Passive Vs. Active Transport
... • The oxygen you are taking in is being passed to all the cells in your body. ...
... • The oxygen you are taking in is being passed to all the cells in your body. ...
Cell Transport Review Worksheet
... C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm ...
... C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm ...
Chapter Outline
... In a hypertonic solution there is a higher percentage of solute outside than inside the cell, which can cause the cells to shrink or shrivel. Transport by Carrier Proteins Carrier proteins are specific; each can combine only with a certain type of molecule or ion, which is then transported through ...
... In a hypertonic solution there is a higher percentage of solute outside than inside the cell, which can cause the cells to shrink or shrivel. Transport by Carrier Proteins Carrier proteins are specific; each can combine only with a certain type of molecule or ion, which is then transported through ...
Prokaryote cells
... Read p14-15 OCR Biology text book 1) Fill in the gaps It was once common practice to classify all living organisms as either animals or plants. With improved knowledge of living things it has become apparent that there are ______ fundamentally different types of cell. The most obvious difference bet ...
... Read p14-15 OCR Biology text book 1) Fill in the gaps It was once common practice to classify all living organisms as either animals or plants. With improved knowledge of living things it has become apparent that there are ______ fundamentally different types of cell. The most obvious difference bet ...
Bacteria are protected by a rigid cell wall composed of
... "nucleoid" refers to the region of the cytoplasm where chromosomal DNA is located, usually a singular, circularchromosome. Bacteria are usually singlecelled, except when they exist ...
... "nucleoid" refers to the region of the cytoplasm where chromosomal DNA is located, usually a singular, circularchromosome. Bacteria are usually singlecelled, except when they exist ...
Chapter 3: Section 3 – Carbon Compounds
... A. Building Blocks of Cells 1. The parts of a cell are made of large, complex molecules called __________________ ____________ _______________. 2. Large, complex biomolecules or organic molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ___________________. 3. These simple molecules or monom ...
... A. Building Blocks of Cells 1. The parts of a cell are made of large, complex molecules called __________________ ____________ _______________. 2. Large, complex biomolecules or organic molecules are built from smaller, simpler molecules called ___________________. 3. These simple molecules or monom ...
Energy Transformations
... 15.) Carbon dioxide and oxygen are molecules that can move freely across a plasma membrane. What determines the direction that carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules move? A.) Orientation of cholesterol in the plasma membrane. B.) Concentration gradient across the plasma membrane. C.) Configuration of ...
... 15.) Carbon dioxide and oxygen are molecules that can move freely across a plasma membrane. What determines the direction that carbon dioxide and oxygen molecules move? A.) Orientation of cholesterol in the plasma membrane. B.) Concentration gradient across the plasma membrane. C.) Configuration of ...
Parts of the Cell: Cellular Organelles 1. Nucleus • The central core of
... • Small, dark spherical body within the nucleus. It is involved in manufacturing ribosomes. 4. Ribosomes • Small, spherical structure. It is the site of protein synthesis (where proteins are made). Ribosomes may be attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) or free-floating in the cytoplasm. 5. Cyto ...
... • Small, dark spherical body within the nucleus. It is involved in manufacturing ribosomes. 4. Ribosomes • Small, spherical structure. It is the site of protein synthesis (where proteins are made). Ribosomes may be attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) or free-floating in the cytoplasm. 5. Cyto ...
SESSION 2: CELLS - THE BASIC UNITS OF LIFE
... also made of cellulose. Cells walls are permeable because they have large pits that allow large molecules to pass through, from one cell to the next. Function of Cell Wall: Cell walls provide plants with a support system. The cell walls act as a rigid frame to hold plants upright as plants do not ha ...
... also made of cellulose. Cells walls are permeable because they have large pits that allow large molecules to pass through, from one cell to the next. Function of Cell Wall: Cell walls provide plants with a support system. The cell walls act as a rigid frame to hold plants upright as plants do not ha ...
Organelles of the Plant Cell - University of Central Oklahoma
... Consists of an inner membrane and an outer membrane Cristae - foldings in the inner membrane Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA ...
... Consists of an inner membrane and an outer membrane Cristae - foldings in the inner membrane Matrix – central space Intermembrane space – space between the membranes Contain their own DNA ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... centrosome of in animal cells o Cilia and flagella = Locomotor organelles ...
... centrosome of in animal cells o Cilia and flagella = Locomotor organelles ...
Organelle Sketch Function Cell Wall Cell Membrane Nucleus
... 4. Give the functions of these two organelles: a. b. 5. Describe, in detail, how lysosomes help to clean up dead organelles and intruders like viruses from a cell. You can get help by looking at http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__lysosomes.html 6. What ...
... 4. Give the functions of these two organelles: a. b. 5. Describe, in detail, how lysosomes help to clean up dead organelles and intruders like viruses from a cell. You can get help by looking at http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__lysosomes.html 6. What ...
Chemicals of Life p. 74
... Amino acids! Proteins are made of amino acids 20 common amino acids can combine/link together to make thousands of different proteins ...
... Amino acids! Proteins are made of amino acids 20 common amino acids can combine/link together to make thousands of different proteins ...
Animal Cell
... Membrane is a structure that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell ...
... Membrane is a structure that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell ...
Cell Processes Study Guide OL Answer Key
... Diffusion Movement of particles from high to low concentration. This is a type of passive transport. Moves particles into and out of cells through cell membrane. ...
... Diffusion Movement of particles from high to low concentration. This is a type of passive transport. Moves particles into and out of cells through cell membrane. ...
Cell Wall
... They are only found in plant cells. Allow the plant to use sunlight to make food (photosynthesis). The stroma is an area inside of the chloroplast where sugars are created. Chlorophyll uses radiant energy to create glucose. ...
... They are only found in plant cells. Allow the plant to use sunlight to make food (photosynthesis). The stroma is an area inside of the chloroplast where sugars are created. Chlorophyll uses radiant energy to create glucose. ...
Plant and Animal cells
... The stroma is an area inside of the chloroplast where sugars are created. Chlorophyll uses radiant energy to create glucose. ...
... The stroma is an area inside of the chloroplast where sugars are created. Chlorophyll uses radiant energy to create glucose. ...
Mr. Martin`s Chapter 30 PowerPoint
... d. Resulting pressure causes flow of sucrose solution through sieve tube (bulk flow) e. At sink sucrose is actively transported out and water follows osmotically ...
... d. Resulting pressure causes flow of sucrose solution through sieve tube (bulk flow) e. At sink sucrose is actively transported out and water follows osmotically ...
Aims - Excellence Gateway
... Levels of Organisation, Identify the Organelle, Nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Golgi Body, Lysosome, Mitochondria. Can be shown as a slide show and students to take notes, or can be hand-outs for the students. ...
... Levels of Organisation, Identify the Organelle, Nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Golgi Body, Lysosome, Mitochondria. Can be shown as a slide show and students to take notes, or can be hand-outs for the students. ...
Cell Transport Review Sheet
... 1. The process of diffusion causes molecules to move from (low to high or high to low) concentrations until a state of ____________________ is reached. 2. The diffusion of water is known as __________________. 3. ________________ diffusion uses proteins to bring materials into the cell from high to ...
... 1. The process of diffusion causes molecules to move from (low to high or high to low) concentrations until a state of ____________________ is reached. 2. The diffusion of water is known as __________________. 3. ________________ diffusion uses proteins to bring materials into the cell from high to ...
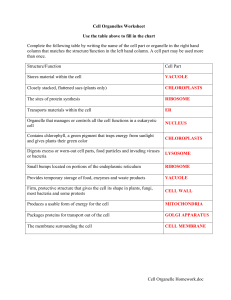
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
... Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
Animal Cell - TeacherWeb
... composed of DNA and proteins, loosely formed when cell is not dividing ...
... composed of DNA and proteins, loosely formed when cell is not dividing ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.