MICROBIOLOGY
... The science of microbiology was developed with inclosing of other science development basically the progressing of the different science such as medicine cytology ,cell physiology ,genetic ,enzymology ,biochemistry ,ecology , etc. Microbiology includes the study of many types of cells, it is concern ...
... The science of microbiology was developed with inclosing of other science development basically the progressing of the different science such as medicine cytology ,cell physiology ,genetic ,enzymology ,biochemistry ,ecology , etc. Microbiology includes the study of many types of cells, it is concern ...
Syllabus for Medical Cell Biology
... The medical cell biology is a subject concerned with life activities, its mechanisms and principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using diffe ...
... The medical cell biology is a subject concerned with life activities, its mechanisms and principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using diffe ...
Biology Unit - Sixth Grade Content Vocabulary Wiki
... Mitochondria: organelles that take nutrients and create usable energy. Endoplasmic reticulum: organelle that helps to move energy to all parts of the cell. Chloroplasts: organelles that allow plants and plant-like protists to carry out photosynthesis and make their own food. Photosynthesis: the proc ...
... Mitochondria: organelles that take nutrients and create usable energy. Endoplasmic reticulum: organelle that helps to move energy to all parts of the cell. Chloroplasts: organelles that allow plants and plant-like protists to carry out photosynthesis and make their own food. Photosynthesis: the proc ...
Chapter 5
... • When phospholipids are added to water, they self-assemble into a bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior • The structure of phospholipids results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes • Phospholipids are the major component of all cell membranes ...
... • When phospholipids are added to water, they self-assemble into a bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior • The structure of phospholipids results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes • Phospholipids are the major component of all cell membranes ...
How Does Alpha-L-Polylactate™ in Cytomax® Work Faster than
... the cell called the mitochondria, also referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” The mitochondria within cells are where oxygen is utilized (Lehninger). Mitochondria form a vast energy production and distribution network, in which the products of food digestion and enzymatic breakdown are burned ...
... the cell called the mitochondria, also referred to as the “powerhouse of the cell.” The mitochondria within cells are where oxygen is utilized (Lehninger). Mitochondria form a vast energy production and distribution network, in which the products of food digestion and enzymatic breakdown are burned ...
CHAPTER 4
... – After the channel is open for a few milliseconds, the movement of K+ ions is “automatically” stopped by a process known as inactivation. – Can exist in three different states: open, inactivated, and closed. ...
... – After the channel is open for a few milliseconds, the movement of K+ ions is “automatically” stopped by a process known as inactivation. – Can exist in three different states: open, inactivated, and closed. ...
Chapter 16 Sense Organs
... – hydrophilic - diffuse through mucus – hydrophobic - transported by odorant-binding protein in mucus ...
... – hydrophilic - diffuse through mucus – hydrophobic - transported by odorant-binding protein in mucus ...
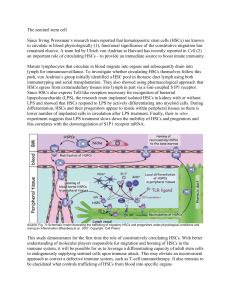
vonandrian_blog_review_120207_jws
... lymph for immunosurveillance. To investigate whether circulating HSCs themselves follow this path, von Andrian’s group initially identified a HSC pool in thoracic duct lymph using both immunotyping and serial transplantation. They also showed using pharmacological approach that HSCs egress from extr ...
... lymph for immunosurveillance. To investigate whether circulating HSCs themselves follow this path, von Andrian’s group initially identified a HSC pool in thoracic duct lymph using both immunotyping and serial transplantation. They also showed using pharmacological approach that HSCs egress from extr ...
Cell Organelle Research Worksheet
... Fluid that fills a cell and all of the organelles are suspended within ...
... Fluid that fills a cell and all of the organelles are suspended within ...
Hemojuvelin N-terminal mutants reach the plasma membrane but do
... kDa, as shown in the mock lane. The histogram illustrates the results of the densitometric analysis of s-HJV species expressed as percentages (%) of total s-HJV. The intensity of the bands was determined using ImageJ software. White bars: 42 kDa s-HJV; gray bars: 30 kDa s-HJV. The experiments were p ...
... kDa, as shown in the mock lane. The histogram illustrates the results of the densitometric analysis of s-HJV species expressed as percentages (%) of total s-HJV. The intensity of the bands was determined using ImageJ software. White bars: 42 kDa s-HJV; gray bars: 30 kDa s-HJV. The experiments were p ...
Chapter 4 - 4.2PowerPoint
... 3.2 Cell Organelles Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... 3.2 Cell Organelles Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
Evolution of Animal Neural Systems
... code within neurons, and those underlying the synaptic code between neurons. Each of these two sections can be further divided into three sub-modules. Proteins from all modules were present in the unicellular ancestor of animals. ...
... code within neurons, and those underlying the synaptic code between neurons. Each of these two sections can be further divided into three sub-modules. Proteins from all modules were present in the unicellular ancestor of animals. ...
Profile
... MITOCHONDRIA to NUCLEOULUS: “We have been faster at all of our jobs! But it means more work for me making the food into energy we can use. Also the Chloroplast in the plant cell said that she had been working non stop also!” ...
... MITOCHONDRIA to NUCLEOULUS: “We have been faster at all of our jobs! But it means more work for me making the food into energy we can use. Also the Chloroplast in the plant cell said that she had been working non stop also!” ...
Neural Communication
... When a neuron is not firing it is said to be at rest. Although it is "at rest", it always has the "potential" to fire, and this potential is expressed as the difference in electrical charges across the membrane of the neuron; differences in the electrical charge, that is, between the inside and outs ...
... When a neuron is not firing it is said to be at rest. Although it is "at rest", it always has the "potential" to fire, and this potential is expressed as the difference in electrical charges across the membrane of the neuron; differences in the electrical charge, that is, between the inside and outs ...
Cells notes only - Brookings School District
... describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (…role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function explain how homeostasis is maintained within living systems; ...
... describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (…role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function explain how homeostasis is maintained within living systems; ...
+ BMP-4
... 8. This inductive mechanism is conserved between vertebrates and invertebrates. 9. BMP-4 is a member of the Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-b) family of signaling molecules. Similar signaling events maybe selectively and focally re-employed later in the nervous system to mediate fine tuning at late ...
... 8. This inductive mechanism is conserved between vertebrates and invertebrates. 9. BMP-4 is a member of the Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-b) family of signaling molecules. Similar signaling events maybe selectively and focally re-employed later in the nervous system to mediate fine tuning at late ...
nervous system - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... signals to muscles or glands; • interneurons are located in the brain and in the spinal cord, they receive information from other neurons. ...
... signals to muscles or glands; • interneurons are located in the brain and in the spinal cord, they receive information from other neurons. ...
Overview: The Molecules of Life
... and compact storage is important, as in seeds. Animals must carry their energy stores with them and benefit from having a more compact fuel reservoir of fat. Humans and other mammals store fats as long-term energy reserves in adipose cells that swell and shrink as fat is deposited or withdrawn from ...
... and compact storage is important, as in seeds. Animals must carry their energy stores with them and benefit from having a more compact fuel reservoir of fat. Humans and other mammals store fats as long-term energy reserves in adipose cells that swell and shrink as fat is deposited or withdrawn from ...
small intestine
... abundant absorption of di- and tripeptides in the small intestine. These small peptides are absorbed into the small intestinal epithelial cell by cotransport with H+ ions via a transporter called PepT1. Once inside the enterocyte, the vast bulk of absorbed di- and tripeptides are digested into amino ...
... abundant absorption of di- and tripeptides in the small intestine. These small peptides are absorbed into the small intestinal epithelial cell by cotransport with H+ ions via a transporter called PepT1. Once inside the enterocyte, the vast bulk of absorbed di- and tripeptides are digested into amino ...
CELL PARTS Chapter 4
... describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (…role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function explain how homeostasis is maintained within living systems; ...
... describe and give examples of chemical reactions required to sustain life (…role of enzymes) describe the relationship between structure and function explain how homeostasis is maintained within living systems; ...
chapter-11-functional-organization-of-nervous
... receive the impulse Most are axo-dendritic or axo-somatic ...
... receive the impulse Most are axo-dendritic or axo-somatic ...
Standard PDF - Wiley Online Library
... Figure 2. Possible molecular mechanisms for mechanotransduction at the AJ, focusing on a-catenin-actin interaction. A: The structure and functional domains of a-catenin, showing bcatenin, vinculin, and F-actin (actin filament) binding regions and an inhibitory region for vinculin binding. The vincul ...
... Figure 2. Possible molecular mechanisms for mechanotransduction at the AJ, focusing on a-catenin-actin interaction. A: The structure and functional domains of a-catenin, showing bcatenin, vinculin, and F-actin (actin filament) binding regions and an inhibitory region for vinculin binding. The vincul ...
In Sweden, Mexico, the United States, and a num
... As an alternative to throwing this tissue away, research has shown that fetal tissue may be useful for treating patients with disabling diseases. For over 50 years, research in animals has demonstrated that fetal tissue has a unique capacity to replace certain cellular deficiencies and so may be use ...
... As an alternative to throwing this tissue away, research has shown that fetal tissue may be useful for treating patients with disabling diseases. For over 50 years, research in animals has demonstrated that fetal tissue has a unique capacity to replace certain cellular deficiencies and so may be use ...
Cell!Transport!Concept!Map! - AHS
... Living cells maintain a _________________________ by controlling material that enter and leave. Without this ability, the cell cannot maintain _____________________________ and will die. The cell must regulate ...
... Living cells maintain a _________________________ by controlling material that enter and leave. Without this ability, the cell cannot maintain _____________________________ and will die. The cell must regulate ...
Chapter 12 – Introduction to the Nervous System
... Afferent vs Efferent Nervous pathways are organized into division based on the direction they carry information • Afferent division: incoming information ...
... Afferent vs Efferent Nervous pathways are organized into division based on the direction they carry information • Afferent division: incoming information ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.