* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
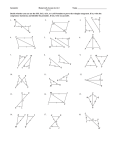
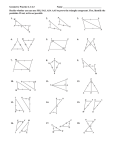
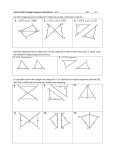
Congruent Triangles Triangle Congruence 4.2 Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles • Congruent Polygons All corresponding sides and all corresponding angles must be congruent to prove congruency. • Triangles require less proof to test for congruence. • Use the SSS Postulate to test for triangle congruence. • Use the SAS Postulate to test for triangle congruence. • Use the ASA Postulate to test for triangle congruence. • included angle • included side Holt Geometry homework Congruent Triangles Congruence of Polygons If all six pairs of corresponding parts (sides and angles) are congruent, then the triangles are congruent. If Sides are congruent and Angles are congruent 1. AB DE 4. A D 2. BC EF 5. B E 3. AC DF 6. C F then ABC Triangles are congruent DEF homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Vocabulary - SAS An included angle is an angle formed by two adjacent sides of a polygon. B is the included angle between sides AB and BC. homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Vocabulary - ASA B An included side is a side formed by two consecutive angles of a polygon. BC is the included side between angles homework B and C. Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles SSS CONGRUENCE POSTULATE POSTULATE Side - Side - Side (SSS) Congruence Postulate If three sides of one triangle are congruent to three sides of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. If Side S MN QR Side S NP RS Side S PM SQ then MNP QRS homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Using the SSS Congruence Postulate Prove that PQW TSW. SOLUTION Paragraph Proof The marks on the diagram show that PQ TS, PW TW, and QW SW. So by the SSS Congruence Postulate, you know that PQW TSW. Holt Geometry homework Congruent Triangles SAS CONGRUENCE POSTULATE POSTULATE Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Congruence Postulate If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. If Side S Angle A Side S PQ WX Q X QS XY then PQS WXY homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles ASA CONGRUENCE POSTULATE POSTULATE Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Congruence Postulate If two angles and the included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the included side of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. A If Angle Q X S Side Angle A PQ WX P W then PQS WXY homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles CONGRUENCE POSTULATES The SSS Congruence Postulate is a shortcut for proving two triangles are congruent without using all six pairs of corresponding parts. The SAS Congruence Postulate is a shortcut for proving two triangles are congruent without using all six pairs of corresponding parts. The ASA Congruence Postulate is a shortcut for proving two triangles are congruent without using all six pairs of corresponding parts. homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Decide if the triangles are congruent by SSS, SAS, ASA a. SAS e. None i. ASA j. b. SSS c. None d. SAS f. g. SAS h. SSS SSS None k. ASA l. None homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Find t so that ∆ADB ∆CDB If t = 4 ∆ADB ∆CDB by SAS homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Find x so that ∆MNO ∆PQR If x = 5 ∆MNO ∆PQR by SSS homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles ∆ABC ∆DBC and AB = 3x + 10. DB = 4x + 4. Find x and AB. 26° x = 6, AB = 28 homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles ∆ABC ∆JKL AB = 2x + 12. JK = 4x – 50. Find x and AB. x = 31, AB = 74 homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles Given: AE DE, BE CE Prove: AEB 1 2 DEC. Statements Reasons 1. AE DE, BE CE 2. 1 2 1. Given 3. AEB DEC 3. SAS Congruence Postulate 2. Vertical Angles Theorem homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles B C Given: Prove: A Statements 1. 2. 3. ΔABG ΔCGB G Reasons 1. Given 2. Reflexive 3. SSS homework Holt Geometry Congruent Triangles DR GIVEN: D AG ADR GRD DRA PROVE: DRG Statements 1. DR 2. 3. AG DRA and DRG are right angles. DRA DRG 4. ADR Holt Geometry Reasons GRD A R G 1. Given 2. Definition of Perpendicular 3. Right Angle Congruence Theorem 4. Given 5. DR DR 5. Reflexive Property 6. DRA DRG 6. ASA Congruence Postulate homework Congruent Triangles Assignment Geometry: 4.2A and 4.2B Section 9 - 19 Holt Geometry