Pride, Prejudice, and Penury of ab initio transport calculations for
... matter physics – even on the level of local or gradient corrected density approximations (LDA,GGA). [18] Still, ground and excited states of correlated electron systems are not single Slater determinants and therefore the validity of applying scattering theories designed for non-interacting particle ...
... matter physics – even on the level of local or gradient corrected density approximations (LDA,GGA). [18] Still, ground and excited states of correlated electron systems are not single Slater determinants and therefore the validity of applying scattering theories designed for non-interacting particle ...
NONLINEAR SCATTERING EFFECTS IN OPTICAL FIBERS
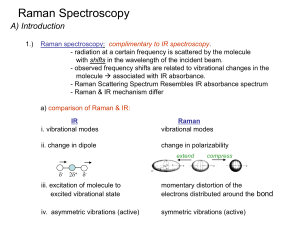
... The Raman scattering effect is the inelastic scattering [1] of a photon with an optical phonon, which originates from a finite response time of the third order nonlinear polarization [20] of the material. When a monochromatic light beam propagates in an optical fiber, spontaneous Raman scattering (Figu ...
... The Raman scattering effect is the inelastic scattering [1] of a photon with an optical phonon, which originates from a finite response time of the third order nonlinear polarization [20] of the material. When a monochromatic light beam propagates in an optical fiber, spontaneous Raman scattering (Figu ...
Quantum Energy Regression using Scattering Transforms
... mensional signal. We define a one-to-one mapping between the molecular state and a real-valued positive function defined over R2 or R3 , which has the physical interpretation of an approximate electron density. This first step circumvents the issue of atom ordering. In numerical applications, we res ...
... mensional signal. We define a one-to-one mapping between the molecular state and a real-valued positive function defined over R2 or R3 , which has the physical interpretation of an approximate electron density. This first step circumvents the issue of atom ordering. In numerical applications, we res ...
26. Electromagnetic Wave Theory and Applications
... In active and passive microwave remote sensing, layered random medium models, which include the anisotropic effects, discrete scatterers, random distribution of discrete scatterers, rough surface effects, have been used to simulate snow-ice fields, forests, vegetation canopies, plowed field, sea ice ...
... In active and passive microwave remote sensing, layered random medium models, which include the anisotropic effects, discrete scatterers, random distribution of discrete scatterers, rough surface effects, have been used to simulate snow-ice fields, forests, vegetation canopies, plowed field, sea ice ...
atomic and molecular physics using positron traps
... positron plasma on a metal plate and measuring the annihilation gamma rays. The rate is then given by Γ = d[ln(Np)]/dt, where t is time. These experiments can be done either in the presence or absence of the N2 buffer gas used for positron trapping. In order to reduce the density of impurity molecul ...
... positron plasma on a metal plate and measuring the annihilation gamma rays. The rate is then given by Γ = d[ln(Np)]/dt, where t is time. These experiments can be done either in the presence or absence of the N2 buffer gas used for positron trapping. In order to reduce the density of impurity molecul ...
fluka-models
... inelastic screening accounted for Please note the ambiguity of the non-elastic exp. results, almost 2-population like Paola Sala, HSS066 ...
... inelastic screening accounted for Please note the ambiguity of the non-elastic exp. results, almost 2-population like Paola Sala, HSS066 ...
Efficient generation of a maximally entangled state by
... noninteracting target qubits A and B sit at a fixed distance from each other along a onedimensional (1D) channel, as sketched in figure 1. The goal of the scheme is to drive A and B into an entangled state with the help of a (flying) qubit, which is sent through the 1D channel and is detected after ...
... noninteracting target qubits A and B sit at a fixed distance from each other along a onedimensional (1D) channel, as sketched in figure 1. The goal of the scheme is to drive A and B into an entangled state with the help of a (flying) qubit, which is sent through the 1D channel and is detected after ...
Measuring and Modelling Light Scattering in Paper
... the requirements that must be fulfilled to ensure valid data. A spectral goniophotometer is used for measuring the light reflected from paper and methods are developed for analyzing the different components, i.e. the fluorescence, surface reflectance and bulk reflectance, separately. A separation of ...
... the requirements that must be fulfilled to ensure valid data. A spectral goniophotometer is used for measuring the light reflected from paper and methods are developed for analyzing the different components, i.e. the fluorescence, surface reflectance and bulk reflectance, separately. A separation of ...
1. ISOL method
... intensities of other fragments are equal to the intensity of the projectile. Instead of the “cross section” value in other modes the ISOL mode operates by defining an “Intensity coefficient” (see Fig.2). However the user Fig.2. The transmission statistic window. can change the intensity coefficient ...
... intensities of other fragments are equal to the intensity of the projectile. Instead of the “cross section” value in other modes the ISOL mode operates by defining an “Intensity coefficient” (see Fig.2). However the user Fig.2. The transmission statistic window. can change the intensity coefficient ...
5. Reflection, refraction and polarization
... Another way of imposing broadband polarization control is to use a device called a Pockels cell. This device is based on a birefringent crystal that is isotropic until a voltage is applied across it. When a voltage is applied across the crystal, a birefringence, that is difference in ne and no devel ...
... Another way of imposing broadband polarization control is to use a device called a Pockels cell. This device is based on a birefringent crystal that is isotropic until a voltage is applied across it. When a voltage is applied across the crystal, a birefringence, that is difference in ne and no devel ...
Slide sem título - Instituto de Física / UFRJ
... The blue band will be the area enclosed by the two ZFITTER DSWW=+-1 \Delta\chi^2 curves. The one-sided 95%CL (90% two-sided) upper limit on MH is given by ZFITTER's DSWW=-1 curve: MH <= 166 GeV (one-sided 95%CL incl. TU) (increasing to 199 GeV when including the LEP-2 direct search limit). ...
... The blue band will be the area enclosed by the two ZFITTER DSWW=+-1 \Delta\chi^2 curves. The one-sided 95%CL (90% two-sided) upper limit on MH is given by ZFITTER's DSWW=-1 curve: MH <= 166 GeV (one-sided 95%CL incl. TU) (increasing to 199 GeV when including the LEP-2 direct search limit). ...
Wireless propagation in buildings: a statistical
... breakpoint is determined by the interference of the direct and ground bounce rays. Several studies have investigated the utility of an empirical power-law approach indoors and have attempted to determine the appropriate power law for buildings of various types [4]–[6]. The second main approach to in ...
... breakpoint is determined by the interference of the direct and ground bounce rays. Several studies have investigated the utility of an empirical power-law approach indoors and have attempted to determine the appropriate power law for buildings of various types [4]–[6]. The second main approach to in ...
Tutorial on Optomechanical Beam Steering Mechanisms
... movements for each degree of freedom of the beam are kept separate. In this tutorial some examples of common optomechanical beam steering elements will be shown and their advantages and disadvantages compared. Additionally a new type of adjustable prism will be described and compared. Spatial light ...
... movements for each degree of freedom of the beam are kept separate. In this tutorial some examples of common optomechanical beam steering elements will be shown and their advantages and disadvantages compared. Additionally a new type of adjustable prism will be described and compared. Spatial light ...
Optical Caustics Observed in Light Scattered by an Oblate Spheroid
... rays through the sphere, a number of previous authors [25–27] have taken the sphere’s entrance plane to be tangent to it at z ¼ −a, and the exit plane tangent to it at Z ¼ a. In this paper, we use another choice [28,29] for the entrance and exit planes for reasons that will become apparent when we c ...
... rays through the sphere, a number of previous authors [25–27] have taken the sphere’s entrance plane to be tangent to it at z ¼ −a, and the exit plane tangent to it at Z ¼ a. In this paper, we use another choice [28,29] for the entrance and exit planes for reasons that will become apparent when we c ...
Chap-7
... Here (3) is a material property that governs the nonlinear response of a medium and all nonlinear processes occurring in that medium. It is therefore important to notice some aspects of (3), even before starting a treatment of specific nonlinear processes. 1) A general expression of the third orde ...
... Here (3) is a material property that governs the nonlinear response of a medium and all nonlinear processes occurring in that medium. It is therefore important to notice some aspects of (3), even before starting a treatment of specific nonlinear processes. 1) A general expression of the third orde ...
Digital Fourier Microscopy for Soft Matter Dynamics
... does not seem to bear any resemblance with the sample itself. It is worth concluding this Introduction by mentioning that DFM is not the only approach that exploits imaging to characterise soft matter samples. Indeed, in the last few years other nonFourier methods have been proposed, such as for ins ...
... does not seem to bear any resemblance with the sample itself. It is worth concluding this Introduction by mentioning that DFM is not the only approach that exploits imaging to characterise soft matter samples. Indeed, in the last few years other nonFourier methods have been proposed, such as for ins ...
Experimental observation of speckle instability in Kerr random
... inset of Fig. 1) is computer-generated and transmitted to a 36.9mm×27.6mm spatial-light-modulator (SLM), spatial resolution 1024×768 pixels, which serves as a 2D random mask. The local voltage applied across the LC film decreases where light impinges on the BSO crystal, inducing local LC reorientati ...
... inset of Fig. 1) is computer-generated and transmitted to a 36.9mm×27.6mm spatial-light-modulator (SLM), spatial resolution 1024×768 pixels, which serves as a 2D random mask. The local voltage applied across the LC film decreases where light impinges on the BSO crystal, inducing local LC reorientati ...
1914
... varying between 5° and 150°. Although over this range the number decreased in the ratio 200,000 to 1, the relation between number and angle agreed with the theory within They found that the scatthe limit of experimental error. tering of different atoms of matter was approximately proportional to the ...
... varying between 5° and 150°. Although over this range the number decreased in the ratio 200,000 to 1, the relation between number and angle agreed with the theory within They found that the scatthe limit of experimental error. tering of different atoms of matter was approximately proportional to the ...
Anisotropic scattering effect of the inclined misfit dislocation on the
... Dong-Dong Jin, Lian-shan Wang, Shao-Yan Yang, Liu-Wan Zhang, Hui-jie Li, Heng Zhang, Jian-xia Wang, Ruofei Xiang, Hong-yuan Wei, Chun-mei Jiao, Xiang-Lin Liu, Qin-Sheng Zhu, and Zhan-Guo Wang Citation: Journal of Applied Physics 115, 043702 (2014); doi: 10.1063/1.4862803 ...
... Dong-Dong Jin, Lian-shan Wang, Shao-Yan Yang, Liu-Wan Zhang, Hui-jie Li, Heng Zhang, Jian-xia Wang, Ruofei Xiang, Hong-yuan Wei, Chun-mei Jiao, Xiang-Lin Liu, Qin-Sheng Zhu, and Zhan-Guo Wang Citation: Journal of Applied Physics 115, 043702 (2014); doi: 10.1063/1.4862803 ...
RTF format - Huw Price
... conditions from a larger sample. We consider a large system of interacting particles of the kind concerned, and consider only those pairs of particles which emerge on two tightly constrained trajectories (one particle on each), having perhaps interacted in a specified region at the intersection of t ...
... conditions from a larger sample. We consider a large system of interacting particles of the kind concerned, and consider only those pairs of particles which emerge on two tightly constrained trajectories (one particle on each), having perhaps interacted in a specified region at the intersection of t ...
n 1n d
... • Probing of other sample compositions (different polymers, LCs, ...) • (Re)filling of the grating structures with high contrast materials (D2O, ...) • Study of photopolymerization kinetics of H-PDLCs by neutron scattering in-situ • Synchronous probing of optical and neutron refractive properties • ...
... • Probing of other sample compositions (different polymers, LCs, ...) • (Re)filling of the grating structures with high contrast materials (D2O, ...) • Study of photopolymerization kinetics of H-PDLCs by neutron scattering in-situ • Synchronous probing of optical and neutron refractive properties • ...
chapter41
... Since, in many cases, the particle is the only part of the system that experiences a change, common language associates the wave function with the particle. There are some examples in which it is important to think of the system wave function instead of the particle wave function. Section 41.1 ...
... Since, in many cases, the particle is the only part of the system that experiences a change, common language associates the wave function with the particle. There are some examples in which it is important to think of the system wave function instead of the particle wave function. Section 41.1 ...
Chapter 7 Kinetics and Structure of Colloidal Aggregates 7.1
... where Nk is the number concentration of aggregates of size k, and the first term on the r.h.s. represents all possible collisions leading to the formation of an aggregate of mass k, while the second is the rate of disappearance of the aggregates of mass k due to aggregation with aggregates of any ma ...
... where Nk is the number concentration of aggregates of size k, and the first term on the r.h.s. represents all possible collisions leading to the formation of an aggregate of mass k, while the second is the rate of disappearance of the aggregates of mass k due to aggregation with aggregates of any ma ...
Cross section (physics)
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made of discrete particles. The cross section of a particle is the same as the cross section of a hard object, if the probabilities of hitting them with a ray are the same. It is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area.In scattering experiments, one is often interested in knowing how likely a given event occurs. However, the rate depends strongly on experimental variables such as the density of the target material, the intensity of the beam, or the area of overlap between the beam and the target material. To control for these mundane differences, one can factor out these variables, resulting in an area-like quantity known as the cross section.