Passive Transport (Section 5-1) Answer Sheet
... 3. hypertonic, plasmolysis : hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the cytosol of a cell. In a hypertonic solution a plant cell will lose water and shrink away from the cell wall, a process called plasmolysis. ...
... 3. hypertonic, plasmolysis : hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the cytosol of a cell. In a hypertonic solution a plant cell will lose water and shrink away from the cell wall, a process called plasmolysis. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... All About Cells! Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
... All About Cells! Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
review for second six weeks common assessment
... 1. Know stages of Mitosis and what happens in each phase 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynth ...
... 1. Know stages of Mitosis and what happens in each phase 2. Passive and Active Transport 3. Diffusion, Osmosis 4. Functions of the cell membrane 5. Differences between plant and animal cells 6. What causes cells to stop growing when grown in a petri dish? 7. Cell organelle responsible for photosynth ...
Activities
... Which of the following organelles would you expect to be especially abundant in muscle cells? A) mitochondria B) ribosomes C) smooth endoplasmic reticulum D) lysosomes ...
... Which of the following organelles would you expect to be especially abundant in muscle cells? A) mitochondria B) ribosomes C) smooth endoplasmic reticulum D) lysosomes ...
Organelles – Who Am I?
... Using your notes, fill in the following statements with the corresponding organelle. 1. I surround the nucleus and protect it. 2. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell and can break down a large molecule into a smaller one. 3. I am a jelly-like fluid that surrounds and support ...
... Using your notes, fill in the following statements with the corresponding organelle. 1. I surround the nucleus and protect it. 2. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell and can break down a large molecule into a smaller one. 3. I am a jelly-like fluid that surrounds and support ...
Chapter 5 Section 1: Passive Transport
... 22. A good example of facilitated diffusion is the transport of ____________. 23. What are ion channels? 24. Ion channels transport ions such as _______________ (Na+), ________________ (K+), ______________ (Ca+), and _______________ (Cl). 25. Each type of ion channel is usually ____________ for one ...
... 22. A good example of facilitated diffusion is the transport of ____________. 23. What are ion channels? 24. Ion channels transport ions such as _______________ (Na+), ________________ (K+), ______________ (Ca+), and _______________ (Cl). 25. Each type of ion channel is usually ____________ for one ...
CELL PARTS MATCHING - SD43 Teacher Sites
... PACKAGES PROTEIN AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE TO THE CELL ...
... PACKAGES PROTEIN AND MAKES IT AVAILABLE TO THE CELL ...
Into and Out of the Cell
... Wastes must be able to leave the cell. The cell membrane is “picky” about what ...
... Wastes must be able to leave the cell. The cell membrane is “picky” about what ...
Cell Transport PP
... Read pages 89-91 in your text book to help you answer these questions! Define the following vocabulary: Active transport: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Read pages 89-91 in your text book to help you answer these questions! Define the following vocabulary: Active transport: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
013368718X_CH02_015
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
... that is stored in food B. Stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials for storage or release C. Convert chemical energy stored in food into a form that can be easily used by the cell ...
An Inside Look: Lysosome
... dense spherical vacuoles. (Approx. diameter ranging up to one micrometer) They can display considerable variation in size and shape as a result of differences in the materials that have been taken up for digestion. This organelle is mainly found in animal cells but are sometimes found in plant cells ...
... dense spherical vacuoles. (Approx. diameter ranging up to one micrometer) They can display considerable variation in size and shape as a result of differences in the materials that have been taken up for digestion. This organelle is mainly found in animal cells but are sometimes found in plant cells ...
Outline
... Lecture Outline: Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic unit of life (all life is cellular and smaller than a cell isn’t alive) 2. All cells come from other cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells prokaryote no internal membranes (or true organelles). 1-10m eg bacteria eukaryote 10-100m always have in ...
... Lecture Outline: Cell Theory 1. Cells are the basic unit of life (all life is cellular and smaller than a cell isn’t alive) 2. All cells come from other cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells prokaryote no internal membranes (or true organelles). 1-10m eg bacteria eukaryote 10-100m always have in ...
Cells - biologybi
... membrane to the cell membrane and is a passage way for things passing through the cell. Golgi Bodies- help package protein. Lysosomes- “suicide sac” structures that contain enzymes in digestion. If one were to burst, it could destroy the cell. ...
... membrane to the cell membrane and is a passage way for things passing through the cell. Golgi Bodies- help package protein. Lysosomes- “suicide sac” structures that contain enzymes in digestion. If one were to burst, it could destroy the cell. ...
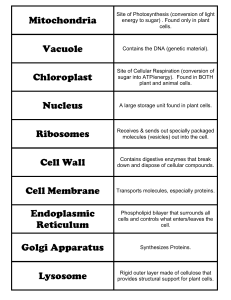
Mitochondria Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to
... Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to sugar) . Found only in plant cells. ...
... Site of Photosynthesis (conversion of light energy to sugar) . Found only in plant cells. ...
Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is
... Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is not used) cell wall plasma (cell) membrane nucleus ribosome lysosome cilia chromosome cytosol ...
... Cell Organelle Function Matching Quiz (One of the terms below is not used) cell wall plasma (cell) membrane nucleus ribosome lysosome cilia chromosome cytosol ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... I regulate activities from day to day. ...
... I regulate activities from day to day. ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
... I transport proteins And other things as well. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.