Cell Division Worksheet PDF
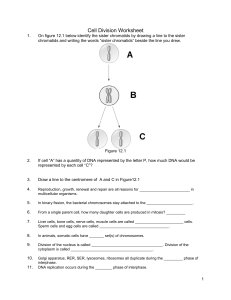
... If cell “A” has a quantity of DNA represented by the letter P, how much DNA would be represented by each cell “C”? ...
... If cell “A” has a quantity of DNA represented by the letter P, how much DNA would be represented by each cell “C”? ...
Cells PPT DH
... – Mitochondria: powerhouse of cell; release energy from sugars & other molecules (active cells such as muscle contain many of these); small oval or rod-shaped structures in the cytoplasm within which potential energy is converted to kinetic energy – Lysosomes: membrane-bound sacs that contain enzyme ...
... – Mitochondria: powerhouse of cell; release energy from sugars & other molecules (active cells such as muscle contain many of these); small oval or rod-shaped structures in the cytoplasm within which potential energy is converted to kinetic energy – Lysosomes: membrane-bound sacs that contain enzyme ...
Class: 11 Subject: Biology Topic: Cell
... (intrinsic). The integral proteins are tightly held in place by strong hydrophilic or hydrophobic interactions or both and are difficult to remove from the membranes. Two peripheral proteins are superficially arranged on either side membrane selectively permeable thus this model explains cell membra ...
... (intrinsic). The integral proteins are tightly held in place by strong hydrophilic or hydrophobic interactions or both and are difficult to remove from the membranes. Two peripheral proteins are superficially arranged on either side membrane selectively permeable thus this model explains cell membra ...
Sample APBio Exam1 - Bruce Rife`s Web Page
... 3. Which of the following observations would provide the strongest evidence that the many different actually related to one another? a. The flowers have the same shape of petals. b. They all produce small seeds. c. None of them can grow without the presence of a specific type of fungus. d. They all ...
... 3. Which of the following observations would provide the strongest evidence that the many different actually related to one another? a. The flowers have the same shape of petals. b. They all produce small seeds. c. None of them can grow without the presence of a specific type of fungus. d. They all ...
Movement Through the Cell Membrane
... 14. Cells are almost always __________ to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh ...
... 14. Cells are almost always __________ to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell. Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh ...
Two Types of Cells Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Let`s SQ3R to
... DNA that floats in the cell’s cytoplasm. Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Som ...
... DNA that floats in the cell’s cytoplasm. Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Som ...
01 - edl.io
... _____ 10. During cell division, sister chromatids are separated at the a. centromere. c. centrosome. b. nucleosome. d. chromosome. _____ 11. Which of these is a network of microtubules that forms during mitosis to pull chromatids to opposite ends of a cell? a. histone c. spindle b. chromatin d. cent ...
... _____ 10. During cell division, sister chromatids are separated at the a. centromere. c. centrosome. b. nucleosome. d. chromosome. _____ 11. Which of these is a network of microtubules that forms during mitosis to pull chromatids to opposite ends of a cell? a. histone c. spindle b. chromatin d. cent ...
A. diffuser - Haiku Learning
... The substance being dissolved in another substance to make a solution is called the ____________? A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower ...
... The substance being dissolved in another substance to make a solution is called the ____________? A. diffuser B. solvent C. solute D. concentrate During diffusion molecules tend to move _____________________ A. up the concentration gradient B. down the concentration gradient C. from an area of lower ...
A novel probe to identify biochemical signals of cells at cell
... proliferation on the biomaterial surface. A specific subset of RNAbinding proteins was also found at the interface. This is consistent with the recent discovery of the association of RNA-binding proteins with the “spreading initiation centres”, a novel structure important for the attachment of cells ...
... proliferation on the biomaterial surface. A specific subset of RNAbinding proteins was also found at the interface. This is consistent with the recent discovery of the association of RNA-binding proteins with the “spreading initiation centres”, a novel structure important for the attachment of cells ...
Cell and Organelle
... Each group will present their work to the class. They will discuss the importance of each cell parts and connect it to the real life situation and their culture. (TEK infusion: connection, cooperation, respect, creativity) Type of assessment: Teacher-made-test Direction: Complete the chart below. Dr ...
... Each group will present their work to the class. They will discuss the importance of each cell parts and connect it to the real life situation and their culture. (TEK infusion: connection, cooperation, respect, creativity) Type of assessment: Teacher-made-test Direction: Complete the chart below. Dr ...
Ch 7-1: Life is Cellular
... Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus: Contains DNA and controls the cell’s activities -Chromatin: Tightly coiled strands of DNA & protein found within the nucleus. • Nucleolus: Dense small region found within the nucleus that makes ribosomes • Nuclear Envelope: Controls what materials go in and out of the nuc ...
... Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus: Contains DNA and controls the cell’s activities -Chromatin: Tightly coiled strands of DNA & protein found within the nucleus. • Nucleolus: Dense small region found within the nucleus that makes ribosomes • Nuclear Envelope: Controls what materials go in and out of the nuc ...
Chapter 19: Cell junctions and the extracellular matrix
... Components of the extracellular matrix Proteoglycans (made of both proteins and GAGs) also differ in physical properties Synthesized in Golgi prior to secretion In addition to structural roles, proteoglycans can also bind hormones (e.g., inflammatory chemokines, FGF, TGFβ) to alter cell signaling p ...
... Components of the extracellular matrix Proteoglycans (made of both proteins and GAGs) also differ in physical properties Synthesized in Golgi prior to secretion In addition to structural roles, proteoglycans can also bind hormones (e.g., inflammatory chemokines, FGF, TGFβ) to alter cell signaling p ...
The cell cycle
... 1. The relative length of different cell cycle phase vary in different cell types 2. Human cells of Tc > Hamster cells of Tc 3. S> G2 > M ...
... 1. The relative length of different cell cycle phase vary in different cell types 2. Human cells of Tc > Hamster cells of Tc 3. S> G2 > M ...
Mitosis Flip Book
... The spindle fibres tug the X shaped chromosomes into a line across the middle of the cell. ...
... The spindle fibres tug the X shaped chromosomes into a line across the middle of the cell. ...
powerpoint
... Mechanisms governing the secondary burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and basic pathways of cell death from hyperoxia. 1: Loss of plasma membrane integrity from lipid peroxidation by ROS. 2: ROS damage to the mitochondria membranes and deactivation of enzyme systems and cytochrome chain. 3: This ...
... Mechanisms governing the secondary burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and basic pathways of cell death from hyperoxia. 1: Loss of plasma membrane integrity from lipid peroxidation by ROS. 2: ROS damage to the mitochondria membranes and deactivation of enzyme systems and cytochrome chain. 3: This ...
Organelle Posters - www.dewittebio.com!
... made up of a double layer of lipids called the lipid bi-‐layer ...
... made up of a double layer of lipids called the lipid bi-‐layer ...
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
... Components of the extracellular matrix Proteoglycans (made of both proteins and GAGs) also differ in physical properties Synthesized in Golgi prior to secretion In addition to structural roles, proteoglycans can also bind hormones (e.g., inflammatory chemokines, FGF, TGFb) to alter cell signaling p ...
... Components of the extracellular matrix Proteoglycans (made of both proteins and GAGs) also differ in physical properties Synthesized in Golgi prior to secretion In addition to structural roles, proteoglycans can also bind hormones (e.g., inflammatory chemokines, FGF, TGFb) to alter cell signaling p ...
Levels of Organization Z
... Community Populations that live together in a defined area Hawk, snake, bison, prairie dog, grass ...
... Community Populations that live together in a defined area Hawk, snake, bison, prairie dog, grass ...
The proteins
... heads facing outwards, and their non-polar, hydrophobic fatty acid tails facing each other in the middle of the bilayer.The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, allowing only certain molecules to diffuse across the membrane. Different kinds of membranes can contain phospholipids with different fatty aci ...
... heads facing outwards, and their non-polar, hydrophobic fatty acid tails facing each other in the middle of the bilayer.The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, allowing only certain molecules to diffuse across the membrane. Different kinds of membranes can contain phospholipids with different fatty aci ...
Inside a Cell - WJHS Team 7A
... fungus cells are sacs called vacuoles. Vacuoles are enclosed by a membrane and can hold water, waste, and other materials. Vacuoles function with the cell membrane to move materials either into or out of the cell. A plant cell has a large central vacuole in which water and other materials can be sto ...
... fungus cells are sacs called vacuoles. Vacuoles are enclosed by a membrane and can hold water, waste, and other materials. Vacuoles function with the cell membrane to move materials either into or out of the cell. A plant cell has a large central vacuole in which water and other materials can be sto ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... 14. DNA is located in the ___________ region of a prokaryote, while the cell______________ and cell _____________ surround the outside of the cell. 15. What makes up the cell wall of bacteria? 16. What organelle without a membrane is found in bacteria & what is its function? 17. What are eukaryotes ...
... 14. DNA is located in the ___________ region of a prokaryote, while the cell______________ and cell _____________ surround the outside of the cell. 15. What makes up the cell wall of bacteria? 16. What organelle without a membrane is found in bacteria & what is its function? 17. What are eukaryotes ...
Histology of Cell Types
... tiny vesicles inside the cell move to and fuse with the neuron’s cell membrane, dumping the special chemicals outside of itself. The next neuron gets the chemical signal because special protein molecules in its cell membrane capture the special chemicals and move them inside. ...
... tiny vesicles inside the cell move to and fuse with the neuron’s cell membrane, dumping the special chemicals outside of itself. The next neuron gets the chemical signal because special protein molecules in its cell membrane capture the special chemicals and move them inside. ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.























