Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... 1) Many of the enzymes that control a deep-sea firefly squid's ability to produce light energy from chemical energy are located A) in membranes. B) in the nucleus. C) within chloroplasts. D) outside of cells. E) within mitochondria. Answer: A 2) The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane a ...
... 1) Many of the enzymes that control a deep-sea firefly squid's ability to produce light energy from chemical energy are located A) in membranes. B) in the nucleus. C) within chloroplasts. D) outside of cells. E) within mitochondria. Answer: A 2) The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane a ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... • The receptive field refers to the part of the visual field that either excites or inhibits a cell in the visual system of the brain. • For a receptor, the receptive field is the point in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field ...
... • The receptive field refers to the part of the visual field that either excites or inhibits a cell in the visual system of the brain. • For a receptor, the receptive field is the point in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field ...
Insulin-Resistance, Browning
... relatively scarce in the adult as an identifiable tissue. Brown fat cells are interspersed within WAT of rodents and humans. Activation of BAT requires 3-adrenergic receptor agonism. ...
... relatively scarce in the adult as an identifiable tissue. Brown fat cells are interspersed within WAT of rodents and humans. Activation of BAT requires 3-adrenergic receptor agonism. ...
The Amino Terminus of Gαz is Required for Receptor Recognition
... cyclase (AC) in a similar fashion (Wong et al., 1992; Kozasa and Gilman, 1995). The sequence identities are even higher when only their C-terminal halves are compared, where the putative receptor- and effector-interacting domains were located. However, subtle differences are found between the amino ...
... cyclase (AC) in a similar fashion (Wong et al., 1992; Kozasa and Gilman, 1995). The sequence identities are even higher when only their C-terminal halves are compared, where the putative receptor- and effector-interacting domains were located. However, subtle differences are found between the amino ...
primary active transport
... sodium) diffuses down its electrochemical gradient, the energy released is used to drive another substance (for instance, glucose) against its electrochemical gradient. Thus, secondary active transport does not require energy directly from ATP or from other high energy phosphate sources. Rather, the ...
... sodium) diffuses down its electrochemical gradient, the energy released is used to drive another substance (for instance, glucose) against its electrochemical gradient. Thus, secondary active transport does not require energy directly from ATP or from other high energy phosphate sources. Rather, the ...
determination of molecular weight
... The extracellular domain of human tumor necrosis factor (TNF- α) type 1 receptor ( sTNF-R1 ) was expressed in 293S human embryonic kidney cells (2). The secreted soluble receptor was purified by chromatography on a TNF-α affinity column and reversed phase HPLC. The molecular mass of this protein is ...
... The extracellular domain of human tumor necrosis factor (TNF- α) type 1 receptor ( sTNF-R1 ) was expressed in 293S human embryonic kidney cells (2). The secreted soluble receptor was purified by chromatography on a TNF-α affinity column and reversed phase HPLC. The molecular mass of this protein is ...
Isolation of specific tRNA molecules
... Mix tRNA with sample buffer (0.1 M sodium acetate (pH 5.0), 8 M urea, 0.05 % bromphenol blue, and 0.05% xylene cyanol) and fractionate on a 6.5% polyacrylamide gel containing 8 M urea in 0.1 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0). Run at 12V/cm until the bromphenol blue dye reaches the bottom of the gel. ...
... Mix tRNA with sample buffer (0.1 M sodium acetate (pH 5.0), 8 M urea, 0.05 % bromphenol blue, and 0.05% xylene cyanol) and fractionate on a 6.5% polyacrylamide gel containing 8 M urea in 0.1 M sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0). Run at 12V/cm until the bromphenol blue dye reaches the bottom of the gel. ...
Chapter 08: The Chemical Senses
... Microvilli project to taste pore Not neurons by standard histological criteria but do form synapses to gustatory ganglion neurons (as well as to basal cells) Receptor potential: Voltage shift occur when taste cells are activated by chemicals Slide 8 ...
... Microvilli project to taste pore Not neurons by standard histological criteria but do form synapses to gustatory ganglion neurons (as well as to basal cells) Receptor potential: Voltage shift occur when taste cells are activated by chemicals Slide 8 ...
Vaccination against allergy
... Identification of expression and function of proteins; to obtain increased knowledge of mechanisms underlying ...
... Identification of expression and function of proteins; to obtain increased knowledge of mechanisms underlying ...
enzyme - Clayton State University
... • Active site is distorted and is not recognised by the substrate • Increasing substrate concentration does not reverse inhibition • Inhibitor is not similar in structure to the substrate ...
... • Active site is distorted and is not recognised by the substrate • Increasing substrate concentration does not reverse inhibition • Inhibitor is not similar in structure to the substrate ...
S-layer and cytoplasmic membrane – exceptions from the typical
... Microorganisms and especially archaea can be found in almost any kind of extreme environment, although they are not limited to them: high temperature, high acidity, high pressure, anoxic, no organic substrates. In those habitats, various species of hyperthermophilic or more generally extremophilic a ...
... Microorganisms and especially archaea can be found in almost any kind of extreme environment, although they are not limited to them: high temperature, high acidity, high pressure, anoxic, no organic substrates. In those habitats, various species of hyperthermophilic or more generally extremophilic a ...
pH-Responsive Calcium Phosphate- Polymer Nanoparticles as a
... Introduction Calcium phosphate (CaP) as the inorganic part of hard tissue is known for its biocompatibility.1 In addition, CaP nanoparticles have a high affinity to nucleic acids and are efficiently taken up by cells and subsequently dissolved in lysosomes at a pH below five.2 Therefore, CaP nanopar ...
... Introduction Calcium phosphate (CaP) as the inorganic part of hard tissue is known for its biocompatibility.1 In addition, CaP nanoparticles have a high affinity to nucleic acids and are efficiently taken up by cells and subsequently dissolved in lysosomes at a pH below five.2 Therefore, CaP nanopar ...
Macronutrient Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism 79
... from the interesting findings that GLUT2, the classic facilitative glucose transporter initially believed to be sequestered to the basolateral membrane, as well as a novel facilitative glucose-specific transporter GLUT7 (SLC2A7), can both be inserted into the brush border in response to high glucose ...
... from the interesting findings that GLUT2, the classic facilitative glucose transporter initially believed to be sequestered to the basolateral membrane, as well as a novel facilitative glucose-specific transporter GLUT7 (SLC2A7), can both be inserted into the brush border in response to high glucose ...
Isolation and Characterization of Cell Wall
... (Table 1). Carotenoids were detected in cell wall (CW I and CW 11) and outer membrane (OM 11) fractions (amounts below 1 % of fraction dry weight). The purified outer membrane fraction (OM 11, Table 1) contained very few peptidoglycan components, due to efficient removal of the peptidoglycan by lyso ...
... (Table 1). Carotenoids were detected in cell wall (CW I and CW 11) and outer membrane (OM 11) fractions (amounts below 1 % of fraction dry weight). The purified outer membrane fraction (OM 11, Table 1) contained very few peptidoglycan components, due to efficient removal of the peptidoglycan by lyso ...
MagneHis™ Protein Purification System Technical Manual
... Two methods for lysis of bacterial cells using the FastBreak™ Cell Lysis Reagent, 10X, are presented in this section. In Method 1, cells are pelleted, and then the FastBreak™ Cell Lysis Reagent, 10X, diluted to 1X concentration, is added to the cell pellet with DNase I. Alternatively, FastBreak™ Cel ...
... Two methods for lysis of bacterial cells using the FastBreak™ Cell Lysis Reagent, 10X, are presented in this section. In Method 1, cells are pelleted, and then the FastBreak™ Cell Lysis Reagent, 10X, diluted to 1X concentration, is added to the cell pellet with DNase I. Alternatively, FastBreak™ Cel ...
(2016) Target selection during protein quality control. Trends
... via ubiquitin molecules on the substrate. Ribosome-associated quality control (RQC): a protein QC pathway that degrades the partially synthesized nascent polypeptides produced by ribosomes that have stalled during translation elongation. ...
... via ubiquitin molecules on the substrate. Ribosome-associated quality control (RQC): a protein QC pathway that degrades the partially synthesized nascent polypeptides produced by ribosomes that have stalled during translation elongation. ...
Metabolism of RBC
... metabolism. • Genetically determined deficiency of the activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, which produces NADPH, is an important cause of hemolytic anemia. ...
... metabolism. • Genetically determined deficiency of the activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, which produces NADPH, is an important cause of hemolytic anemia. ...
Homework
... glass of warm water. The sugar completely dissolved in the water. Which statements do you agree with? Explain WHY A. The sugar melts. B. The sugar loses mass. C. The sugar turns into water molecules. D. The sugar forms a mixture with the water. E. The sugar can’t be separated from the water. F. The ...
... glass of warm water. The sugar completely dissolved in the water. Which statements do you agree with? Explain WHY A. The sugar melts. B. The sugar loses mass. C. The sugar turns into water molecules. D. The sugar forms a mixture with the water. E. The sugar can’t be separated from the water. F. The ...
Regulation of germ line stem cell homeostasis
... on recent findings pertaining to germ cell development and the relationship between spermatogonial stem cells of the testis and their niche. Development of the male germ line In the mouse, the germ line originates from a small population of primordial germ cells (PGCs), which arise from the pluripot ...
... on recent findings pertaining to germ cell development and the relationship between spermatogonial stem cells of the testis and their niche. Development of the male germ line In the mouse, the germ line originates from a small population of primordial germ cells (PGCs), which arise from the pluripot ...
Mechanical models of gastrulation
... epithelium only one cell thick, whereas other embryos often have thicker gastrula walls. Morphogenesis used to be described mainly in terms of concepts of evolutionary biology. It was only during the past two decades that the effect of physical mechanisms on cells and tissues during gastrulation has ...
... epithelium only one cell thick, whereas other embryos often have thicker gastrula walls. Morphogenesis used to be described mainly in terms of concepts of evolutionary biology. It was only during the past two decades that the effect of physical mechanisms on cells and tissues during gastrulation has ...
Sensory Pathways
... can be aggregated so that they are perceived as a single strong stimulus by the CNS. Integration begins in the sensory cell when a number of separate stimuli are added together to depolarize the membrane sufficiently to generate an action potential. Integration continues during transmission, when ma ...
... can be aggregated so that they are perceived as a single strong stimulus by the CNS. Integration begins in the sensory cell when a number of separate stimuli are added together to depolarize the membrane sufficiently to generate an action potential. Integration continues during transmission, when ma ...
Sample
... i. The coastal areas of the world have a climate that is more moderate than inland areas. j. Some springs contain high amounts of arsenic. k. The Great Salt Lake contains high quantities of mineral solutes. Answer: a. Water is cohesive. b. Water has a high heat of vaporization. c. Water is cohesive. ...
... i. The coastal areas of the world have a climate that is more moderate than inland areas. j. Some springs contain high amounts of arsenic. k. The Great Salt Lake contains high quantities of mineral solutes. Answer: a. Water is cohesive. b. Water has a high heat of vaporization. c. Water is cohesive. ...
structure-tertiary-text
... shows that the information required for the proper folding of a protein resides in its primary structure. ...
... shows that the information required for the proper folding of a protein resides in its primary structure. ...
Optogenetic Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ofMRI
... tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and endtidal CO2 was maintained at physiological levels (~3.5%, 34-38 oC). fMRI scans were performed using a gradientecho (GRE) sequence with spiral readout, 750 ms TR and 12 ...
... tube connected to a ventilator with 1.3-1.5% isoflurane, 35% O2, 65% N2O input gas, and a capnometer. Animal body temperature and endtidal CO2 was maintained at physiological levels (~3.5%, 34-38 oC). fMRI scans were performed using a gradientecho (GRE) sequence with spiral readout, 750 ms TR and 12 ...
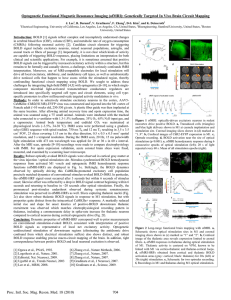
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.