Topic 1 Activities Packet
... one has left yet. How many handshakes have taken place? (a) Often times in math, it’s much easier to look at a simpler problem to solve a harder one. Lets try this strategy here: how many handshakes would have taken place if there were 3 people at the party? How about 4? 5? ...
... one has left yet. How many handshakes have taken place? (a) Often times in math, it’s much easier to look at a simpler problem to solve a harder one. Lets try this strategy here: how many handshakes would have taken place if there were 3 people at the party? How about 4? 5? ...
Geometry Curriculum Map - Cliffside Park School District
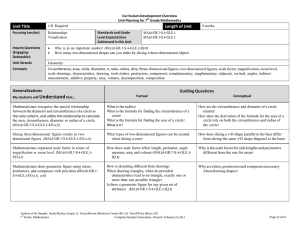
... Find the areas of parallelograms, rhombuses, triangles and circles Simplify square roots Use the Pythagorean theorem and it’s converse Find measures of central angles and arcs Find circumference and arc lengths Find areas of circles, sectors and segment of circles Find the area in the coordinate pla ...
... Find the areas of parallelograms, rhombuses, triangles and circles Simplify square roots Use the Pythagorean theorem and it’s converse Find measures of central angles and arcs Find circumference and arc lengths Find areas of circles, sectors and segment of circles Find the area in the coordinate pla ...
Youngstown City Schools
... and methods of finding their measures. They will also construct inscribed and circumscribed triangles and quadrilateral and discover theorems concerning these polygons. Towards the end of this unit, students for the first time, will be exposed to radian measure when referring to angles and will work ...
... and methods of finding their measures. They will also construct inscribed and circumscribed triangles and quadrilateral and discover theorems concerning these polygons. Towards the end of this unit, students for the first time, will be exposed to radian measure when referring to angles and will work ...
NAME - Livingston Public Schools
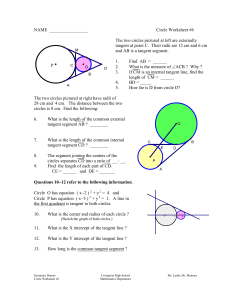
... The segment joining the centers of the circles separates CD into a ratio of __ : __. Find the length of each part of CD. CE = ______ and DE = _______ ...
... The segment joining the centers of the circles separates CD into a ratio of __ : __. Find the length of each part of CD. CE = ______ and DE = _______ ...
6-1 Proportions Ratio—a comparison of two quantities Proportion
... If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides in two distinct points, then it separates these sides into segments of proportional lengths. Theorem 6.5 Converse of the Triangle Proportionality Theorem If a line intersects two sides of a triangle and separates the ...
... If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides in two distinct points, then it separates these sides into segments of proportional lengths. Theorem 6.5 Converse of the Triangle Proportionality Theorem If a line intersects two sides of a triangle and separates the ...
Revision Practice for Target C grade GCSE Geometry
... In these expressions a, b and c represent lengths. Π and 2 have no dimension Three of the expressions represent areas. Tick under the expressions that show area. ...
... In these expressions a, b and c represent lengths. Π and 2 have no dimension Three of the expressions represent areas. Tick under the expressions that show area. ...
Word
... If you have educational notebooks, please move them into a new product. Comment by aritter [ 28/Jun/16 ] "createDetGeom" has been moved to a task to be executed from bin.src/createDetGeom.py (command line task didn't work because there are no data to be processed and no butler to be associated with. ...
... If you have educational notebooks, please move them into a new product. Comment by aritter [ 28/Jun/16 ] "createDetGeom" has been moved to a task to be executed from bin.src/createDetGeom.py (command line task didn't work because there are no data to be processed and no butler to be associated with. ...
New General Mathematics for Secondary Schools 2 Teacher`s Guide
... Students must always give a reason for each statement that they make that is based on some or other theorem, and they either do not give the reason or do not know how. To help the students, you could give them summaries of the theorems and suggestions of the reasons they can give. Below are suggesti ...
... Students must always give a reason for each statement that they make that is based on some or other theorem, and they either do not give the reason or do not know how. To help the students, you could give them summaries of the theorems and suggestions of the reasons they can give. Below are suggesti ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)