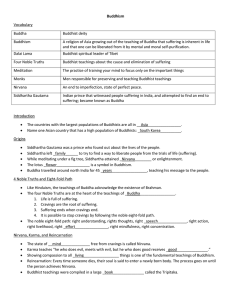
Buddhism - deanworldhistory
... ones lead to bad karma. • "According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good, Doer of evil, evil reaps, Down is the seed and thou shalt taste The fruit thereof." -Buddhist text ...
... ones lead to bad karma. • "According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good, Doer of evil, evil reaps, Down is the seed and thou shalt taste The fruit thereof." -Buddhist text ...
The Eight-Fold Path
... Dharma is understood as the practice (paripatti) of the truth. To take refuge in the Dharma is to take refuge in Buddha. Karma is intentional action, physical, verbal or mental. Good karma brings happiness, bad brings suffering. Avijja and Tanha is ignorance or not knowing the true nature of things ...
... Dharma is understood as the practice (paripatti) of the truth. To take refuge in the Dharma is to take refuge in Buddha. Karma is intentional action, physical, verbal or mental. Good karma brings happiness, bad brings suffering. Avijja and Tanha is ignorance or not knowing the true nature of things ...
Answers
... The state of __mind______________ free from cravings is called Nirvana. Karma teaches “he who does evil, meets with evil, but he who does good receives _good_______________.” Showing compassion to all _living_________________ things is one of the fundamental teachings of Buddhism. Reincarnation: Eve ...
... The state of __mind______________ free from cravings is called Nirvana. Karma teaches “he who does evil, meets with evil, but he who does good receives _good_______________.” Showing compassion to all _living_________________ things is one of the fundamental teachings of Buddhism. Reincarnation: Eve ...
Buddhism Notes
... -He renounced his wealth and became a monk -Instead he sought a state of enlightenment (or nirvana), or no longer fearing death or suffering ...
... -He renounced his wealth and became a monk -Instead he sought a state of enlightenment (or nirvana), or no longer fearing death or suffering ...
Buddhism
... Dukkha: life in this world is filled with suffering Anicca: everything in this world is impermanent Anatta:the self/soul is also impermanent – ...
... Dukkha: life in this world is filled with suffering Anicca: everything in this world is impermanent Anatta:the self/soul is also impermanent – ...
Buddhism PowerPoint
... world, renounced his old life and pursued wisdom One day, he achieved enlightenment, and became known as Buddha, the enlightened one ...
... world, renounced his old life and pursued wisdom One day, he achieved enlightenment, and became known as Buddha, the enlightened one ...
II. Buddhism
... who became known as the Buddha • Born into a noble family and his dad wanted him to be a great world leader • Kept his son isolated within his palace ...
... who became known as the Buddha • Born into a noble family and his dad wanted him to be a great world leader • Kept his son isolated within his palace ...
Buddhism… - Western School District
... Achieving Nirvana means escape from the cycle of rebirth Once Gautama Buddha died, after 80 years of life in this world, having achieved Nirvana and teaching multitudes his way of life, he ceased to exist as a distinct being Buddhism is non-theistic: Buddha is not the Buddhist God – he is just a rev ...
... Achieving Nirvana means escape from the cycle of rebirth Once Gautama Buddha died, after 80 years of life in this world, having achieved Nirvana and teaching multitudes his way of life, he ceased to exist as a distinct being Buddhism is non-theistic: Buddha is not the Buddhist God – he is just a rev ...
File - Mr. Sager AP World History
... today’s date and click on the CNN article – answer the following questions on a post it: 1. How has the government of India attempted to make the caste system a thing of the past? 2. Why is there a feeling of resentment in regards to the attempts to rid India of the caste system? 3. What is the mean ...
... today’s date and click on the CNN article – answer the following questions on a post it: 1. How has the government of India attempted to make the caste system a thing of the past? 2. Why is there a feeling of resentment in regards to the attempts to rid India of the caste system? 3. What is the mean ...
Introductory Notes
... 1. Life is suffering. Both human nature and the world are flawed, which causes people both physical and psychological suffering. 2. The origin of suffering is attachment. To live is to suffer loss, because both life and the world are impermanent. When one is attached to worldly things, through desir ...
... 1. Life is suffering. Both human nature and the world are flawed, which causes people both physical and psychological suffering. 2. The origin of suffering is attachment. To live is to suffer loss, because both life and the world are impermanent. When one is attached to worldly things, through desir ...
Buddhism focuses on the teachings of
... teachings or what is called his “dharma” come from Hinduism. His teachings were written in Buddhist holy books called Tripitaka or Sutras. Buddhism is a religion that is not based on the idea of God—it’s more of a way of life, so it is actually a philosophy, but most people still call Buddhism a rel ...
... teachings or what is called his “dharma” come from Hinduism. His teachings were written in Buddhist holy books called Tripitaka or Sutras. Buddhism is a religion that is not based on the idea of God—it’s more of a way of life, so it is actually a philosophy, but most people still call Buddhism a rel ...
Buddhism
... 2. The cause of suffering is self-centered desire and attachments to worldly things. (Samudaya) Grasping for pleasure Grasping for becoming Grasping for sensual delight Grasping for what we don’t have ...
... 2. The cause of suffering is self-centered desire and attachments to worldly things. (Samudaya) Grasping for pleasure Grasping for becoming Grasping for sensual delight Grasping for what we don’t have ...
Buddhism Notes
... holy man in Nepal (near India), 5th century BCE B. Taught new interpretations of Hinduism C. Renamed “Buddha” which means “enlightened one” D. Buddhism spread from India into China, SE Asia, Japan II. Beliefs A. Buddhism kept Hindu ideas of karma & reincarnation B. Goal of life: to reach perfect pea ...
... holy man in Nepal (near India), 5th century BCE B. Taught new interpretations of Hinduism C. Renamed “Buddha” which means “enlightened one” D. Buddhism spread from India into China, SE Asia, Japan II. Beliefs A. Buddhism kept Hindu ideas of karma & reincarnation B. Goal of life: to reach perfect pea ...
The Essentials of Buddhist Spirituality
... hopeless predicament of those who are their dupes. ~ Three conditions of existence: ▪ impermanence (anitya) ▪ suffering (duhkha) ▪ non-self (anatma) Humankind's History Buddhism sees humankind's history as a gradual, but accelerating, decline and envisages a forthcoming "end of the world", at which ...
... hopeless predicament of those who are their dupes. ~ Three conditions of existence: ▪ impermanence (anitya) ▪ suffering (duhkha) ▪ non-self (anatma) Humankind's History Buddhism sees humankind's history as a gradual, but accelerating, decline and envisages a forthcoming "end of the world", at which ...
Ancient China - MrDowdyClassroomMPHS
... the rise of another iii. Stated that the gods would support a just ruler, but they would not allow anyone corrupt to hold power i. ...
... the rise of another iii. Stated that the gods would support a just ruler, but they would not allow anyone corrupt to hold power i. ...
Buddhism - Mr McEntarfer`s Social Studies Page
... The Buddha – Siddhartha Gautama • The Buddha was born into a wealthy family in India and could have been the leader of his people, but while traveling the countryside he was upset about the human suffering he saw: sickness, poverty and death. He left his home to search for a solution to human suff ...
... The Buddha – Siddhartha Gautama • The Buddha was born into a wealthy family in India and could have been the leader of his people, but while traveling the countryside he was upset about the human suffering he saw: sickness, poverty and death. He left his home to search for a solution to human suff ...
Buddhism - Lomira School District
... After 49 days of meditation he achieved “bodhi” or “enlightenment” Bodhi carries the same meaning as Nirvana, an understanding of the true nature of reality. It also requires a distinction of greed, hate, and delusion. Nirvana is the unchanging state that is reached by enlightened beings, the ...
... After 49 days of meditation he achieved “bodhi” or “enlightenment” Bodhi carries the same meaning as Nirvana, an understanding of the true nature of reality. It also requires a distinction of greed, hate, and delusion. Nirvana is the unchanging state that is reached by enlightened beings, the ...
Buddhism…
... the life of luxury to seek enlightenment and the solution to suffering Followed a strict ascetic lifestyle for six years Rejected this extreme, sat in meditation, achieved Nirvana – an awakening to the truth about life, becoming a Buddha, the “Awakened One”at the age of 35 Spent the remaining 45 yea ...
... the life of luxury to seek enlightenment and the solution to suffering Followed a strict ascetic lifestyle for six years Rejected this extreme, sat in meditation, achieved Nirvana – an awakening to the truth about life, becoming a Buddha, the “Awakened One”at the age of 35 Spent the remaining 45 yea ...
BUDDHA`S TEACHINGS - Castle High School
... Although Buddha’s immediate goal was to eliminate the cause of suffering, his ultimate goal was to become liberated from the cycle of death and rebirth. This was to be accomplished by teaching how we can cease craving and thereby eliminate our attachment to and beliefs in the existence of the illuso ...
... Although Buddha’s immediate goal was to eliminate the cause of suffering, his ultimate goal was to become liberated from the cycle of death and rebirth. This was to be accomplished by teaching how we can cease craving and thereby eliminate our attachment to and beliefs in the existence of the illuso ...
12.4_quiz
... Which of these statements about Buddhism in India is true? a It was taught from a single sacred book. b It became the major religion. c Gurus became Buddhist missionaries. d Hinduism adopted many Buddhist ...
... Which of these statements about Buddhism in India is true? a It was taught from a single sacred book. b It became the major religion. c Gurus became Buddhist missionaries. d Hinduism adopted many Buddhist ...
Buddhism - USC US
... Buddhism – The Basics Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha). Buddha was a wealthy prince who gave up his riches to pursue enlightenment. Four Noble Truths ...
... Buddhism – The Basics Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha). Buddha was a wealthy prince who gave up his riches to pursue enlightenment. Four Noble Truths ...
Buddhism - Hempfield Area School District
... 2. The cause of suffering is self-centered desire and attachments to worldly things. (Samudaya) Grasping for pleasure Grasping for becoming Grasping for sensual delight Grasping for what we don’t have ...
... 2. The cause of suffering is self-centered desire and attachments to worldly things. (Samudaya) Grasping for pleasure Grasping for becoming Grasping for sensual delight Grasping for what we don’t have ...
Buddhism Vocab (p. 103-107 can be used as a reference
... the soul will be free from suffering forever. If you do not achieve nirvana, you will be reborn to live through the cycle of suffering again. Buddhists teach that anyone can achieve nirvana, and it can be achieved in one lifetime. ...
... the soul will be free from suffering forever. If you do not achieve nirvana, you will be reborn to live through the cycle of suffering again. Buddhists teach that anyone can achieve nirvana, and it can be achieved in one lifetime. ...