Cell Unit Review Worksheet | Part I KEY
... x. Which organelle is studded with ribosomes & is the site of protein synthesis? Rough ER y. Which organelle breaks down alcohol, and can make lipids? Smooth ER z. Which organelle carries materials from one part of the cell to another? Vesicle aa. Which organelle is a sac filled with fluid insid ...
... x. Which organelle is studded with ribosomes & is the site of protein synthesis? Rough ER y. Which organelle breaks down alcohol, and can make lipids? Smooth ER z. Which organelle carries materials from one part of the cell to another? Vesicle aa. Which organelle is a sac filled with fluid insid ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... 3. nucleolus = makes ribosomes (which make proteins) Function: controls all of the cells activities; controls which proteins are made Other: chromosomes contain genes that control the characteristics of an organism and pass on the traits C. cytoplasm Type of cell: both plant and animal Location: fou ...
... 3. nucleolus = makes ribosomes (which make proteins) Function: controls all of the cells activities; controls which proteins are made Other: chromosomes contain genes that control the characteristics of an organism and pass on the traits C. cytoplasm Type of cell: both plant and animal Location: fou ...
Any Questions??
... During path from cis to trans, products from ER are modified into final form tags, sorts, & packages materials into transport vesicles Golgi = “UPS headquarters” Transport vesicles = “UPS trucks” ...
... During path from cis to trans, products from ER are modified into final form tags, sorts, & packages materials into transport vesicles Golgi = “UPS headquarters” Transport vesicles = “UPS trucks” ...
Georgia Science Standard S7L2.d Grade 7
... Photosynthesis is the process by which cells, such as plant cells, use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen. Photosynthesis takes place in a cell’s chloroplasts, such as the one shown below. Chloroplasts have two membranes and their own DNA. Chloroplasts are green because the ...
... Photosynthesis is the process by which cells, such as plant cells, use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen. Photosynthesis takes place in a cell’s chloroplasts, such as the one shown below. Chloroplasts have two membranes and their own DNA. Chloroplasts are green because the ...
Cell - BMCB - Cornell University
... "Previous research has focused on the enzymes called kinases that add phosphates to proteins or lipids (on-switch). We considered the alternative that phosphatases (off-switch) have crucial roles in regulating essential signaling pathways that take place at the cell surface," explained first-author ...
... "Previous research has focused on the enzymes called kinases that add phosphates to proteins or lipids (on-switch). We considered the alternative that phosphatases (off-switch) have crucial roles in regulating essential signaling pathways that take place at the cell surface," explained first-author ...
File
... 3. Saltwater fish remove extra salt from their body by active transport through the gills. What is the result of this activity? A. The salt becomes more chemically active. B. Water balance is maintained in the blood. C. The rate of energy production is decreased. D. The cell membrane becomes less pe ...
... 3. Saltwater fish remove extra salt from their body by active transport through the gills. What is the result of this activity? A. The salt becomes more chemically active. B. Water balance is maintained in the blood. C. The rate of energy production is decreased. D. The cell membrane becomes less pe ...
Cell Structure and Function - KEY Structure In Eukaryotes
... nucleus, consists of double membrane containing pores ...
... nucleus, consists of double membrane containing pores ...
Membrane Structure
... Membrane Structure The plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings. It makes life possible by its ability to discriminate in its chemical exchanges with the environment. This membrane: • Is about 8 nm thick • Surrounds the cell and controls chemica ...
... Membrane Structure The plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings. It makes life possible by its ability to discriminate in its chemical exchanges with the environment. This membrane: • Is about 8 nm thick • Surrounds the cell and controls chemica ...
Chap 5 – Transport Across Membranes
... Examples: ion channels, aquaporin, GLUT1 (glucose) transporter ...
... Examples: ion channels, aquaporin, GLUT1 (glucose) transporter ...
Animal Cells powerpoint
... Contains genes (made of DNA) on 46 chromosomes. Thousands of strands of DNA can fit onto one chromosome. These have all the instructions for your body. ...
... Contains genes (made of DNA) on 46 chromosomes. Thousands of strands of DNA can fit onto one chromosome. These have all the instructions for your body. ...
BIOL260 Chap 4 Review
... 10. Compare and contrast the cell walls of Gram positive and Gram negative prokaryotes in terms of structure and Gram staining (this is very important to understand). 11. Describe the critical implications of the structure of the Gram negative cell wall. 12. Describe why drugs which target the cell ...
... 10. Compare and contrast the cell walls of Gram positive and Gram negative prokaryotes in terms of structure and Gram staining (this is very important to understand). 11. Describe the critical implications of the structure of the Gram negative cell wall. 12. Describe why drugs which target the cell ...
How the living matter is organized
... they form a compound. Carbon dioxide is a compound made up of the elements carbon and oxygen. Most elements in living things occur in the form of compounds. The smallest unit of many compounds is called a molecule. A molecule of carbon dioxide consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Water ...
... they form a compound. Carbon dioxide is a compound made up of the elements carbon and oxygen. Most elements in living things occur in the form of compounds. The smallest unit of many compounds is called a molecule. A molecule of carbon dioxide consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Water ...
Cells
... • In multicelluar organisms cells are just the start of how things are organized. – Cells – Tissues: groups of cells that function together to perform an activity – Organs: groups of tissues performing one main function ...
... • In multicelluar organisms cells are just the start of how things are organized. – Cells – Tissues: groups of cells that function together to perform an activity – Organs: groups of tissues performing one main function ...
Slide ()
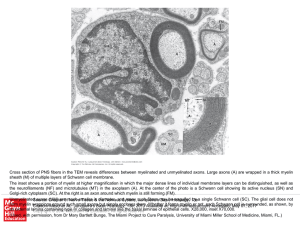
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
PPT File
... Made of proteins and RNA No membrane Made in nucleolus Location of protein synthesis Free ribosomes make proteins used by the cell Ribosomes on rER make proteins for export to other cells ...
... Made of proteins and RNA No membrane Made in nucleolus Location of protein synthesis Free ribosomes make proteins used by the cell Ribosomes on rER make proteins for export to other cells ...
Name
... In A, water will ____________ the cell (_____% is greater than _____%) In B, water will ____________ the cell (_____% is greater than _____%) In C, the water concentrations are __________, so it is at _________________. Active Transport Objective 9: Define and describe forms of active transport and ...
... In A, water will ____________ the cell (_____% is greater than _____%) In B, water will ____________ the cell (_____% is greater than _____%) In C, the water concentrations are __________, so it is at _________________. Active Transport Objective 9: Define and describe forms of active transport and ...
cells
... • Cells are divided into 2 categories: 1. Prokaryotes 2. Eukaryotes *divided into these 2 categories to separate cells that contain a nucleus and organelles (eukaryotes) and those that do not (prokaryotes) ...
... • Cells are divided into 2 categories: 1. Prokaryotes 2. Eukaryotes *divided into these 2 categories to separate cells that contain a nucleus and organelles (eukaryotes) and those that do not (prokaryotes) ...
The Cell Quiz 1
... 1 The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the followin ...
... 1 The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the followin ...
Cell transport ppt. - student notes
... _______ to ______ concentrations. ____________ is the diffusion of water. _________________ solutions could cause a cell to burst. Facilitated diffusion uses proteins to allow ___________ and amino acids into or out of the cell. Ion channels are proteins with special __________ that can open or clos ...
... _______ to ______ concentrations. ____________ is the diffusion of water. _________________ solutions could cause a cell to burst. Facilitated diffusion uses proteins to allow ___________ and amino acids into or out of the cell. Ion channels are proteins with special __________ that can open or clos ...
BIOLOGY 12 UNIT 1b – The Cell Membrane
... Has a particular shape that allows a specific molecule, such as a hormone, to bind to it. Catalyzes a specific chemical reaction. ...
... Has a particular shape that allows a specific molecule, such as a hormone, to bind to it. Catalyzes a specific chemical reaction. ...
Cell Transport
... Sodium ions inside the cell bind to the carrier protein which changes shape and releases sodium ions outside the cell membrane As a result a phosphate group is released from the pump, returning the channel protein to its original shape, and releasing potassium ions inside the cell For every three so ...
... Sodium ions inside the cell bind to the carrier protein which changes shape and releases sodium ions outside the cell membrane As a result a phosphate group is released from the pump, returning the channel protein to its original shape, and releasing potassium ions inside the cell For every three so ...
Wednesday, September 20, 2006
... 2. Transport proteins can be saturated therefore, they have a maximum rate of moving stuff due to limited # of proteins within membrane 3. Transport proteins can be inhibited 4. ‘Catalyze’ physical movement of stuff that would not be able to cross membrane B. Molecules move down concentration gradie ...
... 2. Transport proteins can be saturated therefore, they have a maximum rate of moving stuff due to limited # of proteins within membrane 3. Transport proteins can be inhibited 4. ‘Catalyze’ physical movement of stuff that would not be able to cross membrane B. Molecules move down concentration gradie ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.