Electron-Positron Scattering
... that DF (x − y) satisfies the Klein-Gordon equation everywhere except at y = x. At y = x, we would have to add an infinite (delta function) potential term to the Klein-Gordon equation, to represent the disturbance that creates the particle. This infinite potential term results in an infinite wavefunctio ...
... that DF (x − y) satisfies the Klein-Gordon equation everywhere except at y = x. At y = x, we would have to add an infinite (delta function) potential term to the Klein-Gordon equation, to represent the disturbance that creates the particle. This infinite potential term results in an infinite wavefunctio ...
Light Scattering
... Consider light moving in the x̂ direction, that is linearly polarized with an E field in the ẑ direction (Fig. 1, top). The dipole moment is then in the ẑ direction. The resulting scattered light is then polarized in the ẑ direction, and has the highest intensity in the ŷ direction (where θ=0), ...
... Consider light moving in the x̂ direction, that is linearly polarized with an E field in the ẑ direction (Fig. 1, top). The dipole moment is then in the ẑ direction. The resulting scattered light is then polarized in the ẑ direction, and has the highest intensity in the ŷ direction (where θ=0), ...
ART OF COMPLAINING
... When the size of the particles becomes roughly equivalent to the wavelength of the illuminating light, then a complex function of maxima and minima with ...
... When the size of the particles becomes roughly equivalent to the wavelength of the illuminating light, then a complex function of maxima and minima with ...
• Cross sections • Atomic units • Atomic and molecular beams
... • Embedding molecules, clusters and weakly bound complexes in helium nanodroplets allows to study them by means of absorption and emission spectroscopy with vibrational/rotational resolution. • In the superfluid helium droplet the guest (“dopant”) molecules can rotate at very low temperatures with l ...
... • Embedding molecules, clusters and weakly bound complexes in helium nanodroplets allows to study them by means of absorption and emission spectroscopy with vibrational/rotational resolution. • In the superfluid helium droplet the guest (“dopant”) molecules can rotate at very low temperatures with l ...
Homework 8 - spacibm configuration notes
... (d) Now substitute your compound motion for parts (a) and (b) into the Lorentz force equation and solve again for both components to the motion. This develops higher order contributions to the motion. Repeat the process to obtain an infinite series for each component to provide an exact description ...
... (d) Now substitute your compound motion for parts (a) and (b) into the Lorentz force equation and solve again for both components to the motion. This develops higher order contributions to the motion. Repeat the process to obtain an infinite series for each component to provide an exact description ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI M.Sc. SECOND
... 10. Explain optical theorem with reference to scattering cross section. PART B ...
... 10. Explain optical theorem with reference to scattering cross section. PART B ...
... calculate u (v,X) sinX dX dcp, the relative probability of a molecule being scattered out of the beam into a given solid angle sinX dX dcp. The term, cp, is the angle between the plane of the trajectory and some reference plane. Trajectories with their impact parameter lying in the range b, b db and ...
Q 2
... The scattering process involves a transition between an initial quantum state: |i = incoming e-, target p and a final state |f = scattered e-, recoil p . The transition rate if can be calculated from “Fermi’s Golden Rule”, a basic prescription in quantum mechanics: (ch. 2) Units: s-1 ...
... The scattering process involves a transition between an initial quantum state: |i = incoming e-, target p and a final state |f = scattered e-, recoil p . The transition rate if can be calculated from “Fermi’s Golden Rule”, a basic prescription in quantum mechanics: (ch. 2) Units: s-1 ...
Stramski_IOCCG 2016_Interaction of Light and Matter
... • From Maxwell’s equations in differential form we obtain in free space ...
... • From Maxwell’s equations in differential form we obtain in free space ...
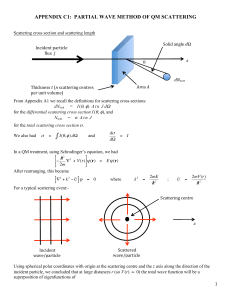
APPENDIX C1: PARTIAL WAVE METHOD OF QM SCATTERING
... The values of V0 and R for the potential well are found to be different in the triplet and singlet states: V0 = 39 MeV and R = 1.4 fm for the triplet state (S = 1) V0 = 14 MeV and R = 2.5 fm for the singlet state (S = 0) The larger V0 in the triplet case can lead to the formation of a bound state (2 ...
... The values of V0 and R for the potential well are found to be different in the triplet and singlet states: V0 = 39 MeV and R = 1.4 fm for the triplet state (S = 1) V0 = 14 MeV and R = 2.5 fm for the singlet state (S = 0) The larger V0 in the triplet case can lead to the formation of a bound state (2 ...
Slides - nanoHUB
... Consider instead specimen of N atoms / unit thickness. Total cross section for scattering from specimen: Q T = Nσ T = ...
... Consider instead specimen of N atoms / unit thickness. Total cross section for scattering from specimen: Q T = Nσ T = ...
Electric charge distribution - User web pages on web
... However, this doesn’t work in practice, because the integral has to be done over a complete range of q from 0 to ∞, and no experiment can ever span an infinite range of momentum transfer! (It is bad enough trying to acquire data at large momentum transfer because the basic cross-section drops like q ...
... However, this doesn’t work in practice, because the integral has to be done over a complete range of q from 0 to ∞, and no experiment can ever span an infinite range of momentum transfer! (It is bad enough trying to acquire data at large momentum transfer because the basic cross-section drops like q ...
rutherford scattering
... charged particles. Initial experiments with both electrons and alpha particles seemed to confirm Thomson's picture, but the work raised questions in Ernest Rutherford's laboratory. A more detailed study was therefore proposed by Rutherford and carried out by Hans Geiger with assistance from Ernest M ...
... charged particles. Initial experiments with both electrons and alpha particles seemed to confirm Thomson's picture, but the work raised questions in Ernest Rutherford's laboratory. A more detailed study was therefore proposed by Rutherford and carried out by Hans Geiger with assistance from Ernest M ...
PHYS 832 Problem Set #4 Due: April 9, 2015 1. Jackson 14.4 Using
... where f(x) is a cutoff function having the value unity at x=0 and vanishing rapidly for x >> 1 [e.g., f ≅ exp(–ω/ωc)], and ωc =(3/2)(eB/m)(E/mc2) cos θ, where θ is the pitch angle of the hel ...
... where f(x) is a cutoff function having the value unity at x=0 and vanishing rapidly for x >> 1 [e.g., f ≅ exp(–ω/ωc)], and ωc =(3/2)(eB/m)(E/mc2) cos θ, where θ is the pitch angle of the hel ...
Cross Products next
... The angular momentum of a particle (L) with momentum p and position r relative to the position at which the angular momentum is measured is given by ...
... The angular momentum of a particle (L) with momentum p and position r relative to the position at which the angular momentum is measured is given by ...
pres
... If a signal is detected: confirmation of LDM If not, the LDM scenario is possibly ruled out ...
... If a signal is detected: confirmation of LDM If not, the LDM scenario is possibly ruled out ...
Scattering and propagation of light in mesoscopic random
... beam of variable diameter w. For a liquid suspension of strongly scattering colloidal particles we demonstrate that the temporal fluctuations due to long-range correlations C2 can be modeled quantitatively in this "narrow-beam limit". Our experimental results provide further evidence that the effect ...
... beam of variable diameter w. For a liquid suspension of strongly scattering colloidal particles we demonstrate that the temporal fluctuations due to long-range correlations C2 can be modeled quantitatively in this "narrow-beam limit". Our experimental results provide further evidence that the effect ...
Slide
... • Resistances may not add !! • Resistances may be tunable by altering phase (e.g. path-length, temperature, magnetic field) ...
... • Resistances may not add !! • Resistances may be tunable by altering phase (e.g. path-length, temperature, magnetic field) ...
Summary
... atoms were scattered out of the final state or served as a gain medium for higher-order processes. We have now realized a Raman atom amplifier in which the gain medium and the amplified atoms are in different internal states [3]. Such a system has analogies to an optical laser in which different tra ...
... atoms were scattered out of the final state or served as a gain medium for higher-order processes. We have now realized a Raman atom amplifier in which the gain medium and the amplified atoms are in different internal states [3]. Such a system has analogies to an optical laser in which different tra ...
On the Annihilation Cross Section of the Antinucleon and the Nucleon
... and the electron-neutron interaction. According to these results, the proton has the electro-magnetic radius, r•. v . . rm,v= (0.77 ± 0.10) X 10-13 em, ...
... and the electron-neutron interaction. According to these results, the proton has the electro-magnetic radius, r•. v . . rm,v= (0.77 ± 0.10) X 10-13 em, ...
SCATTERING OF ELECTRONS BY DIATOMIC MOLECULES IN
... with allowance for exchange (formula (22)). For the singlet and triplet seattering lengths, the mean values a+= 5.97 ao and a-= 1.77 ao, respectively, were used, as obtained by Schwartz[BJ by a variational method for the problem of electron scattering by a hydrogen atom. We could use also other valu ...
... with allowance for exchange (formula (22)). For the singlet and triplet seattering lengths, the mean values a+= 5.97 ao and a-= 1.77 ao, respectively, were used, as obtained by Schwartz[BJ by a variational method for the problem of electron scattering by a hydrogen atom. We could use also other valu ...
Polarization and Optical Properties of n-Layer Doped with Au Nanoparticles
... to the state of polarization of the incident light intensity Io to a particular scattering plane (i.e. in our case, the horizontal scattering plane). As a result it is often needed to obtain results for parallel, perpendicular polarization as well as unpolarised incidence. In particular the ratio (S ...
... to the state of polarization of the incident light intensity Io to a particular scattering plane (i.e. in our case, the horizontal scattering plane). As a result it is often needed to obtain results for parallel, perpendicular polarization as well as unpolarised incidence. In particular the ratio (S ...
Cross section (physics)
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made of discrete particles. The cross section of a particle is the same as the cross section of a hard object, if the probabilities of hitting them with a ray are the same. It is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area.In scattering experiments, one is often interested in knowing how likely a given event occurs. However, the rate depends strongly on experimental variables such as the density of the target material, the intensity of the beam, or the area of overlap between the beam and the target material. To control for these mundane differences, one can factor out these variables, resulting in an area-like quantity known as the cross section.