buddhism WHAT`S THE DIFFERENCE? REINCARNATION
... *Understand the difference between Western Buddhist and Asian Buddhists. Most Asian Buddhist are from a Buddhist culture, Buddhism is not only a theology for them, but part of their culture and link to their community. To leave Buddhism for Christianity, for Asian Buddhists may mean leaving their cu ...
... *Understand the difference between Western Buddhist and Asian Buddhists. Most Asian Buddhist are from a Buddhist culture, Buddhism is not only a theology for them, but part of their culture and link to their community. To leave Buddhism for Christianity, for Asian Buddhists may mean leaving their cu ...
2306 Foundations of Buddhism
... The paper deals with the main doctrines and practices of mainstream (pre-Mahāyāna) Buddhism, as reflected by the surviving literature of the various schools. Tutorials will enable students to further discuss and analyse the main topics dealt with during the course, thus representing an ideal complem ...
... The paper deals with the main doctrines and practices of mainstream (pre-Mahāyāna) Buddhism, as reflected by the surviving literature of the various schools. Tutorials will enable students to further discuss and analyse the main topics dealt with during the course, thus representing an ideal complem ...
Hinduism and Buddhism
... • Nirvana is the ultimate reality, the end of the self and a reunion with the Great World Soul • No worshiping of Siddhartha or his image • Often viewed as philosophy not a religion. ...
... • Nirvana is the ultimate reality, the end of the self and a reunion with the Great World Soul • No worshiping of Siddhartha or his image • Often viewed as philosophy not a religion. ...
Buddhism Buddhism - World Relief Nashville
... Historic Background: Buddhism was founded as a form of atheism that rejected more ancient beliefs in a permanent, personal, creator God (Ishvara) who controlled the eternal destiny of human souls. Siddhartha Gautama rejected these more ancient theistic beliefs because of difficulty he had over recon ...
... Historic Background: Buddhism was founded as a form of atheism that rejected more ancient beliefs in a permanent, personal, creator God (Ishvara) who controlled the eternal destiny of human souls. Siddhartha Gautama rejected these more ancient theistic beliefs because of difficulty he had over recon ...
Brochure - TheBuddhistCentre
... Who was the Buddha? The term Buddha means ‘one who is awake’. To be awake means to have unlimited loving-kindness, complete understanding of the human experience, and perfect peace. The Buddha learned to let go of his reactions, feelings, and thoughts – he was no longer dissatisfied. The Buddha said ...
... Who was the Buddha? The term Buddha means ‘one who is awake’. To be awake means to have unlimited loving-kindness, complete understanding of the human experience, and perfect peace. The Buddha learned to let go of his reactions, feelings, and thoughts – he was no longer dissatisfied. The Buddha said ...
220 Outline of Buddhism
... History of Buddhism I. Primitive Buddhism (540-385 B.C.) A. The Three Jewels- Tri-Ratna 1. The Founder- known as Gautama or Sakyamuni (563-85 B.C.) 2. The Teaching (dhamma or dharma)- The Middle Way a. The Four Noble Truths b. The Noble Eightfold Path c. The Ten Rules of Conduct 3. The Order of Monk ...
... History of Buddhism I. Primitive Buddhism (540-385 B.C.) A. The Three Jewels- Tri-Ratna 1. The Founder- known as Gautama or Sakyamuni (563-85 B.C.) 2. The Teaching (dhamma or dharma)- The Middle Way a. The Four Noble Truths b. The Noble Eightfold Path c. The Ten Rules of Conduct 3. The Order of Monk ...
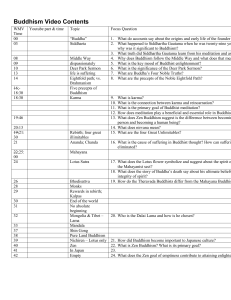
Buddhism Video Contents
... What does Zen Buddhism suggest is the difference between becomin person and becoming a human being? 14. What does nirvana mean? 15. What are the four Great Unlimitables? ...
... What does Zen Buddhism suggest is the difference between becomin person and becoming a human being? 14. What does nirvana mean? 15. What are the four Great Unlimitables? ...
The Growth and Spread of Buddhism
... for their living, they were generally located near settlements, often on hillsides, etc. Often the monasteries were located on trade routes frequented by merchant caravans. They offered shelter to the merchants, who in return made generous donations. When Buddha died, stupas or mounds were construct ...
... for their living, they were generally located near settlements, often on hillsides, etc. Often the monasteries were located on trade routes frequented by merchant caravans. They offered shelter to the merchants, who in return made generous donations. When Buddha died, stupas or mounds were construct ...
Temple Organisat - Max Planck Institut für ethnologische Forschung
... sangha – the community of monks and, where recognised, nuns – is one of the "three jewels" (together with the Buddha and his teachings). While the first monks where itinerant mendicants, their successors settled down, eventually establishing prosperous and often very long-lived institutions. When th ...
... sangha – the community of monks and, where recognised, nuns – is one of the "three jewels" (together with the Buddha and his teachings). While the first monks where itinerant mendicants, their successors settled down, eventually establishing prosperous and often very long-lived institutions. When th ...
REL440S04PTopics1
... Schopen discusses what he calls the Protestant assumptions in the study of Indian Buddhism. First, briefly summarize (one page) Schopen’s key arguments. Second, see what the potential strengths and weaknesses of his argument are by applying it to one or two of the sutras we are sampling in this cour ...
... Schopen discusses what he calls the Protestant assumptions in the study of Indian Buddhism. First, briefly summarize (one page) Schopen’s key arguments. Second, see what the potential strengths and weaknesses of his argument are by applying it to one or two of the sutras we are sampling in this cour ...
classical india - Ms. Flores AP World History
... Left family, searching for salvation from cycle of incarnation Gained enlightenment, taught an ascetic doctrine His disciples began to lead a monastic life Mahavira became Jina, the "conqueror," and followers, Jains Inspired by the Upanishads Everything in the universe possessed a soul Striving to p ...
... Left family, searching for salvation from cycle of incarnation Gained enlightenment, taught an ascetic doctrine His disciples began to lead a monastic life Mahavira became Jina, the "conqueror," and followers, Jains Inspired by the Upanishads Everything in the universe possessed a soul Striving to p ...
CLASSICAL INDIA
... Left family, searching for salvation from cycle of incarnation Gained enlightenment, taught an ascetic doctrine His disciples began to lead a monastic life Mahavira became Jina, the "conqueror," and followers, Jains Inspired by the Upanishads Everything in the universe possessed a soul Striving to p ...
... Left family, searching for salvation from cycle of incarnation Gained enlightenment, taught an ascetic doctrine His disciples began to lead a monastic life Mahavira became Jina, the "conqueror," and followers, Jains Inspired by the Upanishads Everything in the universe possessed a soul Striving to p ...
CLASSICAL INDIA
... Left family, searching for salvation from cycle of incarnation Gained enlightenment, taught an ascetic doctrine His disciples began to lead a monastic life Mahavira became Jina, the "conqueror," and followers, Jains Inspired by the Upanishads Everything in the universe possessed a soul Striving to p ...
... Left family, searching for salvation from cycle of incarnation Gained enlightenment, taught an ascetic doctrine His disciples began to lead a monastic life Mahavira became Jina, the "conqueror," and followers, Jains Inspired by the Upanishads Everything in the universe possessed a soul Striving to p ...
File
... • Buddha rejected the many gods of Hinduism • Buddha also rejected the accommodations that priests received – Rejected the caste system ...
... • Buddha rejected the many gods of Hinduism • Buddha also rejected the accommodations that priests received – Rejected the caste system ...
Mahayana Buddhism
... liberal form of Buddhism Mahayana means “Great Vehicle” • Largest of the three ...
... liberal form of Buddhism Mahayana means “Great Vehicle” • Largest of the three ...
The Art of India - Groupfusion.net
... beliefs and practices, but these teachings are generally of importance to all • Buddhism flourished over the course of its 2,500 year history • It is the dominant religion in countries such as Japan, Burma, Sri Lanka, and much of mainland Southeast Asia ...
... beliefs and practices, but these teachings are generally of importance to all • Buddhism flourished over the course of its 2,500 year history • It is the dominant religion in countries such as Japan, Burma, Sri Lanka, and much of mainland Southeast Asia ...
Buddhism - TeacherWeb
... animals Everyone has to work on themselvespriests can’t help Thought people who died didn’t reach nirvana and were reincarnated until they did Opposed the caste system-many lower classes followed ...
... animals Everyone has to work on themselvespriests can’t help Thought people who died didn’t reach nirvana and were reincarnated until they did Opposed the caste system-many lower classes followed ...
Drag king5-8 351 Kb 03/11/14
... but because the wait to receive a number, it can not go around offering food to Buddha are all necessary. To take a leaf wrapped food into circulation between the people present were very far away to send the same instant, so do not use foods wrap to throw some leaves with some spa. I to the presen ...
... but because the wait to receive a number, it can not go around offering food to Buddha are all necessary. To take a leaf wrapped food into circulation between the people present were very far away to send the same instant, so do not use foods wrap to throw some leaves with some spa. I to the presen ...
Buddhist Teachings on Animals
... ultimate reality, where sorrows, trouble and death cannot intrude. In Buddhist terms, this is often called “enlightenment,” “Buddhahood,” or “Nirvana.” One enters Nirvana by training one’s mind to directly intuit the ultimate reality that lies hidden behind the appearances of everyday life while sim ...
... ultimate reality, where sorrows, trouble and death cannot intrude. In Buddhist terms, this is often called “enlightenment,” “Buddhahood,” or “Nirvana.” One enters Nirvana by training one’s mind to directly intuit the ultimate reality that lies hidden behind the appearances of everyday life while sim ...
The University of Toronto / McMaster University
... The phrase ‘practices of the self ’ was introduced by the French thinkers Michel Foucault and Pierre Hadot, to refer to ways of life in Hellenistic Greece and Imperial Rome (Hadot speaks of ‘spiritual exercises’) where philosophical discourse was engaged in not simply to produce changes in the ideas ...
... The phrase ‘practices of the self ’ was introduced by the French thinkers Michel Foucault and Pierre Hadot, to refer to ways of life in Hellenistic Greece and Imperial Rome (Hadot speaks of ‘spiritual exercises’) where philosophical discourse was engaged in not simply to produce changes in the ideas ...
Buddhism P. 156-161
... V. Buddhism spreads A. Asoka, a powerful king in India, became Buddhist and built Buddhist temples and schools throughout India B. Missionaries spread Buddhism to other countries in Asia C. Eventually Buddhism spread via the Silk Road into China, Korea, and Japan. ...
... V. Buddhism spreads A. Asoka, a powerful king in India, became Buddhist and built Buddhist temples and schools throughout India B. Missionaries spread Buddhism to other countries in Asia C. Eventually Buddhism spread via the Silk Road into China, Korea, and Japan. ...
Greco-Buddhism
.jpeg?width=300)
Greco-Buddhism, sometimes spelled Graeco-Buddhism, refers to the cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism, which developed between the 4th century BCE and the 5th century CE in Bactria and the Indian subcontinent, corresponding to the territories of modern day Afghanistan, India, and Pakistan. It was a cultural consequence of a long chain of interactions begun by Greek forays into India from the time of Alexander the Great, carried further by the establishment of the Indo-Greek Kingdom and extended during the flourishing of the Hellenized Kushan Empire. Greco-Buddhism influenced the artistic, and perhaps the spiritual development of Buddhism, particularly Mahayana Buddhism. Buddhism was then adopted in Central and Northeastern Asia from the 1st century CE, ultimately spreading to China, Korea, Japan, Philippines, Siberia, and Vietnam.