More with Buddhism
... Based on principle of ahimsa – non-violence to other living things and their souls Believed that everything (including both animate and inanimate objects) had a soul Only by unselfishness could you release yourself from burdens of karma and reach a state of bliss ...
... Based on principle of ahimsa – non-violence to other living things and their souls Believed that everything (including both animate and inanimate objects) had a soul Only by unselfishness could you release yourself from burdens of karma and reach a state of bliss ...
Buddhism PowerPoint
... Once Gautama Buddha died, after 80 years of life in this world, having achieved Nirvana and teaching multitudes his way of life, he ceased to exist as a distinct being ...
... Once Gautama Buddha died, after 80 years of life in this world, having achieved Nirvana and teaching multitudes his way of life, he ceased to exist as a distinct being ...
6: Buddhism - White Rocket Books
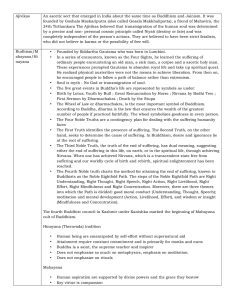
... Right views, right intention, right speech, right action, right livelihood, right effort, right mindfulness, right concentration. “The Eightfold Path” Follow this, to break the bonds that tie one to life— Release from the cycle. Extinguishing of tanha (desire, craving) “Nirvana” (“ ...
... Right views, right intention, right speech, right action, right livelihood, right effort, right mindfulness, right concentration. “The Eightfold Path” Follow this, to break the bonds that tie one to life— Release from the cycle. Extinguishing of tanha (desire, craving) “Nirvana” (“ ...
Buddhism
... The Four Noble Truths • The Buddha taught that life was inherently suffering, that it is caused by craving, but that this condition was curable – 1) Suffering: Birth is suffering, aging is suffering, illness is suffering, death is suffering; union with what is displeasing is suffering; separation f ...
... The Four Noble Truths • The Buddha taught that life was inherently suffering, that it is caused by craving, but that this condition was curable – 1) Suffering: Birth is suffering, aging is suffering, illness is suffering, death is suffering; union with what is displeasing is suffering; separation f ...
Theravada Buddhism
... Pali scriptures (the Pali Canon) and the nontheistic ideal of self-purification to nirvana The oldest record of the Buddha's teachings Dominant in southern Asia ...
... Pali scriptures (the Pali Canon) and the nontheistic ideal of self-purification to nirvana The oldest record of the Buddha's teachings Dominant in southern Asia ...
THE BUDDHIST SCRIPTURES COMPARED WITH THE BIBLE
... The evolution of different schools or sects of Buddhism accompanied its spread and growth. The two main traditions are Theravada or Hinayana Buddhism and Mahayana Buddhism. The emphasis of the Theravada ("The Way of the Elders") tradition is on attaining the status of an arahat, one who has conquere ...
... The evolution of different schools or sects of Buddhism accompanied its spread and growth. The two main traditions are Theravada or Hinayana Buddhism and Mahayana Buddhism. The emphasis of the Theravada ("The Way of the Elders") tradition is on attaining the status of an arahat, one who has conquere ...
Buddhism - Soren Kerk
... not “set apart” from the world in a special way; one who is not ordained or a member of the professional religious class. • Dharma - the collected teachings of the Buddha concerning how one should live • Many tried to turn HIM into a God. ...
... not “set apart” from the world in a special way; one who is not ordained or a member of the professional religious class. • Dharma - the collected teachings of the Buddha concerning how one should live • Many tried to turn HIM into a God. ...
Lecture: 4. Buddhism
... > suffering is inevitable as it is part of the human condition > suffering is caused by self-centered desires and cravings > suffering can be overcome by eliminating our self-centered desires and cravings > the way to achieve this is to follow the Eightfold Path 4. The Eightfold Path - right views, ...
... > suffering is inevitable as it is part of the human condition > suffering is caused by self-centered desires and cravings > suffering can be overcome by eliminating our self-centered desires and cravings > the way to achieve this is to follow the Eightfold Path 4. The Eightfold Path - right views, ...
Buddhism - Hudson City Schools
... The oldest school of Buddhism. Buddhism A monastic life Focused on wisdom & meditation. ...
... The oldest school of Buddhism. Buddhism A monastic life Focused on wisdom & meditation. ...
Buddhism (583 C.E.
... Buddhism’s Beginnings The founder of Buddhism was born in a part of India that is in present day Nepal. His name was Siddhartha Gautama. Siddhartha was born into a wealthy, noble family and lived a privileged life. After experiencing pain and suffering, he sought to find ways to rid the world of the ...
... Buddhism’s Beginnings The founder of Buddhism was born in a part of India that is in present day Nepal. His name was Siddhartha Gautama. Siddhartha was born into a wealthy, noble family and lived a privileged life. After experiencing pain and suffering, he sought to find ways to rid the world of the ...
220 Outline of Buddhism
... 1. Establishment of the orthodox Theravada (Doctrine of the Elders)- the Theravadin becomes the Southern School of Buddhism. The Mahasenghika (Great Assembly) that is to grow into the Northern School. The Jatakas (recast from Hindu fables)- accepted by both Southern and Northern Schools. Tales of th ...
... 1. Establishment of the orthodox Theravada (Doctrine of the Elders)- the Theravadin becomes the Southern School of Buddhism. The Mahasenghika (Great Assembly) that is to grow into the Northern School. The Jatakas (recast from Hindu fables)- accepted by both Southern and Northern Schools. Tales of th ...
Buddhism
... finite desire that can only be realized in other incarnations; in this sense at least these persons live on. But what about the Arhat, the holy one who has extinguished all such desires; does such a one continue to exist? –Smith, p117 ...
... finite desire that can only be realized in other incarnations; in this sense at least these persons live on. But what about the Arhat, the holy one who has extinguished all such desires; does such a one continue to exist? –Smith, p117 ...
Buddhism - PhilosophicalAdvisor.com
... finite desire that can only be realized in other incarnations; in this sense at least these persons live on. But what about the Arhat, the holy one who has extinguished all such desires; does such a one continue to exist? –Smith, p117 ...
... finite desire that can only be realized in other incarnations; in this sense at least these persons live on. But what about the Arhat, the holy one who has extinguished all such desires; does such a one continue to exist? –Smith, p117 ...
Buddhism
... break the cycle, the way to end suffering His new life goal: to teach this way, or path, to others Mara (evil in human form) tried to convince him that his insights should not be taught; they were too complex and too difficult ...
... break the cycle, the way to end suffering His new life goal: to teach this way, or path, to others Mara (evil in human form) tried to convince him that his insights should not be taught; they were too complex and too difficult ...
Buddhism…
... What is Buddhism… The “Middle Way of Wisdom and Compassion” Based on the teachings of the Buddha (the enlightened one). Buddhism is Non-theistic: Buddha is not the Buddhist God – he is just a revered teacher Once Buddha died, after 80 years of life in this world, having achieved “Nirvana” (enlighte ...
... What is Buddhism… The “Middle Way of Wisdom and Compassion” Based on the teachings of the Buddha (the enlightened one). Buddhism is Non-theistic: Buddha is not the Buddhist God – he is just a revered teacher Once Buddha died, after 80 years of life in this world, having achieved “Nirvana” (enlighte ...
Brahman - Spokane Public Schools
... -Theravada (Teaching of the Elders) portrayed Buddha as a wise teacher and model but not divine -Mahayana (Great Vehicle) developed in the early centuries CE and claimed that help was available for the strenuous journey through bodhisattvas or spiritually developed individuals who had postponed entr ...
... -Theravada (Teaching of the Elders) portrayed Buddha as a wise teacher and model but not divine -Mahayana (Great Vehicle) developed in the early centuries CE and claimed that help was available for the strenuous journey through bodhisattvas or spiritually developed individuals who had postponed entr ...
Buddhism
... • HOWEVER: saw that there was a lot of suffering in the world • Searched for a cure for human suffering… • Got rid of his royal clothes, shaved his head, abandoned his family and sought to find the true meaning of life • Sought to see things in a new way ...
... • HOWEVER: saw that there was a lot of suffering in the world • Searched for a cure for human suffering… • Got rid of his royal clothes, shaved his head, abandoned his family and sought to find the true meaning of life • Sought to see things in a new way ...
Buddhism: a religion founded in India based on the
... and does not achieve enlightenment, then one will have suffering. Nirvana: a state of perfect peace. The ultimate goal of Buddhism is to be released from the cycle of death and rebirth. ...
... and does not achieve enlightenment, then one will have suffering. Nirvana: a state of perfect peace. The ultimate goal of Buddhism is to be released from the cycle of death and rebirth. ...
Buddhism Buddhism - World Relief Nashville
... they could not tolerate Buddhism as a rival faith, they ...
... they could not tolerate Buddhism as a rival faith, they ...
Buddhism - The Faith Project
... into three basic subdivisions: Ethical actions of body, speech and mind; Concentration, which includes Mindfulness practices; and Wisdom— the direct perception into the nature of reality which eliminates the roots of ignorance (avidya in Sanskrit). Through the teaching of the Four ...
... into three basic subdivisions: Ethical actions of body, speech and mind; Concentration, which includes Mindfulness practices; and Wisdom— the direct perception into the nature of reality which eliminates the roots of ignorance (avidya in Sanskrit). Through the teaching of the Four ...
Ajivikas An ascetic sect that emerged in India about the same time
... The First Truth identifies the presence of suffering. The Second Truth, on the other hand, seeks to determine the cause of suffering. In Buddhism, desire and ignorance lie at the root of suffering. The Third Noble Truth, the truth of the end of suffering, has dual meaning, suggesting either the end ...
... The First Truth identifies the presence of suffering. The Second Truth, on the other hand, seeks to determine the cause of suffering. In Buddhism, desire and ignorance lie at the root of suffering. The Third Noble Truth, the truth of the end of suffering, has dual meaning, suggesting either the end ...
Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism
... 11. Teaching: Siddhartha, now become the Buddha, decided it was useless to teach others. The King of the gods asks him to teach those “with little dust on their eyes.” For 45 years, expounds on his first sermon, The Wheel Sutra. 12. Final Nirvana: Ill from some bad almsfood, gathers disciples, What ...
... 11. Teaching: Siddhartha, now become the Buddha, decided it was useless to teach others. The King of the gods asks him to teach those “with little dust on their eyes.” For 45 years, expounds on his first sermon, The Wheel Sutra. 12. Final Nirvana: Ill from some bad almsfood, gathers disciples, What ...