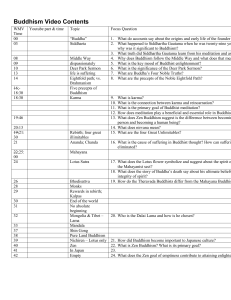
Buddhism Video Contents
... 2. What happened to Siddhartha Gautama when he was twenty-nine ye why was it significant to Buddhism? 3. What truth did Siddhartha Gautama learn from his meditation and as 4. Why does Buddhism follow the Middle Way and what does that mea 5. What is the key mood of Buddhist enlightenment? 6. What is ...
... 2. What happened to Siddhartha Gautama when he was twenty-nine ye why was it significant to Buddhism? 3. What truth did Siddhartha Gautama learn from his meditation and as 4. Why does Buddhism follow the Middle Way and what does that mea 5. What is the key mood of Buddhist enlightenment? 6. What is ...
Name Class Date Two major religions, Hinduism and Buddhism
... Two major religions, Hinduism and Buddhism, emerged in ancient India. Although Hinduism grew out of the overlapping religious ideas of diverse groups, all Hindus share basic beliefs. One force, the brahman, is the basis of everything. People have an essential self, or atman. Their goal is to achieve ...
... Two major religions, Hinduism and Buddhism, emerged in ancient India. Although Hinduism grew out of the overlapping religious ideas of diverse groups, all Hindus share basic beliefs. One force, the brahman, is the basis of everything. People have an essential self, or atman. Their goal is to achieve ...
File
... • Siddhartha Gautama founded the new religion of Buddhism • Four Noble Truths 1. All life is full of suffering, pain, and sorrow 2. The cause of suffering is the desire for things that are really illusions, such as riches, power, and long life 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire 4. ...
... • Siddhartha Gautama founded the new religion of Buddhism • Four Noble Truths 1. All life is full of suffering, pain, and sorrow 2. The cause of suffering is the desire for things that are really illusions, such as riches, power, and long life 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire 4. ...
Buddhism also began in India and is centered on the teachings of
... practices provide guidelines to every person (regardless of caste) on how to break reincarnation. Since caste is meaningless, there is no purpose for Dharma in Buddhism. Karma is however, very important. ...
... practices provide guidelines to every person (regardless of caste) on how to break reincarnation. Since caste is meaningless, there is no purpose for Dharma in Buddhism. Karma is however, very important. ...
Lecture Notes_India
... o Abandoned family to become a wandering ascetic o After six years of self-deprivation, he regarded asceticism as no more likely to produce spiritual insight than the luxury of his pervious life o Middle Path Moderation Sitting under a tree near Benares on the Ganges River he gained a sudden and ...
... o Abandoned family to become a wandering ascetic o After six years of self-deprivation, he regarded asceticism as no more likely to produce spiritual insight than the luxury of his pervious life o Middle Path Moderation Sitting under a tree near Benares on the Ganges River he gained a sudden and ...
BUDDHISM The religion known as Buddhism was founded by
... According to Buddha, man needed to go through several rebirths before he could overcome his desires. Those who finally rid themselves of all desires would reach “nirvana.” In nirvana, man’s soul would stop its cycle of rebirth and become one with the universe. While Siddhartha accepted the idea of ...
... According to Buddha, man needed to go through several rebirths before he could overcome his desires. Those who finally rid themselves of all desires would reach “nirvana.” In nirvana, man’s soul would stop its cycle of rebirth and become one with the universe. While Siddhartha accepted the idea of ...
Buddhism…
... Nirvana – an awakening to the truth about life, becoming a Buddha, the “Awakened One”at the age of 35 Spent the remaining 45 years of his life teaching others how to achieve the peace of mind he had achieved ...
... Nirvana – an awakening to the truth about life, becoming a Buddha, the “Awakened One”at the age of 35 Spent the remaining 45 years of his life teaching others how to achieve the peace of mind he had achieved ...
Buddhism - Hayden Emerson
... the world is a work in progress. Things in this universe are constantly changing and will always be changing, so the creation of the world is a neverending process. ...
... the world is a work in progress. Things in this universe are constantly changing and will always be changing, so the creation of the world is a neverending process. ...
The Origins of Buddhism
... • Asoka also spread Buddhism throughout the rest of Asia through the use of missionaries. ...
... • Asoka also spread Buddhism throughout the rest of Asia through the use of missionaries. ...
Buddhism
... • The Buddha taught that life was inherently suffering, that it is caused by craving, but that this condition was curable – 1) Suffering: – 2) The origin of suffering: – 3) The cessation of suffering: ...
... • The Buddha taught that life was inherently suffering, that it is caused by craving, but that this condition was curable – 1) Suffering: – 2) The origin of suffering: – 3) The cessation of suffering: ...
buddhism ppt - Valhalla High School
... The Middle Path or Moderate Way Avoid extremes– either an overt pursuit of passionate worldly desire or extreme asceticism Live a moderate lifestyle characterized by quiet contemplation, thoughtful reflection, and disciplined selfcontrol Reduces desire for material goods and other worldly att ...
... The Middle Path or Moderate Way Avoid extremes– either an overt pursuit of passionate worldly desire or extreme asceticism Live a moderate lifestyle characterized by quiet contemplation, thoughtful reflection, and disciplined selfcontrol Reduces desire for material goods and other worldly att ...
PB on Atman - Avery Solomon
... As an example, take the most prominent feature of many spiritual traditions: the nature of the individual I. Both Buddhism and Hinduism, to name two, have fundamental practices of searching for the I. In Mahayana practice, one searches for the I in such teachings as the “selflessness of persons.” ...
... As an example, take the most prominent feature of many spiritual traditions: the nature of the individual I. Both Buddhism and Hinduism, to name two, have fundamental practices of searching for the I. In Mahayana practice, one searches for the I in such teachings as the “selflessness of persons.” ...
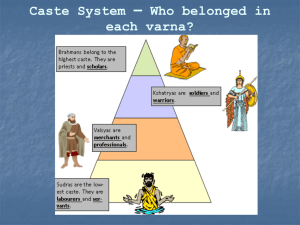
Caste System – Who belonged in each varna?
... Like Hindus, the Buddha believed in reincarnation, but people could end the cycle of rebirth by following the Eightfold Path rather than their dharma. ...
... Like Hindus, the Buddha believed in reincarnation, but people could end the cycle of rebirth by following the Eightfold Path rather than their dharma. ...
India*s Great Civilizations
... – Buddha viewed as devine – Bodhisattvas (individuals who reached spiritual perfection, but intentionally delayed nirvana to help others – Monasteries accepted gifts from wealthy individuals ...
... – Buddha viewed as devine – Bodhisattvas (individuals who reached spiritual perfection, but intentionally delayed nirvana to help others – Monasteries accepted gifts from wealthy individuals ...
Buddhism
... 2. Cause of suffering is desire - When you get what you desire, you then want something else 3. Only way to end suffering is to crush desire - Nirvana = condition of wanting nothing Buddhist’s ultimate goal 4. Follow the Eightfold Path ...
... 2. Cause of suffering is desire - When you get what you desire, you then want something else 3. Only way to end suffering is to crush desire - Nirvana = condition of wanting nothing Buddhist’s ultimate goal 4. Follow the Eightfold Path ...
Buddhism Notes
... A religion of Asia growing out of the teaching of Buddha that suffering is inherent in life and that one can be liberated from it by mental and moral self-purification. Buddhist spiritual leader of Tibet Buddhist teachings about the cause and elimination of suffering The practice of training your mi ...
... A religion of Asia growing out of the teaching of Buddha that suffering is inherent in life and that one can be liberated from it by mental and moral self-purification. Buddhist spiritual leader of Tibet Buddhist teachings about the cause and elimination of suffering The practice of training your mi ...
Buddhism… - Start.ca
... Dukkha: life in this world is filled with suffering Anicca: everything in this world is impermanent Anatta:the self/soul is also impermanent – ...
... Dukkha: life in this world is filled with suffering Anicca: everything in this world is impermanent Anatta:the self/soul is also impermanent – ...
Buddhism - University of Mount Union
... experience enlightenment(bodhi) but who have taken a special vow to continue being reborn into samsara["the great runaround"](rather than entering nirvana) so as to deliver others form their suffering by aiding in the attainment of enlightenment. ...
... experience enlightenment(bodhi) but who have taken a special vow to continue being reborn into samsara["the great runaround"](rather than entering nirvana) so as to deliver others form their suffering by aiding in the attainment of enlightenment. ...
Buddhism… - MrNaborsClass
... The “middle way of wisdom and compassion” A 2500 year old tradition that began in India and spread toChina and Japan It is a philosophy and religion followed by more than 300 million people Based on the teachings of the Buddha ...
... The “middle way of wisdom and compassion” A 2500 year old tradition that began in India and spread toChina and Japan It is a philosophy and religion followed by more than 300 million people Based on the teachings of the Buddha ...
wh43notes
... Siddhartha Gautama meditated and fasted for 49 days to understand the causes of human ...
... Siddhartha Gautama meditated and fasted for 49 days to understand the causes of human ...