electron scattering (2)
... where Vn is the normalization volume for the plane wave electron states, and if is the transition rate from the initial to final state, which we calculate using a standard result from quantum mechanics known as “Fermi’s Golden Rule:” ...
... where Vn is the normalization volume for the plane wave electron states, and if is the transition rate from the initial to final state, which we calculate using a standard result from quantum mechanics known as “Fermi’s Golden Rule:” ...
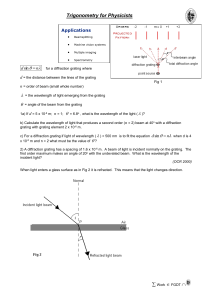
trigonometry
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
Differential Cross Section Measurements in Ion
... a potential in the range of 6 to 20 kV applied to the ion source, mass analyzed by a bending magnet, and are accelerated to energies up to 250 keV. Then the ion beam is directed down a long beam line by an electric field deflector system. A schematic diagram of the long beam line is shown in Fig. 2. ...
... a potential in the range of 6 to 20 kV applied to the ion source, mass analyzed by a bending magnet, and are accelerated to energies up to 250 keV. Then the ion beam is directed down a long beam line by an electric field deflector system. A schematic diagram of the long beam line is shown in Fig. 2. ...
Bound-Free Transitions
... • Recall dt = krdx. We need to calculate k, the absorption coefficient per gram of material • First calculate the atomic absorption coefficient a (per absorbing atom or ion) • Multiply by number of absorbing atoms or ions per gram of stellar material (this depends on temperature and pressure) ...
... • Recall dt = krdx. We need to calculate k, the absorption coefficient per gram of material • First calculate the atomic absorption coefficient a (per absorbing atom or ion) • Multiply by number of absorbing atoms or ions per gram of stellar material (this depends on temperature and pressure) ...
Influence of ionised electrons on heavy nuclei
... Abstract. For the collision systems 1.4MeVu-' U3'+ and 5.9 MeVu-' U65+ on Ne, transverse (with respect to the beam axis) momentum distributions of recoiling target atoms have been measured applying a time-of-flight technique. In the case of isotropic electron emission, the transverse momenta of the ...
... Abstract. For the collision systems 1.4MeVu-' U3'+ and 5.9 MeVu-' U65+ on Ne, transverse (with respect to the beam axis) momentum distributions of recoiling target atoms have been measured applying a time-of-flight technique. In the case of isotropic electron emission, the transverse momenta of the ...
Diamagnetic Screening of Transverse Current
... the position of neutron r arises from electrons in the crystal with coordinates ri and momenta Pi· We stress that it is an operator and should be subjected to quantum and thermodynamical averaging before it is compared with any measurement.*> The differential cross section cJ2(J/ dQdE' for the scatt ...
... the position of neutron r arises from electrons in the crystal with coordinates ri and momenta Pi· We stress that it is an operator and should be subjected to quantum and thermodynamical averaging before it is compared with any measurement.*> The differential cross section cJ2(J/ dQdE' for the scatt ...
Scattering time τ
... – In general, this is difficult. Rigorously, this must be approached by using the classical (or the quantum mechanical generalization of) Boltzmann Transport Equation. We will only briefly discuss this, to get an overview. ...
... – In general, this is difficult. Rigorously, this must be approached by using the classical (or the quantum mechanical generalization of) Boltzmann Transport Equation. We will only briefly discuss this, to get an overview. ...
Scattering theory - Theory of Condensed Matter
... = R2 and σtot → 4πR2 . $ Info. Ultracold atomic gases provide a topical arena in which resonant scattering phenomena are exploited. In particular, experimentalists make use of Feshbach resonance phenomena to tune the effective interaction between atoms. This tunability arises from the coupling of fr ...
... = R2 and σtot → 4πR2 . $ Info. Ultracold atomic gases provide a topical arena in which resonant scattering phenomena are exploited. In particular, experimentalists make use of Feshbach resonance phenomena to tune the effective interaction between atoms. This tunability arises from the coupling of fr ...
Direct Search of Dark Matter in High
... with “quark momentum” These interactions are not suppressed even if the DM mass is much larger than the W/Z boson mass. J. Hisano, S. Matsumoto, M. Nojiri, O. Saito, Phys. Rev. D 71 (2005) 015007. ...
... with “quark momentum” These interactions are not suppressed even if the DM mass is much larger than the W/Z boson mass. J. Hisano, S. Matsumoto, M. Nojiri, O. Saito, Phys. Rev. D 71 (2005) 015007. ...
Course Syllabus
... Modern atomic physics incorporates a broad range of subjects including, quantum optics, collisions, Bose and Fermi condensates, and the interactions of light with matter. It is impossible to do justice to all of these topics so no attempt will be made to touch on all of them. Rather, the interaction ...
... Modern atomic physics incorporates a broad range of subjects including, quantum optics, collisions, Bose and Fermi condensates, and the interactions of light with matter. It is impossible to do justice to all of these topics so no attempt will be made to touch on all of them. Rather, the interaction ...
rutherford - RTF Technologies
... re-zero the angle scale to compensate for instrumental effects and possible offset of the last calibration. A count over 100s is acquired for each angle near zero in 5 degree increments and the angle producing the largest count is defined as center. This calibration procedure re-zeros the scale to w ...
... re-zero the angle scale to compensate for instrumental effects and possible offset of the last calibration. A count over 100s is acquired for each angle near zero in 5 degree increments and the angle producing the largest count is defined as center. This calibration procedure re-zeros the scale to w ...
Nucleon Transfer within Distorted Wave Born Approximation
... 2.3. Bound state: Entrance channel This section (see Fig. 4) is used to specify the quantum state parameters and the interaction potential for the composite system a = (b + x) in the entrance channel. The quantity Ebound is the binding energy in MeV. The quantity Nr is the main quantum number, Jtr , ...
... 2.3. Bound state: Entrance channel This section (see Fig. 4) is used to specify the quantum state parameters and the interaction potential for the composite system a = (b + x) in the entrance channel. The quantity Ebound is the binding energy in MeV. The quantity Nr is the main quantum number, Jtr , ...
+ (Z 2 +Z 1 )
... For a single mode thermal source emitting a power, P in a bandwidth , with an emissivity, The occupation number is: N = (P/2h)(1/ ) ...
... For a single mode thermal source emitting a power, P in a bandwidth , with an emissivity, The occupation number is: N = (P/2h)(1/ ) ...
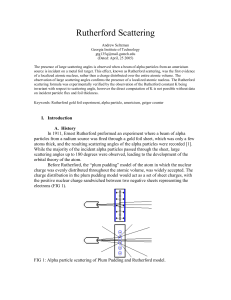
Atom 1 - UF Physics
... Armed with the Rutherford model of the atom, one can calculate the scattering rate as a function of angle from the Coulomb scattering of the α-particle off a gold nucleus (i.e. the scattering of 2 charged particles using electromagnetism). The derivation of the Rutherford Scattering formulae will no ...
... Armed with the Rutherford model of the atom, one can calculate the scattering rate as a function of angle from the Coulomb scattering of the α-particle off a gold nucleus (i.e. the scattering of 2 charged particles using electromagnetism). The derivation of the Rutherford Scattering formulae will no ...
RESEARCHERS WANT TO SIMPLIFY THE URINE ANALYSIS
... a light beam of high intensity. When the particles are hit by the light they will look like they are shining themselves. The concept is quite similar to a well-known scenario: driving a car during a snowy night. The headlights of the car make the otherwise invisible snowflakes visible within the lig ...
... a light beam of high intensity. When the particles are hit by the light they will look like they are shining themselves. The concept is quite similar to a well-known scenario: driving a car during a snowy night. The headlights of the car make the otherwise invisible snowflakes visible within the lig ...
Powerweld Coolant MSDS - Weld
... Handling Procedures and Equipment: N/A Waste Disposal: Dispose of any waste material according to local, provincial and federal regulations. Storage Requirements: Keep containers closed when not in use. Special Shipping Information: N/A Section 8: First Aid Measures Ingestion: If swallowed, induce v ...
... Handling Procedures and Equipment: N/A Waste Disposal: Dispose of any waste material according to local, provincial and federal regulations. Storage Requirements: Keep containers closed when not in use. Special Shipping Information: N/A Section 8: First Aid Measures Ingestion: If swallowed, induce v ...
Elementary Particle Physics
... electronvolt we derive the units keV, MeV, GeV and TeV that are successively three orders of magnitude larger than the preceeding unit. You will find that in atomic physics the energy scale is usually in the eV range, in nuclear physics keV to MeV and particle physics GeV to TeV. Mass is usually ex ...
... electronvolt we derive the units keV, MeV, GeV and TeV that are successively three orders of magnitude larger than the preceeding unit. You will find that in atomic physics the energy scale is usually in the eV range, in nuclear physics keV to MeV and particle physics GeV to TeV. Mass is usually ex ...
Light Scattering, Sedimenation, Gel Electrophoresis, Higher
... retardation elements or non-dipole elements because of their greater sensitivity to polarizability. The elements h, j, and k are identically zero in the orientation average unless the induced electric field, due to interactions within the particle, is accounted for (Harris and McClain, 1985). The e ...
... retardation elements or non-dipole elements because of their greater sensitivity to polarizability. The elements h, j, and k are identically zero in the orientation average unless the induced electric field, due to interactions within the particle, is accounted for (Harris and McClain, 1985). The e ...
Download PDF
... To prove the g–ϕ relationship, by definition, g represents the average cosine of the scattering angle for a single scattering event. Recently, we have extended this concept to continuous distributions of scattering media, such as tissues [9]. We showed that, since ls also means the distance over whi ...
... To prove the g–ϕ relationship, by definition, g represents the average cosine of the scattering angle for a single scattering event. Recently, we have extended this concept to continuous distributions of scattering media, such as tissues [9]. We showed that, since ls also means the distance over whi ...
03 nuclear size and shape
... optical diffraction) - these different amplitudes are summed to get the total amplitude at some scattering angle θ and this gives rise to the diffraction pattern. The contribution to the amplitude from the part of the wavefront which passes at a distance r from the centre of the nucleus is proportio ...
... optical diffraction) - these different amplitudes are summed to get the total amplitude at some scattering angle θ and this gives rise to the diffraction pattern. The contribution to the amplitude from the part of the wavefront which passes at a distance r from the centre of the nucleus is proportio ...
Cross section (physics)
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made of discrete particles. The cross section of a particle is the same as the cross section of a hard object, if the probabilities of hitting them with a ray are the same. It is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area.In scattering experiments, one is often interested in knowing how likely a given event occurs. However, the rate depends strongly on experimental variables such as the density of the target material, the intensity of the beam, or the area of overlap between the beam and the target material. To control for these mundane differences, one can factor out these variables, resulting in an area-like quantity known as the cross section.