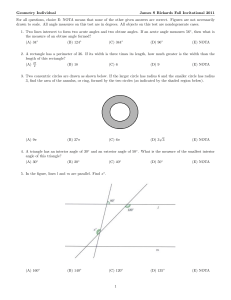
Ai - Glencoe
... Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act, no part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, without prior permission of the publis ...
... Copyright © by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act, no part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system, without prior permission of the publis ...
Geometry
... The student will a) investigate and identify properties of quadrilaterals involving opposite sides and angles, consecutive sides and angles, and diagonals; b) prove these properties of quadrilaterals, using algebraic and coordinate methods as well as deductive reasoning; and c) use properties of qua ...
... The student will a) investigate and identify properties of quadrilaterals involving opposite sides and angles, consecutive sides and angles, and diagonals; b) prove these properties of quadrilaterals, using algebraic and coordinate methods as well as deductive reasoning; and c) use properties of qua ...
Measurement and Data 3 - DMPS Elementary Mathematics
... What does this standard mean the students will know and be able to do? This standard calls for students to explore the connection between angles (measure of rotation) and circular measurement (360 degrees). Students explore an angle as a series of ―one degree turns.‖ A water sprinkler rotates one de ...
... What does this standard mean the students will know and be able to do? This standard calls for students to explore the connection between angles (measure of rotation) and circular measurement (360 degrees). Students explore an angle as a series of ―one degree turns.‖ A water sprinkler rotates one de ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)