microbiology-1st-edition-wessner-test-bank
... Section Reference: Section 2.4 The cell envelope 19) What conditions must be met in order for an “active transport system” to transport of a nutrient into a cell? a) The nutrient concentration must be higher on the outside of the cell. b) The nutrient concentration must be lower on the inside of the ...
... Section Reference: Section 2.4 The cell envelope 19) What conditions must be met in order for an “active transport system” to transport of a nutrient into a cell? a) The nutrient concentration must be higher on the outside of the cell. b) The nutrient concentration must be lower on the inside of the ...
Organelle communication - Repositorio Académico
... serving as a platform that anchors molecular complexes to subcellular regions. Fact 3. Organelle interfaces serve as nucleation sites for pathways such as stress signals, mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy. Fact 4. Organelle communication regulates important cellular processes such as metabolism, ...
... serving as a platform that anchors molecular complexes to subcellular regions. Fact 3. Organelle interfaces serve as nucleation sites for pathways such as stress signals, mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy. Fact 4. Organelle communication regulates important cellular processes such as metabolism, ...
A Rab4-like GTPase in Dictyostelium discoideum
... 675 (end of the TAA stop codon) into the RSET bacteria fusion protein vector at the PstI and EcoRI sites (Invitrogen). This vector construct was transformed into the Escherichia coli strain JM109, followed by induction of the synthesis of the RabD fusion protein. RabD was then purified from cells re ...
... 675 (end of the TAA stop codon) into the RSET bacteria fusion protein vector at the PstI and EcoRI sites (Invitrogen). This vector construct was transformed into the Escherichia coli strain JM109, followed by induction of the synthesis of the RabD fusion protein. RabD was then purified from cells re ...
The origin of the eukaryotic cell: A genomic investigation
... actin and tubulin and their prokaryotic counterparts FtsA and FtsZ. He determined that the rate by which actin and tubulin varied in the eukaryotic cells was very slow (10% change per billion years). The calculated time when the bacterial FtsA and FtsZ proteins began to diverge from their possible e ...
... actin and tubulin and their prokaryotic counterparts FtsA and FtsZ. He determined that the rate by which actin and tubulin varied in the eukaryotic cells was very slow (10% change per billion years). The calculated time when the bacterial FtsA and FtsZ proteins began to diverge from their possible e ...
Cell Wall
... •New wall materials are deposited immediately outside membrane. •Microfibrils are synthesize by rosettes: cellulose synthase which reside on a cells membrane • As cellulose fibrils are synthesized and grow extracellularly they push up against neighboring cells. Since the neighboring cell can not mov ...
... •New wall materials are deposited immediately outside membrane. •Microfibrils are synthesize by rosettes: cellulose synthase which reside on a cells membrane • As cellulose fibrils are synthesized and grow extracellularly they push up against neighboring cells. Since the neighboring cell can not mov ...
mechanotransduction in lymphatic endothelial cells
... FAK phosphorylation is a critical event also in stretching of cells (29,30). It induces the activation of ERK1/2 and p38 suggesting that mechanotransduction occurs at focal adhesions. Traditionally mechanotransduction differs from other types of signal transduction in that it is thought to occur ind ...
... FAK phosphorylation is a critical event also in stretching of cells (29,30). It induces the activation of ERK1/2 and p38 suggesting that mechanotransduction occurs at focal adhesions. Traditionally mechanotransduction differs from other types of signal transduction in that it is thought to occur ind ...
Targeted Drug Delivery to the Nucleus and its Potential Role in
... both the site of storage and replication of the cell's genetic material, and of processes such as transcription and ribosome assembly that are central to synthesising the cellular complement of proteins that carry out all of its functions. The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell cytoplasm ...
... both the site of storage and replication of the cell's genetic material, and of processes such as transcription and ribosome assembly that are central to synthesising the cellular complement of proteins that carry out all of its functions. The nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell cytoplasm ...
Exosome-Depleted FBS Using Beckman Coulter Centrifugation:
... Much of the research involving exosomes uses a cell culture platform, although exosomes are routinely isolated from other bodily fluids such as plasma, serum, urine, and breast milk. In cell culture, fetal bovine serum (FBS) is usually incorporated into media, despite FBS containing extremely high l ...
... Much of the research involving exosomes uses a cell culture platform, although exosomes are routinely isolated from other bodily fluids such as plasma, serum, urine, and breast milk. In cell culture, fetal bovine serum (FBS) is usually incorporated into media, despite FBS containing extremely high l ...
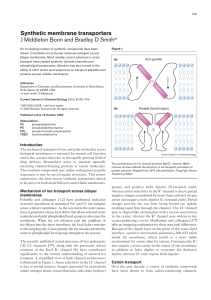
Synthetic membrane transporters J Middleton Boon and Bradley D
... ischemia. The Tat and Antennapedia conjugate peptides were half as effective. Wender and co-workers [46] have also developed peptoid transporter 20, which is superior to polyarginine. The structure of 20 suggests that the peptide backbone is not a crucial element in the transport process, but the le ...
... ischemia. The Tat and Antennapedia conjugate peptides were half as effective. Wender and co-workers [46] have also developed peptoid transporter 20, which is superior to polyarginine. The structure of 20 suggests that the peptide backbone is not a crucial element in the transport process, but the le ...
1 Evolutionary conservation and emerging functional diversity of the
... hydrophobic pocket known to bind short hydrophobic patches on client proteins thus determining their substrate specificity (Cheetham and Caplan 1998). All other J proteins that do not fit into either class I or class II are arbitrarily placed in class III. Thus, class III J proteins are structurally ...
... hydrophobic pocket known to bind short hydrophobic patches on client proteins thus determining their substrate specificity (Cheetham and Caplan 1998). All other J proteins that do not fit into either class I or class II are arbitrarily placed in class III. Thus, class III J proteins are structurally ...
Chapter 4
... Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells (< 5 µm long) Are very reproductively successful and so are more abundant Have a simple internal structure Surrounded by a stiff cell wall, which provides shape and protection Can take the shape of rods, spheres, or helices Copyright ...
... Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells (< 5 µm long) Are very reproductively successful and so are more abundant Have a simple internal structure Surrounded by a stiff cell wall, which provides shape and protection Can take the shape of rods, spheres, or helices Copyright ...
Evolution of Cell Division
... This size-dependant growth rate results in larger cells to grow faster and smaller cells to grow slower. Thus, checkpoints are required to stop the large cells from excess growth and encourage the small cells to grow to the appropriate size and hence, keep the average size of the cells constant. Des ...
... This size-dependant growth rate results in larger cells to grow faster and smaller cells to grow slower. Thus, checkpoints are required to stop the large cells from excess growth and encourage the small cells to grow to the appropriate size and hence, keep the average size of the cells constant. Des ...
Acute Inflammation
... detachment, resulting in increased permeability. In acute inflammation, this form of injury is largely restricted to vascular sites, such as venules and pulmonary and glomerular capillaries, where leukocytes adhere for prolonged periods to the endothelium.[12] ...
... detachment, resulting in increased permeability. In acute inflammation, this form of injury is largely restricted to vascular sites, such as venules and pulmonary and glomerular capillaries, where leukocytes adhere for prolonged periods to the endothelium.[12] ...
biological membranes - Biochemical Society
... composition and cholesterol content. At low temperatures, the hydrocarbon tails of bilayer lipids can pack closely together to form an ordered arrangement (or gel state) which is fairly rigid. As temperature is increased, the lipid molecules vibrate more rapidly, causing the bilayer to ‘melt’ into a ...
... composition and cholesterol content. At low temperatures, the hydrocarbon tails of bilayer lipids can pack closely together to form an ordered arrangement (or gel state) which is fairly rigid. As temperature is increased, the lipid molecules vibrate more rapidly, causing the bilayer to ‘melt’ into a ...
The plant formin AtFH4 interacts with both actin and microtubules
... sedimented with microtubules, whereas AtFH4D6 remained in the supernatant. Fragment AtFH4D4 noticeably decreased the proportion of tubulin remaining in the supernatant (Fig. 2C; supplementary material Fig. S2). To test its bundling potential, AtFH4D4 was mixed with taxol-stabilised and Oregon-Greenl ...
... sedimented with microtubules, whereas AtFH4D6 remained in the supernatant. Fragment AtFH4D4 noticeably decreased the proportion of tubulin remaining in the supernatant (Fig. 2C; supplementary material Fig. S2). To test its bundling potential, AtFH4D4 was mixed with taxol-stabilised and Oregon-Greenl ...
What the Distribution of Cell Lengths in the Root Meristem Does and
... The variation in the length of mitotic cells was analyzed in detail for both maize and wheat by Dobrochaev and Ivanov (2001). Interestingly, a considerable amount of variation in length among cells was explained by a correlation between the lengths of mitotic and interphase cells within individual ® ...
... The variation in the length of mitotic cells was analyzed in detail for both maize and wheat by Dobrochaev and Ivanov (2001). Interestingly, a considerable amount of variation in length among cells was explained by a correlation between the lengths of mitotic and interphase cells within individual ® ...
BSC-110 Biology
... cilia and describe the major function of each D. Describe the difference between diffusion and active transport using various solutions where differences in concentrations affect the direction of movement E. Diagram and label the double phospholipid structure of the cell membrane F. Com ...
... cilia and describe the major function of each D. Describe the difference between diffusion and active transport using various solutions where differences in concentrations affect the direction of movement E. Diagram and label the double phospholipid structure of the cell membrane F. Com ...
autophagy - Botanik in Bonn
... regulated catabolic processes, all of which deliver cytoplasmic components to the lysosome for degradation In animals and yeasts, autophagy is often divided into three main types: Chaperone-mediated autophagy, Microautophagy, Macroautophagy. ...
... regulated catabolic processes, all of which deliver cytoplasmic components to the lysosome for degradation In animals and yeasts, autophagy is often divided into three main types: Chaperone-mediated autophagy, Microautophagy, Macroautophagy. ...
equisetum - Natuurtijdschriften
... trichoblast is helicoidalwith the sive lamellae and with the ...
... trichoblast is helicoidalwith the sive lamellae and with the ...
Lysis by Agents of Microbial Origin
... examples of micro-organisms or microbial products digesting the cells of various bacteria have often been reported since the very beginnings of bacteriology. Research in this field was undertaken from many different angles according to the fashion of the day. Early studies were mostly conducted with ...
... examples of micro-organisms or microbial products digesting the cells of various bacteria have often been reported since the very beginnings of bacteriology. Research in this field was undertaken from many different angles according to the fashion of the day. Early studies were mostly conducted with ...
PDF with detailed project information
... should therefore be an evolutionary dead end. However, accumulating evidence for at least occasional biparental transmission (or paternal leakage) provides opportunities for sporadic sexual recombination events between organellar genomes. Those could significantly slow down Muller’s ratchet, but the ...
... should therefore be an evolutionary dead end. However, accumulating evidence for at least occasional biparental transmission (or paternal leakage) provides opportunities for sporadic sexual recombination events between organellar genomes. Those could significantly slow down Muller’s ratchet, but the ...
Paul M. Nurse - Nobel Lecture
... and cell division and subsequent screens carried out together with Kim Nasmyth identified more mutants defective in S-phase (Nurse, Thuriaux et al. 1976). These cdc mutants identified genes required for the events of S-phase, mitosis and cell division, but it was not possible to determine which, if ...
... and cell division and subsequent screens carried out together with Kim Nasmyth identified more mutants defective in S-phase (Nurse, Thuriaux et al. 1976). These cdc mutants identified genes required for the events of S-phase, mitosis and cell division, but it was not possible to determine which, if ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.