Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 2 – Due Oct 13,...
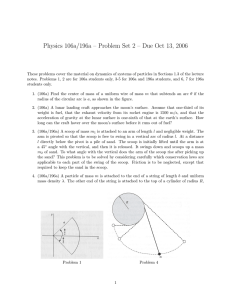
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
Untitled
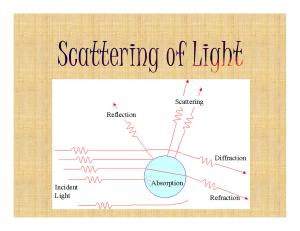
... • Definition:“ Light scattering is a form of scattering in which light is the form of propagating energy which is scattered. Light scattering can be thought of as the deflection of a ray from a straight path, for example by irregularities in the propagation medium, particles, or in the interface bet ...
... • Definition:“ Light scattering is a form of scattering in which light is the form of propagating energy which is scattered. Light scattering can be thought of as the deflection of a ray from a straight path, for example by irregularities in the propagation medium, particles, or in the interface bet ...
lecture 18 - CLASSE Cornell
... Random ground motion, with a mean square amplitude ( ∆x )2 , will produce angular kicks (by misaligning quadrupoles) given by ...
... Random ground motion, with a mean square amplitude ( ∆x )2 , will produce angular kicks (by misaligning quadrupoles) given by ...
Rayleigh scattering. Scattering and absorption by aerosols and
... water. Thus, to calculate the absorption and scattering cross sections of cloud droplets, one needs to know the size of droplets and the refractive index of water ...
... water. Thus, to calculate the absorption and scattering cross sections of cloud droplets, one needs to know the size of droplets and the refractive index of water ...
Physics 535 lecture notes: - 10 Oct 4th, 2007 Homework: 6.2, 6.3
... similar properties relative to the strong force, and whether they are expected to be more massive. These particles can also be in ground or excited spin and angular momentum states. To classify a particle and understand it’s interactions all these quantum numbers need to be determined. In addition, ...
... similar properties relative to the strong force, and whether they are expected to be more massive. These particles can also be in ground or excited spin and angular momentum states. To classify a particle and understand it’s interactions all these quantum numbers need to be determined. In addition, ...
Theoretical study of the phase evolution in a quantum dot in the
... The single level Anderson model (SLAM) is not sufficient to capture the whole physics contained in the experimental device which can be viewed as an artificial atom. One may try to start with a many level Anderson model (MLAM) description of the system. We have chosen another route and introduced th ...
... The single level Anderson model (SLAM) is not sufficient to capture the whole physics contained in the experimental device which can be viewed as an artificial atom. One may try to start with a many level Anderson model (MLAM) description of the system. We have chosen another route and introduced th ...
Slide 1
... region and constant over the period of time needed to obtain the average value of the received power. ...
... region and constant over the period of time needed to obtain the average value of the received power. ...
PHYS4016 Nuclear Physics
... learned from it. They should be familiar with the quark model and hadrons as a bound state of quarks in low-energy Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD). They should understand what the hadron resonance spectrum is, how it can be studied and what can be learned from it. They should be familia ...
... learned from it. They should be familiar with the quark model and hadrons as a bound state of quarks in low-energy Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD). They should understand what the hadron resonance spectrum is, how it can be studied and what can be learned from it. They should be familia ...
Photo Acoustic Effect And it`s usage for spectroscopy
... depend on transmission or reflection of the light beam – can work with opaque materials, higher immunity to scattering effects May work in various wavelengths Signal depends on various characteristics of medium in addition to absorption (heat capacity, acoustic velocity) that may be used to impr ...
... depend on transmission or reflection of the light beam – can work with opaque materials, higher immunity to scattering effects May work in various wavelengths Signal depends on various characteristics of medium in addition to absorption (heat capacity, acoustic velocity) that may be used to impr ...
Accelerators - UC Davis Physics
... • at one or more points on the ring, insert a cavity in which there is an oscillating RF electromagnetic field • set RF frequency such that every time the particles pass, they are accelerated in the direction of the field (hence the name synchrotron) ...
... • at one or more points on the ring, insert a cavity in which there is an oscillating RF electromagnetic field • set RF frequency such that every time the particles pass, they are accelerated in the direction of the field (hence the name synchrotron) ...
spp-scatt_01
... channel heating due to Joule losses and low thermal coupling to leads It exists, however, a relaxation mechanism which transfers the energy directly to the substrate without intermediate exchange with the SWNT lattice (phonons) which is an inelastic remote optical phonon scattering Pioneering work b ...
... channel heating due to Joule losses and low thermal coupling to leads It exists, however, a relaxation mechanism which transfers the energy directly to the substrate without intermediate exchange with the SWNT lattice (phonons) which is an inelastic remote optical phonon scattering Pioneering work b ...
Introduction to RXS-CDW
... • If the core hole is an n=1 state, this is called a K-edge, if n=2 an L edge, if n=3 an M edge, and so on. • For example in an L-edge absorption of a transition metal one excites an electron from a full 2p shell to a 3d state. ...
... • If the core hole is an n=1 state, this is called a K-edge, if n=2 an L edge, if n=3 an M edge, and so on. • For example in an L-edge absorption of a transition metal one excites an electron from a full 2p shell to a 3d state. ...
Welcome to BME 495: Advanced Physical and Applied Optics
... Jones’ matrix formalism, OCT as an example of the application of partial temporary coherence, enhanced backscattering as an example of the application of partial spatial coherence) II. Light Scattering Phenomena – Lecture 4: Light Scattering I (integral equation of scattering, near field and far fie ...
... Jones’ matrix formalism, OCT as an example of the application of partial temporary coherence, enhanced backscattering as an example of the application of partial spatial coherence) II. Light Scattering Phenomena – Lecture 4: Light Scattering I (integral equation of scattering, near field and far fie ...
Lecture 2 EMS - San Jose State University
... The photon is the physical form of a quantum, the basic particle of energy studied in quantum mechanics (which deals with the physics of the very small, that is, particles and their behavior at atomic and subatomic levels). The photon is also described as the messenger particle for EM force or as th ...
... The photon is the physical form of a quantum, the basic particle of energy studied in quantum mechanics (which deals with the physics of the very small, that is, particles and their behavior at atomic and subatomic levels). The photon is also described as the messenger particle for EM force or as th ...
Cold encounters: Electrons and molecules
... Two types of experiment have been developed. The first are those that form cold electrons or Rydberg atoms in situ with a target gas to study exclusively DA [3,4,5,7]. The exquisite precision of recent DA measurements is illustrated by data in [8J, involving CH 3 I + electron ~ 1- + CH 3, showing ho ...
... Two types of experiment have been developed. The first are those that form cold electrons or Rydberg atoms in situ with a target gas to study exclusively DA [3,4,5,7]. The exquisite precision of recent DA measurements is illustrated by data in [8J, involving CH 3 I + electron ~ 1- + CH 3, showing ho ...
totem_tchr_v1.1 - Quarknet
... In general, the scattering angles for the red and green dots in any given event will be very close to each other. If you guide students to notice this, they might be able to conclude (correctly) that this is a result of conservation of momentum. This also means that if we measure the momentum of a p ...
... In general, the scattering angles for the red and green dots in any given event will be very close to each other. If you guide students to notice this, they might be able to conclude (correctly) that this is a result of conservation of momentum. This also means that if we measure the momentum of a p ...
Thomson scattering: - Ira-Inaf
... Compton scattering ''In physics, Compton scattering or the Compton effect, is the decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of an Xray or gamma ray photon, when it interacts with matter. Inverse Compton scattering also exists, where the photon gains energy (decreasing i ...
... Compton scattering ''In physics, Compton scattering or the Compton effect, is the decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of an Xray or gamma ray photon, when it interacts with matter. Inverse Compton scattering also exists, where the photon gains energy (decreasing i ...
Cross section (physics)
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made of discrete particles. The cross section of a particle is the same as the cross section of a hard object, if the probabilities of hitting them with a ray are the same. It is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area.In scattering experiments, one is often interested in knowing how likely a given event occurs. However, the rate depends strongly on experimental variables such as the density of the target material, the intensity of the beam, or the area of overlap between the beam and the target material. To control for these mundane differences, one can factor out these variables, resulting in an area-like quantity known as the cross section.