Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Review Questions
... d. An internal membrane system in which components _____ Mitochondria of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed e. Saclike structure that stores materials f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces protein following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down ...
... d. An internal membrane system in which components _____ Mitochondria of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed e. Saclike structure that stores materials f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces protein following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down ...
Cell Study Guide
... of something that is semi-permeable. 6. a) Define diffusion IN YOUR OWN WORDS (as always!!!). b) Give three examples of molecules that can get in or out of cells by diffusion. c) What do these molecules have in common with each other? 7. Explain three factors that affect the rate of diffusion across ...
... of something that is semi-permeable. 6. a) Define diffusion IN YOUR OWN WORDS (as always!!!). b) Give three examples of molecules that can get in or out of cells by diffusion. c) What do these molecules have in common with each other? 7. Explain three factors that affect the rate of diffusion across ...
cell-transport-g9
... region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ ...
... region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ ...
Document
... 2. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleic acid? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide? Nucleic acids are molecules that contain our genetic information – more specifically, the code for protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nu ...
... 2. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleic acid? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide? Nucleic acids are molecules that contain our genetic information – more specifically, the code for protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nu ...
The cell is the smallest unit of life
... Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________. The ________ ________ is a rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. The cell wall is made of a tough, yet flexible, material called __________________. Th ...
... Cells contain tiny structures that perform specific functions that are called ___________. The ________ ________ is a rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. The cell wall is made of a tough, yet flexible, material called __________________. Th ...
Mitochondrion 1
... Double membranes divide the mitochondrion into two distinct parts: the intermembrane space and the mitochondrial matrix. The intermembrane space is the narrowest part between the two membranes while the mitochondrial matrix is the part enclosed in the innermost membrane. ...
... Double membranes divide the mitochondrion into two distinct parts: the intermembrane space and the mitochondrial matrix. The intermembrane space is the narrowest part between the two membranes while the mitochondrial matrix is the part enclosed in the innermost membrane. ...
Unit 3 Quarter Review Biology
... Carbon special for living things? It makes four bonds It forms single, double and triple Lots of variety for protein, nucleic acids, lipids & carbohydrates ...
... Carbon special for living things? It makes four bonds It forms single, double and triple Lots of variety for protein, nucleic acids, lipids & carbohydrates ...
What are we made of? Specifics and the organic molecules
... essential because they are obtained through diet. If you do not eat them your body will “eat itself” by breaking down muscle for amino acids! Proteins are the structural components of cells, and combine with lipids to make membranes. They are also messengers, but most importantly assist in cell reac ...
... essential because they are obtained through diet. If you do not eat them your body will “eat itself” by breaking down muscle for amino acids! Proteins are the structural components of cells, and combine with lipids to make membranes. They are also messengers, but most importantly assist in cell reac ...
Passive Transport: Osmosis and Diffusion
... separating the cell from its external environment. •These molecules can move apart to allow larger particles to move in or out of the cell. ...
... separating the cell from its external environment. •These molecules can move apart to allow larger particles to move in or out of the cell. ...
Cell Organelles
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
Cell Organelles
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
... • contains DNA, in the form of long strands called chromatin. (chromatin coils to form chromosomes) • DNA genetic information - and direction for making proteins • site of ribosome synthesis ...
Cell Motility - Cochran`s Half Acre
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
... Components of the Cytoskeleton: • Intermediate Filaments – Only in animal cells of specific tissues – Mechanically strengthen cells or cell parts and help maintain shape ...
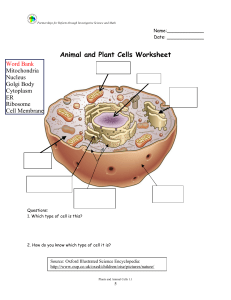
Plant and Animal Cells
... goes in and out of the cell. Ribosomes are found in the nucleus where they carry out photosynthesis. Plant cells are irregular in shape. They have a cell membrane that gives support to the cell. Like animal cells, they have vacuoles where energy is produced for use by the cell. We use methylene blue ...
... goes in and out of the cell. Ribosomes are found in the nucleus where they carry out photosynthesis. Plant cells are irregular in shape. They have a cell membrane that gives support to the cell. Like animal cells, they have vacuoles where energy is produced for use by the cell. We use methylene blue ...
Name: Per. _____ UNIT 4 – CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... 2. By doing this study sheet and then by studying from it. How did the microscope lead to the study of microbiology and ultimately, to the discovery of cells? ...
... 2. By doing this study sheet and then by studying from it. How did the microscope lead to the study of microbiology and ultimately, to the discovery of cells? ...
cells - SCF Faculty Site Homepage
... • Eukaryotic Cells (animals, plants, fungi, protists) – Complex & relatively large. – Membrane-bound nucleus & organelles. – 80-S Ribosomes. ...
... • Eukaryotic Cells (animals, plants, fungi, protists) – Complex & relatively large. – Membrane-bound nucleus & organelles. – 80-S Ribosomes. ...
Ch_4-5_Review
... (a) Both Na and K ions into the cell (cytosol) (b) Both Na and K ions out of the cell (ECM) (c) Na ions into the ECM, K ions into cytosol (d) Na ions into the cytosol, K ions into ECM ...
... (a) Both Na and K ions into the cell (cytosol) (b) Both Na and K ions out of the cell (ECM) (c) Na ions into the ECM, K ions into cytosol (d) Na ions into the cytosol, K ions into ECM ...
BIOL121 Summary
... • Water-soluble ions and water pass through special protein channels/gates/pumps. • Some molecules are too large to fit through protein channels (e.g. glucose) so a special carrier protein is used (facilitated diffusion). The structure of the cell membrane consists of the following: Functions of Cel ...
... • Water-soluble ions and water pass through special protein channels/gates/pumps. • Some molecules are too large to fit through protein channels (e.g. glucose) so a special carrier protein is used (facilitated diffusion). The structure of the cell membrane consists of the following: Functions of Cel ...
Section 3 - HCABIOLOGY
... CLEARLY circle the best answer for each question, or write in the correct answer in the blank provided. 10 points each! ...
... CLEARLY circle the best answer for each question, or write in the correct answer in the blank provided. 10 points each! ...
Cell Structure and Function1
... What is an organelle? • What do you think? • Organelle - a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is separately enclosed within its own membrane • What do organelles remind you of? – OUR ORGANS! – they function in very similar ways ...
... What is an organelle? • What do you think? • Organelle - a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is separately enclosed within its own membrane • What do organelles remind you of? – OUR ORGANS! – they function in very similar ways ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.