Solutions #7
... Construct the line through A and B. This yields two points of intersection with the already constructed circle C ; call one of the points of intersection D. By constructing the perpendicular bisector of the segment BD, construct the midpoint M of BD, so that | MB| = | MD|. Finally, construct C 0 = C ...
... Construct the line through A and B. This yields two points of intersection with the already constructed circle C ; call one of the points of intersection D. By constructing the perpendicular bisector of the segment BD, construct the midpoint M of BD, so that | MB| = | MD|. Finally, construct C 0 = C ...
Geometry Lesson Plan - Blue Ribbon Mathematics
... In groups of four, students will now create 4 examples of two or more regular polygons that can tile a plane. Each student must participate and each student must have the 4 created patterns. You may want them to color them with colored pencils. They must compile a list of surfaces that are tessellat ...
... In groups of four, students will now create 4 examples of two or more regular polygons that can tile a plane. Each student must participate and each student must have the 4 created patterns. You may want them to color them with colored pencils. They must compile a list of surfaces that are tessellat ...
Geometry Honors – Curriculum Pacing Guide – 2015
... figures to represent and describe real-world objects. Construct geometric figures using a variety of tools, including a compass, a straightedge, dynamic geometry software, and paper folding, and use these constructions to make conjectures about geometric relationships. Given two points, find the poi ...
... figures to represent and describe real-world objects. Construct geometric figures using a variety of tools, including a compass, a straightedge, dynamic geometry software, and paper folding, and use these constructions to make conjectures about geometric relationships. Given two points, find the poi ...
Geometry key concepts
... 6. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems. (5-7) 7. Use Pythagorean inequalities to classify triangles. (5-7) 8. Apply properties of Special Right Triangles (5-8) 9. Classify polygons based on their sides and angles. (6-1) 10. Find measures of interior and exterior angles of ...
... 6. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to solve problems. (5-7) 7. Use Pythagorean inequalities to classify triangles. (5-7) 8. Apply properties of Special Right Triangles (5-8) 9. Classify polygons based on their sides and angles. (6-1) 10. Find measures of interior and exterior angles of ...
PDF
... one set of opposite sides (called the legs) congruent, the other set of opposite sides (called the bases) disjointly parallel, and, at one of the bases, both angles are right angles. Since the angle sum of a triangle in hyperbolic geometry is strictly less than π radians, the angle sum of a quadrila ...
... one set of opposite sides (called the legs) congruent, the other set of opposite sides (called the bases) disjointly parallel, and, at one of the bases, both angles are right angles. Since the angle sum of a triangle in hyperbolic geometry is strictly less than π radians, the angle sum of a quadrila ...
MATH 329
... Some Theorems from Euclids Elements The …rst 28 propositions from Book I do not require Euclid’s Parallel Postulate. I.1 Construct an equilateral triangle on a given segment. I.2 Place at a given point a segment equal to a give segment. I.3 Given two unequal segments, cut o¤ from the greater a segm ...
... Some Theorems from Euclids Elements The …rst 28 propositions from Book I do not require Euclid’s Parallel Postulate. I.1 Construct an equilateral triangle on a given segment. I.2 Place at a given point a segment equal to a give segment. I.3 Given two unequal segments, cut o¤ from the greater a segm ...
Solutions - FloridaMAO
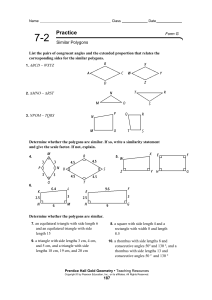
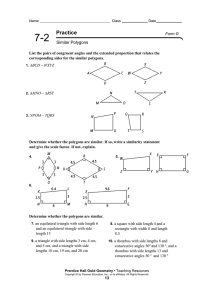
... The measure of an angle in a regular polygon is give by . Setting this expression equal to 156, we get . Solving for n we get 360/24 = 15 sides = B. The perimeter of a rhombus with diagonals of lengths 12 and 14 can be found by splitting the rhombus into four right triangles using the diagonals. The ...
... The measure of an angle in a regular polygon is give by . Setting this expression equal to 156, we get . Solving for n we get 360/24 = 15 sides = B. The perimeter of a rhombus with diagonals of lengths 12 and 14 can be found by splitting the rhombus into four right triangles using the diagonals. The ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)