Unit 4: Coordinate Geometry - Test
... y = 8/9 x + b 0 = 8/9(6) + b 16/3 = b Y = 8/9x + 16/3 Next, they need to find the equation of the line that is parallel to AB and passes through C. Y = -2/5x + b 10 = -2/5(10) + b 10 = -4 + b 14 = b y = -2/5x + 14 Lastly, students need to see that the point D would be the intersection of those two l ...
... y = 8/9 x + b 0 = 8/9(6) + b 16/3 = b Y = 8/9x + 16/3 Next, they need to find the equation of the line that is parallel to AB and passes through C. Y = -2/5x + b 10 = -2/5(10) + b 10 = -4 + b 14 = b y = -2/5x + 14 Lastly, students need to see that the point D would be the intersection of those two l ...
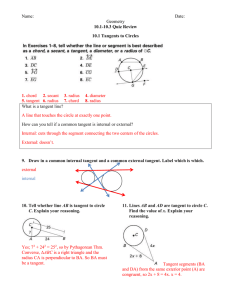
2-3 Practice
... sides they do not share are opposite rays. 11. A leap year is a year that has 366 days because one day is added to the month ...
... sides they do not share are opposite rays. 11. A leap year is a year that has 366 days because one day is added to the month ...
2-3 Practice
... sides they do not share are opposite rays. 11. A leap year is a year that has 366 days because one day is added to the month ...
... sides they do not share are opposite rays. 11. A leap year is a year that has 366 days because one day is added to the month ...
Lesson Plan Format
... b) There is a myth that the Great Wall of China is the only man-made object visible from the Moon. The Great Wall is barely visible in photographs taken from 180 miles above Earth. The Moon is about 237,000 miles from Earth. Therefore, the myth cannot be true. ANSWER: The conclusion is based on logi ...
... b) There is a myth that the Great Wall of China is the only man-made object visible from the Moon. The Great Wall is barely visible in photographs taken from 180 miles above Earth. The Moon is about 237,000 miles from Earth. Therefore, the myth cannot be true. ANSWER: The conclusion is based on logi ...