Is there a negative absolute temperature?
... bottom to top) or SB with one particle larger, i.e., N = 2, 3, 6, etc. Temperature for N=1 cannot be properly defined. ...
... bottom to top) or SB with one particle larger, i.e., N = 2, 3, 6, etc. Temperature for N=1 cannot be properly defined. ...
Slides1 - University of Guelph
... Two-mode squeezed vacuum • This state is the most entangled state for a given amount of energy (its subsystems are thermal states, which have the highest entropy for a fixed energy) ...
... Two-mode squeezed vacuum • This state is the most entangled state for a given amount of energy (its subsystems are thermal states, which have the highest entropy for a fixed energy) ...
8.04 Final Review Schr¨ ary conditions.
... ∂x ∂x If there is no time dependence, the flux is constant across all boundaries. In the case of negative energies (a particle is bound), the possible energies are quantized. Specifically, for a particle with the nth bound energy level travelling along a complete path, the Wilson-Sommerfeld quantiza ...
... ∂x ∂x If there is no time dependence, the flux is constant across all boundaries. In the case of negative energies (a particle is bound), the possible energies are quantized. Specifically, for a particle with the nth bound energy level travelling along a complete path, the Wilson-Sommerfeld quantiza ...
9. Entropy 2nd and 3rd laws/ Thermodynamic processes / Droplet
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
T. Dammak - TU-MRS
... due to the difference between the dielectric constant of the quantum wells and the barrier layers. It is thought to increase the binding energy of excitons. More recently, the hybrid organic inorganic layered perovskite, with general formula (RNH3)2MX4 (R; CnH2n+1, X; halogen) were extensively studi ...
... due to the difference between the dielectric constant of the quantum wells and the barrier layers. It is thought to increase the binding energy of excitons. More recently, the hybrid organic inorganic layered perovskite, with general formula (RNH3)2MX4 (R; CnH2n+1, X; halogen) were extensively studi ...
Lecture 01
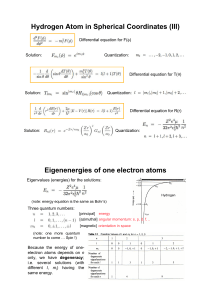
... with eigenvalue 0 for each of these. Classically, any component of the angular momentum must be less than or equal to the magnitude of the overall angular momentum vector. Quantum mechanically, the average value of any component of the angular momentum must be less than or equal to the square root o ...
... with eigenvalue 0 for each of these. Classically, any component of the angular momentum must be less than or equal to the magnitude of the overall angular momentum vector. Quantum mechanically, the average value of any component of the angular momentum must be less than or equal to the square root o ...
A PRIMER ON THE ANGULAR MOMENTUM AND PARITY
... P̂ ψ = pψ where p is the ”quantum number” for parity. And again: P̂ P̂ ψ = P̂ pψ = p2 ψ. ...
... P̂ ψ = pψ where p is the ”quantum number” for parity. And again: P̂ P̂ ψ = P̂ pψ = p2 ψ. ...
The Learnability of Quantum States
... The Quantum Optics Model A rudimentary subset of quantum computing, involving only non-interacting bosons, and not based on qubits ...
... The Quantum Optics Model A rudimentary subset of quantum computing, involving only non-interacting bosons, and not based on qubits ...
History of Particle Physics (lecture notes)
... But they were not clearly recognized as particles prior to revolutionary developments inaugurated by Einstein's photoelectric theory, starting in 1905. Indeed the wave theory of light and then its fusio ...
... But they were not clearly recognized as particles prior to revolutionary developments inaugurated by Einstein's photoelectric theory, starting in 1905. Indeed the wave theory of light and then its fusio ...
Class 25
... 2. square of wave function defines distribution of electrons around the nucleus high electron density - high probability of finding an electron at this location ...
... 2. square of wave function defines distribution of electrons around the nucleus high electron density - high probability of finding an electron at this location ...
rtf
... Information processing is concerned today with very large quantities of very complex data. The complexity arises from the diversity of the type of data and the relationships between data and the different types of relationships. At present semantic complexity can only be processed at the surface lev ...
... Information processing is concerned today with very large quantities of very complex data. The complexity arises from the diversity of the type of data and the relationships between data and the different types of relationships. At present semantic complexity can only be processed at the surface lev ...
Fundamentals of quantum mechanics Quantum Theory of Light and Matter
... Elementary description in terms of wavefunction ψ(x) |ψ(x)|2 : probability measuring particle at position x ...
... Elementary description in terms of wavefunction ψ(x) |ψ(x)|2 : probability measuring particle at position x ...