TOPIC: Cells AIM: How are materials transported into and out of cells?
... (1.) DNA (2.) ADP (3.) ATP (4.) RNA ...
... (1.) DNA (2.) ADP (3.) ATP (4.) RNA ...
Chapter 6 Question 2 Activity: Prokaryotic Cell
... They are the sites of reactions that convert chemical energy to ATP. They contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Their matrix contains enzymes that function in cellular respiration. Their inner membrane has infoldings called cristae. ...
... They are the sites of reactions that convert chemical energy to ATP. They contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Their matrix contains enzymes that function in cellular respiration. Their inner membrane has infoldings called cristae. ...
Cell City Project – You are the Designer!
... Floating around in the cytoplasm of a cell are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. In order to survive, the cell must be able to interact with its surroundings, use energy, produce materi ...
... Floating around in the cytoplasm of a cell are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. In order to survive, the cell must be able to interact with its surroundings, use energy, produce materi ...
AP Bio Summer Assignment 2016
... available for extra help to anyone who finds they lack a good background in any of these chapters. Please do not hesitate to email me with questions. You can reach me at [email protected]. I look forward to getting to know you, and getting to know Biology together, next year. ...
... available for extra help to anyone who finds they lack a good background in any of these chapters. Please do not hesitate to email me with questions. You can reach me at [email protected]. I look forward to getting to know you, and getting to know Biology together, next year. ...
SCNS480 Cell Biology Laboratory
... Prerequisites: SCNS210 or SCNS310 Instructor(s): Michael Wolfgang Lassalle ...
... Prerequisites: SCNS210 or SCNS310 Instructor(s): Michael Wolfgang Lassalle ...
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue (Chapter 12) Lecture Materials for
... 1. Depolarization to threshold:! - a graded potential depolarizes local ! membrane and flows toward the axon! - if threshold is met (-55mV) at the hillock, an ! action potential will be triggered! 2. Activation of sodium channels and rapid ! depolarization:! - at threshold (-55mV), voltage-regulated ...
... 1. Depolarization to threshold:! - a graded potential depolarizes local ! membrane and flows toward the axon! - if threshold is met (-55mV) at the hillock, an ! action potential will be triggered! 2. Activation of sodium channels and rapid ! depolarization:! - at threshold (-55mV), voltage-regulated ...
Protein: Amino Acids
... • After reading Chapter 5, class discussion and activities you will be able to: – Describe the role of proteins – Distinguish between complete and incomplete proteins – Identify sources of quality protein – Calculate calories from protein ...
... • After reading Chapter 5, class discussion and activities you will be able to: – Describe the role of proteins – Distinguish between complete and incomplete proteins – Identify sources of quality protein – Calculate calories from protein ...
Protein: Amino Acids
... • After reading Chapter 5, class discussion and activities you will be able to: – Describe the role of proteins – Distinguish between complete and incomplete proteins – Identify sources of quality protein – Calculate calories from protein ...
... • After reading Chapter 5, class discussion and activities you will be able to: – Describe the role of proteins – Distinguish between complete and incomplete proteins – Identify sources of quality protein – Calculate calories from protein ...
Photolabeling of Proteins and Cells
... (22), which encodes a homolog of mouse Su(var)3-9 and fission yeast clr4 (12). These are K9-specific histone H3 methyltransferases characterized by a specific SET [Su(var)3-9, Enhancer-of-zeste, Trithotrax] domain. Arabidopsis has up to 15 genes that potentially encode this class of proteins (23), a ...
... (22), which encodes a homolog of mouse Su(var)3-9 and fission yeast clr4 (12). These are K9-specific histone H3 methyltransferases characterized by a specific SET [Su(var)3-9, Enhancer-of-zeste, Trithotrax] domain. Arabidopsis has up to 15 genes that potentially encode this class of proteins (23), a ...
Biol 211 (1) Chapter 29 Worksheet
... 16. Provide at least three reasons why prokaryotes are important. a. b. c. ...
... 16. Provide at least three reasons why prokaryotes are important. a. b. c. ...
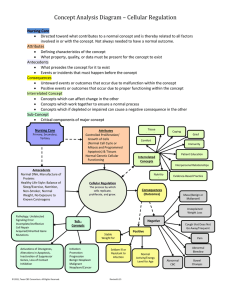
Concept Analysis Diagram * Cellular Regulation
... Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, healthy life-style: balance of sleep/exercise/nut ...
... Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, healthy life-style: balance of sleep/exercise/nut ...
The Localization of PABPC1 in HeLa Cells
... My study looks to find if PABPC1 is found in the nucleus when the DNA is not inhibited. In this study, PABPC1 I imaged in human cells rather than yeast cells. In addition, I studied the number of cells expressing PABPC1 in the nucleus. I used HeLa cells as a model and immunoflorescence techniques to ...
... My study looks to find if PABPC1 is found in the nucleus when the DNA is not inhibited. In this study, PABPC1 I imaged in human cells rather than yeast cells. In addition, I studied the number of cells expressing PABPC1 in the nucleus. I used HeLa cells as a model and immunoflorescence techniques to ...
NADPH Oxidase 1, a novel molecular source of ROS in
... While oxidative stress has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the molecular mechanism underlying selective vulnerability of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway to oxidative damage remains unknown. Increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) result in a ...
... While oxidative stress has been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the molecular mechanism underlying selective vulnerability of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway to oxidative damage remains unknown. Increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) result in a ...
Lecture 11b Neurophysiology
... • Imagine a cell with high K+ inside and high Na+ outside. • At time = 0, the membrane is impermeable • Say that we now put K+ channels in the cell, making it permeable to only K+. What happens to K+? • Will it continue to move until it is the same on both sides (in and out)? ...
... • Imagine a cell with high K+ inside and high Na+ outside. • At time = 0, the membrane is impermeable • Say that we now put K+ channels in the cell, making it permeable to only K+. What happens to K+? • Will it continue to move until it is the same on both sides (in and out)? ...
Intercellular Communication during Plant
... et al., 2010; Kinoshita et al., 2010). Signal transduction through these complexes restricts expression of WUSCHEL, a homeodomain transcription factor that non-cell-autonomously promotes stem cell identity (Brand et al., 2000). Thus, the CLV3 signaling system functions to regulate the critical balan ...
... et al., 2010; Kinoshita et al., 2010). Signal transduction through these complexes restricts expression of WUSCHEL, a homeodomain transcription factor that non-cell-autonomously promotes stem cell identity (Brand et al., 2000). Thus, the CLV3 signaling system functions to regulate the critical balan ...
Presentation
... chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. The mechanism is not fully understood, but proteins may anchor the daughter chromosomes to specific sites on the plasma membrane. ...
... chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. The mechanism is not fully understood, but proteins may anchor the daughter chromosomes to specific sites on the plasma membrane. ...
EGFR_Instructor
... EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) is a receptor tyrosine kinase. Upon binding its specific ligand (for example, EGF) the EGFR dimerizes and its receptor tyrosine kinase activity is activated. Kinases add phosphate groups to proteins. In the case of EGFR, this kinase autophosphorylates, adding ...
... EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) is a receptor tyrosine kinase. Upon binding its specific ligand (for example, EGF) the EGFR dimerizes and its receptor tyrosine kinase activity is activated. Kinases add phosphate groups to proteins. In the case of EGFR, this kinase autophosphorylates, adding ...
Bovine Serum Albumin, pH 7.0
... pyrogens and toxic metals from the cells. It acts as a major antioxidant in cell culture media. It forms complexes with molecules that cause oxidative damage in non-bound state. These include bilirubin, free radicals, cysteine, glutathione, fatty acids, pyridoxal phosphate etc. Albumin also function ...
... pyrogens and toxic metals from the cells. It acts as a major antioxidant in cell culture media. It forms complexes with molecules that cause oxidative damage in non-bound state. These include bilirubin, free radicals, cysteine, glutathione, fatty acids, pyridoxal phosphate etc. Albumin also function ...
Complementing IHC with real-time interaction analysis on tissue
... traces for three antibodies with 1nM affinity and different interaction dynamics. Look at 2 hours of incubation at 10 nM concentration, then 7 hours of retention. ...
... traces for three antibodies with 1nM affinity and different interaction dynamics. Look at 2 hours of incubation at 10 nM concentration, then 7 hours of retention. ...
Macromolecules
... Contains coded information that programs all cell activity Contains directions for its own replication Is copied and passed from one generation of cells to another In eukaryotic cells, is found primarily in the nucleus Makes up genes that contain instructions for protein synthesis-genes that do not ...
... Contains coded information that programs all cell activity Contains directions for its own replication Is copied and passed from one generation of cells to another In eukaryotic cells, is found primarily in the nucleus Makes up genes that contain instructions for protein synthesis-genes that do not ...
Lecture 11b Neurophysiology
... • Imagine a cell with high K+ inside and high Na+ outside. • At time = 0, the membrane is impermeable • Say that we now put K+ channels in the cell, making it permeable to only K+. What happens to K+? • Will it continue to move until it is the same on both sides (in and out)? ...
... • Imagine a cell with high K+ inside and high Na+ outside. • At time = 0, the membrane is impermeable • Say that we now put K+ channels in the cell, making it permeable to only K+. What happens to K+? • Will it continue to move until it is the same on both sides (in and out)? ...
Caffeine as a cause of coral bleaching: Effects of caffeine on
... PhastSystem with gradient 8-14 gels. The results indicated that our extraction procedure was successful in producing sufficient yields of protein; however, the resolution of the gels was too poor to show differences in the protein bands. We are now sending our extracted proteins to the School of Bio ...
... PhastSystem with gradient 8-14 gels. The results indicated that our extraction procedure was successful in producing sufficient yields of protein; however, the resolution of the gels was too poor to show differences in the protein bands. We are now sending our extracted proteins to the School of Bio ...
ASM book 1.8.7.20 vgv - BioQUEST Curriculum Consortium
... To interactively explore the ribbon diagram above, click on VRML (default options) on top of the list. A 3D structural model will appear. To change the model’s size, click on the Walk and move the cursor up or down. To rotate the model freely, click on Study. ...
... To interactively explore the ribbon diagram above, click on VRML (default options) on top of the list. A 3D structural model will appear. To change the model’s size, click on the Walk and move the cursor up or down. To rotate the model freely, click on Study. ...
supporting cells - Daniela Sartori
... binding sites – Opens when 2 AChs bind – Permits diffusion of Na+ into and K+ out of postsynaptic cell – Inward flow of Na+ dominates – Produces EPSPs ...
... binding sites – Opens when 2 AChs bind – Permits diffusion of Na+ into and K+ out of postsynaptic cell – Inward flow of Na+ dominates – Produces EPSPs ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.