many atoms in a single mode of an atom trap (which is the atomic equivalent of an optical resonator) ...
... The possibility of creating optical fields with many photons in a single mode of a resonator was realized with the creation of the laser in 1960. The possibility of creating a matter-wave field with many atoms in a single mode of an atom trap (which is the atomic equivalent of an optical resonator) ...
Martin Raith - Publikationsserver der Universität Regensburg
... is given by the spin of either the donor electron or the nucleus of 31 P, with coherence times of seconds in isotopically purified silicon [75–77]. Worthy of mention, a nuclear spin of 29 Si can preserve coherence for minutes [78], yielding a possible alternative to the donor. The drawback of those s ...
... is given by the spin of either the donor electron or the nucleus of 31 P, with coherence times of seconds in isotopically purified silicon [75–77]. Worthy of mention, a nuclear spin of 29 Si can preserve coherence for minutes [78], yielding a possible alternative to the donor. The drawback of those s ...
Quantum hair on black holes
... Rather, to calculate the influence of the gravitational interaction between such a particle and another particle, we simply calculate Feynman graphs for graviton exchange. (Thought)-experimental attempts to “see” the nominal gravitational field at distance R, by considering scattering at very small ...
... Rather, to calculate the influence of the gravitational interaction between such a particle and another particle, we simply calculate Feynman graphs for graviton exchange. (Thought)-experimental attempts to “see” the nominal gravitational field at distance R, by considering scattering at very small ...
Electron Attraction Mediated by Coulomb Repulsion
... to exactly null the internal field. Conversely, in a dipole with small inter-site tunneling, an entire electron will polarize between the two sites, creating an internal field that is much larger, and of opposite sign to the external field. This forms our basic ‘sign-inverter’. Unlike continuous cha ...
... to exactly null the internal field. Conversely, in a dipole with small inter-site tunneling, an entire electron will polarize between the two sites, creating an internal field that is much larger, and of opposite sign to the external field. This forms our basic ‘sign-inverter’. Unlike continuous cha ...
Precision Spectroscopy of Atomic Lithium
... the isotope shift is several times their combined uncertainties for both the isotope shift and 7 Li fine structure measurements. The data presented by Brown et al [1] and Sansonetti et al. [2] is the same data present with different analysis based on the evaluation of systematics in the system. The ...
... the isotope shift is several times their combined uncertainties for both the isotope shift and 7 Li fine structure measurements. The data presented by Brown et al [1] and Sansonetti et al. [2] is the same data present with different analysis based on the evaluation of systematics in the system. The ...
Outline - Concordia University
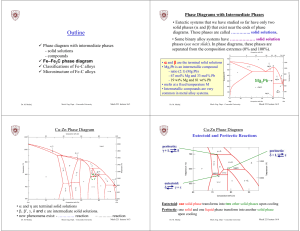
... • Interstitial lattice positions are much larger than ferrite (higher C%) • Is not stable below the eutectic temperature (727 °C) unless cooled rapidly (Chapter 10). δ -ferrite solid solution of C in ……. Fe • The same structure as α -ferrite • Stable only at high T, above 1394 °C • Also has low solu ...
... • Interstitial lattice positions are much larger than ferrite (higher C%) • Is not stable below the eutectic temperature (727 °C) unless cooled rapidly (Chapter 10). δ -ferrite solid solution of C in ……. Fe • The same structure as α -ferrite • Stable only at high T, above 1394 °C • Also has low solu ...
Selection rules and transition moment integral
... Franck-Condon principle was proposed by German physicist James Franck (1882-1964) and U.S. physicist Edward U. Condon (1902-1974) in 1926. This principle states that when an electronic transition takes place, the time scale of this transition is so fast compared to nucleus motion that we can conside ...
... Franck-Condon principle was proposed by German physicist James Franck (1882-1964) and U.S. physicist Edward U. Condon (1902-1974) in 1926. This principle states that when an electronic transition takes place, the time scale of this transition is so fast compared to nucleus motion that we can conside ...
Electronic quantum optics beyond the integer quantum Hall effect
... achieved [4, 25]. Concerning the asymmetric profile (lower panel), the contrast is smaller than 1. Also in this case both the numerical and the analytical approaches agree very well. The HOM interferometry with fermions is thus characterized by a dip in the zero-frequency current cross-correlations ...
... achieved [4, 25]. Concerning the asymmetric profile (lower panel), the contrast is smaller than 1. Also in this case both the numerical and the analytical approaches agree very well. The HOM interferometry with fermions is thus characterized by a dip in the zero-frequency current cross-correlations ...
A quantum gas with tunable interactions in an optical lattice
... The invention of laser-cooling techniques gave birth to the field of ultracold gases, where dilute samples of atoms can be prepared at microkelvin temperatures. Evaporative cooling made it possible to achieve even lower temperatures and reach the quantum gas regime. Here, the motion of the atoms can ...
... The invention of laser-cooling techniques gave birth to the field of ultracold gases, where dilute samples of atoms can be prepared at microkelvin temperatures. Evaporative cooling made it possible to achieve even lower temperatures and reach the quantum gas regime. Here, the motion of the atoms can ...
Momentum-resolved tunneling into fractional
... in the experimentally obtained dI/dV, thus enabling microscopic characterization of real QH edges. When 2DES⬜ is in a QH state at a Laughlin-series filling factor 1,p , it supports a single branch of edge excitations just like at ⫽1, and the calculation of the differential tunneling conductance ...
... in the experimentally obtained dI/dV, thus enabling microscopic characterization of real QH edges. When 2DES⬜ is in a QH state at a Laughlin-series filling factor 1,p , it supports a single branch of edge excitations just like at ⫽1, and the calculation of the differential tunneling conductance ...
Electronic Structure of Atoms
... come from analysis of the light either emitted or absorbed by substances. To understand electronic structure, therefore, we must first learn more about light. The light that we can see with our eyes, visible light, is an example of electromagnetic radiation. Because electromagnetic radiation carries ...
... come from analysis of the light either emitted or absorbed by substances. To understand electronic structure, therefore, we must first learn more about light. The light that we can see with our eyes, visible light, is an example of electromagnetic radiation. Because electromagnetic radiation carries ...
Quantum-dot lithium in zero magnetic field: Electronic properties
... Monte Carlo 共QMC兲 methods,26 –34 density-functional theory,35–39 and other methods,40– 46 were applied to study their properties, for a recent review see Ref. 47. Until recently most theoretical work was performed in the regime of strong magnetic fields, when all electron spins are fully polarized. ...
... Monte Carlo 共QMC兲 methods,26 –34 density-functional theory,35–39 and other methods,40– 46 were applied to study their properties, for a recent review see Ref. 47. Until recently most theoretical work was performed in the regime of strong magnetic fields, when all electron spins are fully polarized. ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.