cell - Demarest School District
... An organism is a living thing. A cell is the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A unicellular organism is made of a single cell. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Created by I. Cavalli ...
... An organism is a living thing. A cell is the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A unicellular organism is made of a single cell. A multicellular organism is made up of more than one cell. Created by I. Cavalli ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
... defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not good ...
... defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not good ...
A. diffuser
... Why is it able to pass through the plastic bag?______________________________________ When molecules move DOWN the concentration gradient it means they are moving from ______________ A. an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration B. an area of high concentration to an area of low ...
... Why is it able to pass through the plastic bag?______________________________________ When molecules move DOWN the concentration gradient it means they are moving from ______________ A. an area of low concentration to an area of higher concentration B. an area of high concentration to an area of low ...
Cell Wall Ribosomes Nucleus Chloroplast Cytoplasm Endoplasmic
... The cell membrane is on the outside of an The lysosomes have special digestive enzymes that are The major difference between plant and animal cells is animal cell and is found just underneath the used to digest old cell parts. It's like a garbage disposal that plant cells have cell walls and chlorop ...
... The cell membrane is on the outside of an The lysosomes have special digestive enzymes that are The major difference between plant and animal cells is animal cell and is found just underneath the used to digest old cell parts. It's like a garbage disposal that plant cells have cell walls and chlorop ...
Tiny Cells and Agar Gels
... If one were to fill the same area with these smaller cells as was occupied by our large example, the volume covered would remain the same, but the total surface area provided by many smaller cells would be much increased, allowing for more efficient exchange. Put another way, a group of smaller cell ...
... If one were to fill the same area with these smaller cells as was occupied by our large example, the volume covered would remain the same, but the total surface area provided by many smaller cells would be much increased, allowing for more efficient exchange. Put another way, a group of smaller cell ...
Cell Transport Worksheet
... following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT ________________________ diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis ion channels ...
... following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT ________________________ diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis ion channels ...
Chapter 4
... show two objects as being separate. This is the clarity of the objects. Magnification and resolving power must be balanced to observe the image. When magnification is increased, resolving power is decreased. When resolving power is increased, magnification is decreased. Many kinds of microscopes ava ...
... show two objects as being separate. This is the clarity of the objects. Magnification and resolving power must be balanced to observe the image. When magnification is increased, resolving power is decreased. When resolving power is increased, magnification is decreased. Many kinds of microscopes ava ...
A. diffuser
... following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT ________________________ diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis ion channels ...
... following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT ________________________ diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis ion channels ...
Study Guide
... Exchanging materials as cell grows, exchange of materials across membrane is harder because food and oxygen is being used quicker ...
... Exchanging materials as cell grows, exchange of materials across membrane is harder because food and oxygen is being used quicker ...
3.2-Cell Membrane
... Some of the proteins embedded in the membrane make it selectively permeable = this means the proteins (transport proteins) control which materials can enter and leave the cell Nutrients enter the cell and wastes are removed Ex. Na+/K+ pump proteins in nerve cells cause electrical signals to flow alo ...
... Some of the proteins embedded in the membrane make it selectively permeable = this means the proteins (transport proteins) control which materials can enter and leave the cell Nutrients enter the cell and wastes are removed Ex. Na+/K+ pump proteins in nerve cells cause electrical signals to flow alo ...
Parts of the Cell Fact Sheets
... Ribosomes are where protein synthesis occurs (making proteins). Proteins are essential molecules and perform a wide variety of functions in the cell. They are used to make new cells, speed up chemical reactions (enzymes), act as hormones, and are an essential part of the immune ...
... Ribosomes are where protein synthesis occurs (making proteins). Proteins are essential molecules and perform a wide variety of functions in the cell. They are used to make new cells, speed up chemical reactions (enzymes), act as hormones, and are an essential part of the immune ...
Cell Transport PPT - Effingham County Schools
... • [water inside] < [water outside] • Solutes are higher inside the cell. • Water flows in, cell swells. • Cell could burst if water flow continues. ...
... • [water inside] < [water outside] • Solutes are higher inside the cell. • Water flows in, cell swells. • Cell could burst if water flow continues. ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... Excitable tissues of nerves and muscles cells have higher potentials than other cells (epithelial cells and connective tissue cells). Dead cells do not have membrane potentials. ...
... Excitable tissues of nerves and muscles cells have higher potentials than other cells (epithelial cells and connective tissue cells). Dead cells do not have membrane potentials. ...
Walmart is like a human cell - MyClass at TheInspiredInstructor.com
... • The Nuclear membrane is like Walmart’s security- they get rid of bad people ...
... • The Nuclear membrane is like Walmart’s security- they get rid of bad people ...
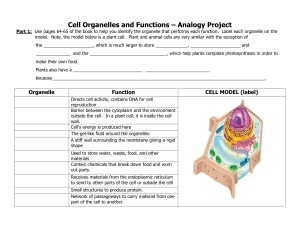
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
CHAPTER 12 THE CELL CYCLE
... 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria. 2. List the phases of the cell cycle and describe the sequence of events that occurs d ...
... 2. Explain how chromatin, chromosomes and genomes relate to one another 3. Describe the difference between a somatic cell and a gamete. The Mitotic Cell Cycle 1. Describe the process of binary fission in bacteria. 2. List the phases of the cell cycle and describe the sequence of events that occurs d ...
Cell division Objectives
... Describe a model that expresses the key elements of signal transduction pathways by which a signal is converted to a cellular response. Justify claims based on scientific evidence that changes in signal transduction pathways can alter cellular response. Describe a model that expresses key elements t ...
... Describe a model that expresses the key elements of signal transduction pathways by which a signal is converted to a cellular response. Justify claims based on scientific evidence that changes in signal transduction pathways can alter cellular response. Describe a model that expresses key elements t ...
Diffusion Through a Cell Membrane
... • The cell controls its food and water content by moving ions, molecules, and larger particles into or out of itself. This is how the cell maintains homeostasis. ...
... • The cell controls its food and water content by moving ions, molecules, and larger particles into or out of itself. This is how the cell maintains homeostasis. ...
Cell Structure Answers Worksheet
... membranes, noticeably around the nucleus) and eukaryotes (larger and more organised cells which have internal membranes surrounding its cell components which are then called organelles). 9. Plant cells contain chlorophyll in chloroplasts, a cell wall as well as a cell membrane, and larger vacuoles, ...
... membranes, noticeably around the nucleus) and eukaryotes (larger and more organised cells which have internal membranes surrounding its cell components which are then called organelles). 9. Plant cells contain chlorophyll in chloroplasts, a cell wall as well as a cell membrane, and larger vacuoles, ...
ACTIVITY: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION, IMPORTANCE OF CELL
... Starting questions for discussion: What types of molecules move passively across membranes in response to these principles? (What types of molecules cannot move passively and how does cell transport them?) Is 'being small' a strange state in the living world, or a common one? How is the 'lifestyle' ...
... Starting questions for discussion: What types of molecules move passively across membranes in response to these principles? (What types of molecules cannot move passively and how does cell transport them?) Is 'being small' a strange state in the living world, or a common one? How is the 'lifestyle' ...
Directions
... Directions: In the space provided below, draw an animal cell. Make sure to draw and label all of the part listed below. Identify each part by coloring it the color indicated in the word box. cell membrane (yellow) mitochondria (orange) smooth ER (brown) ...
... Directions: In the space provided below, draw an animal cell. Make sure to draw and label all of the part listed below. Identify each part by coloring it the color indicated in the word box. cell membrane (yellow) mitochondria (orange) smooth ER (brown) ...
Chapter 3: The Living Units
... 3) transcytosis – moving substances into, across, and out of cell 4) trafficking – moving substances from one part of the cell to another 5) phagocytosis – cell eating 6) pinocy tosis – cell drinking V. The Cytoplasm A. cell-forming material B. cellular material between the plasma membrane and nucle ...
... 3) transcytosis – moving substances into, across, and out of cell 4) trafficking – moving substances from one part of the cell to another 5) phagocytosis – cell eating 6) pinocy tosis – cell drinking V. The Cytoplasm A. cell-forming material B. cellular material between the plasma membrane and nucle ...
The Cell - oteroteacher
... BACK: (function) Mitochondria are rodshaped organelles that can be considered the power generators of the cell, converting oxygen and nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ...
... BACK: (function) Mitochondria are rodshaped organelles that can be considered the power generators of the cell, converting oxygen and nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.