The Influence of Magnesium on Cell Division
... The ability of other divalent metallic ions to activate cell division was determined when inocula of filamentous cells from magnesium-deficient cultures (Cl. welchii, Cl. tertium, Bacillus mycoides, B. vulgatus and B. subtilis var. viscosus) were subcultured in medium M in which the Mg++ was replace ...
... The ability of other divalent metallic ions to activate cell division was determined when inocula of filamentous cells from magnesium-deficient cultures (Cl. welchii, Cl. tertium, Bacillus mycoides, B. vulgatus and B. subtilis var. viscosus) were subcultured in medium M in which the Mg++ was replace ...
Ion Channels and Electrical Activity
... and charged; requires energy to break attractive forces between the ion and the waters. 2) Energy is also required to move a charged highly hydrophilic particle into the highly hydrophobic area of the lipid bilayer that contains the “tails” of the ...
... and charged; requires energy to break attractive forces between the ion and the waters. 2) Energy is also required to move a charged highly hydrophilic particle into the highly hydrophobic area of the lipid bilayer that contains the “tails” of the ...
Cellular Adaptations in Disease
... metabolism controlled by the action of protease enzymes termed CASPASES DNA is ...
... metabolism controlled by the action of protease enzymes termed CASPASES DNA is ...
An immunologist`s perspective on nutrition, immunity, and infectious
... minant of disease resistance and susceptibility. These early responses are dedicated to the containment of the pathogens, holding infections to a level that can be resolved by the ensuing development of acquired immune mechanisms. The innate immune system is a rapidly induced, phylogenetically conse ...
... minant of disease resistance and susceptibility. These early responses are dedicated to the containment of the pathogens, holding infections to a level that can be resolved by the ensuing development of acquired immune mechanisms. The innate immune system is a rapidly induced, phylogenetically conse ...
D. Research Support
... proteomics and analytical chemistry, allows me to bridge both sides of systems biology (the technology required for system-wide measurements and the interpretation of the biology). My laboratory’s current focus is on applying quantitative proteomics to understand many different areas of host-pathoge ...
... proteomics and analytical chemistry, allows me to bridge both sides of systems biology (the technology required for system-wide measurements and the interpretation of the biology). My laboratory’s current focus is on applying quantitative proteomics to understand many different areas of host-pathoge ...
Cellular Adaptations in Disease
... metabolism controlled by the action of protease enzymes termed CASPASES DNA is ...
... metabolism controlled by the action of protease enzymes termed CASPASES DNA is ...
B2 Protein structure and function
... (subunits). These subunits may be identical or different. The same forces which stabilize tertiary structure hold these subunits together. This level of organization called quaternary structure. ...
... (subunits). These subunits may be identical or different. The same forces which stabilize tertiary structure hold these subunits together. This level of organization called quaternary structure. ...
Fig. 9.1. Basic concepts for electrolyte and H2O movements into and
... 2. K+ is pumped into the cell from the peritubular fluid and typically exits to the tubular fluid through an opened K+ channel. When hypokalemia is present, K+ may return to the peritubular fluid via an opened basolateral membrane channel (K+ is recycled). 3. Typically, the Na+-K+-ATPase pump result ...
... 2. K+ is pumped into the cell from the peritubular fluid and typically exits to the tubular fluid through an opened K+ channel. When hypokalemia is present, K+ may return to the peritubular fluid via an opened basolateral membrane channel (K+ is recycled). 3. Typically, the Na+-K+-ATPase pump result ...
Cellular Respiration
... C. Cellular Respiration – occurs only if oxygen is present. 1. Have you ever stopped to think about how the foods you consume on a daily basis are broken down to produce energy? Not only do you eat food on a regular basis, but you usually drink some type of water-based beverage with your meal & you ...
... C. Cellular Respiration – occurs only if oxygen is present. 1. Have you ever stopped to think about how the foods you consume on a daily basis are broken down to produce energy? Not only do you eat food on a regular basis, but you usually drink some type of water-based beverage with your meal & you ...
peptides-text
... Proteins with more than one polypeptide chains are called multimeric proteins; ...
... Proteins with more than one polypeptide chains are called multimeric proteins; ...
msc_botnay_pre_pap1_bl1 - Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open
... cell. The surfaces of plant and bacterial cells exhibit many of these same properties, but they also exhibit a few unique features that are not shared by the cells of animals. Plant cell walls provide a supporting framework for intact plants. In addition to providing mechanical support & strength fo ...
... cell. The surfaces of plant and bacterial cells exhibit many of these same properties, but they also exhibit a few unique features that are not shared by the cells of animals. Plant cell walls provide a supporting framework for intact plants. In addition to providing mechanical support & strength fo ...
Gene Section KSR1 (kinase suppressor of ras 1)
... Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascade. However, there are several published studies that sustain that KSR1 has catalytic activity. KSR1 is recognized as a pseudokinase, since mammalian KSR1 does not possess the lysine responsible for ATP orientation and hydrolysis in the putative kinase domain. This lysine is ...
... Raf/MEK/ERK kinase cascade. However, there are several published studies that sustain that KSR1 has catalytic activity. KSR1 is recognized as a pseudokinase, since mammalian KSR1 does not possess the lysine responsible for ATP orientation and hydrolysis in the putative kinase domain. This lysine is ...
§ 58-10-90
... limitations of this Chapter and the investments in a protected cell or cells may not be taken into account in applying the investment limitations otherwise applicable to the investments of the protected cell company. (c) Assets attributed to a protected cell must be valued at their fair value on the ...
... limitations of this Chapter and the investments in a protected cell or cells may not be taken into account in applying the investment limitations otherwise applicable to the investments of the protected cell company. (c) Assets attributed to a protected cell must be valued at their fair value on the ...
Foundations of Biology
... of a group of genes (i.e., heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e., metallothionein) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression To achieve high levels of expression, several different transcription factors binding to d ...
... of a group of genes (i.e., heat shock proteins) A single gene may be regulated by a number of independent transcription factors (i.e., metallothionein) Eukaryotic regulation does not seem to involve repression To achieve high levels of expression, several different transcription factors binding to d ...
Slide 1
... and causes the insertion of several C9 molecules. bind to this complex and lead to formation of a hole in the membrane resulting in cell lysis. • The lysis of target cell by C5b6789 complex is nonenzymatic and is believed to be due to a physical change in the ...
... and causes the insertion of several C9 molecules. bind to this complex and lead to formation of a hole in the membrane resulting in cell lysis. • The lysis of target cell by C5b6789 complex is nonenzymatic and is believed to be due to a physical change in the ...
Chapter 2: Basic Biological Principles Lesson 2: Structural and
... functions such as obtaining and using energy, responding to the environment, and reproducing. The function a cell must carry out influences its physical features and its internal organization. We also know that different types of cells—even within the same organism—may have their own unique function ...
... functions such as obtaining and using energy, responding to the environment, and reproducing. The function a cell must carry out influences its physical features and its internal organization. We also know that different types of cells—even within the same organism—may have their own unique function ...
Second test Spr 02
... This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the Part I questions on this sheet, below. Answer the Part II questions on the question pages. Please use BLOCK CAPITAL letters like this --- A, B, C, D, E. Not lowercase! ...
... This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth two points. Answer the Part I questions on this sheet, below. Answer the Part II questions on the question pages. Please use BLOCK CAPITAL letters like this --- A, B, C, D, E. Not lowercase! ...
occasional article intracellular protein degradation: from a vague
... conditions, starvation for example, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum membranes, glycogen bodies and other cytoplasmic entities, can also be engulfed by a process called macroautophagy (see, for example, Ref. 12; the different modes of action of the lysosome in digesting extra- and intracellular p ...
... conditions, starvation for example, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum membranes, glycogen bodies and other cytoplasmic entities, can also be engulfed by a process called macroautophagy (see, for example, Ref. 12; the different modes of action of the lysosome in digesting extra- and intracellular p ...
Ataxia Telangiectasia-Mutated–Dependent DNA Damage
... chromatin structure (4). More than 400 mutations in this large gene (62 exons spanning f150 kb) have been documented in ataxia telangiectasia (AT) patients, of which f70% are truncating mutations and 30% are missense mutations (5-8). Although all the mutations affect ATM functions in DNA damage resp ...
... chromatin structure (4). More than 400 mutations in this large gene (62 exons spanning f150 kb) have been documented in ataxia telangiectasia (AT) patients, of which f70% are truncating mutations and 30% are missense mutations (5-8). Although all the mutations affect ATM functions in DNA damage resp ...
Roles of Plant Growth Regulating Substances
... Raton, FL., pp. 35-75 and 119-122. [This article provides extensive information about the concepts of the physiology of flowering.] Bernier G. and Kinet J.M. (1986). The Control of Flower Initiation and Development. In: Plant Growth Substances, 1985 (M. Bopp, ed.), Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 293-3 ...
... Raton, FL., pp. 35-75 and 119-122. [This article provides extensive information about the concepts of the physiology of flowering.] Bernier G. and Kinet J.M. (1986). The Control of Flower Initiation and Development. In: Plant Growth Substances, 1985 (M. Bopp, ed.), Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 293-3 ...
Ch16.Special.Senses
... – Complete receptor cells specialized epithelial cells or small neurons • Monitor most types of special sensory information ...
... – Complete receptor cells specialized epithelial cells or small neurons • Monitor most types of special sensory information ...
advanced placement biology - Freehold Regional High School District
... The AP Biology curriculum emphasizes critical and independent thinking in order to facilitate a “big picture” understanding of biology. This includes a considerable amount of studying, memorizing, and analyzing the structure and function of living organisms. The rigor of the course is equivalent to ...
... The AP Biology curriculum emphasizes critical and independent thinking in order to facilitate a “big picture” understanding of biology. This includes a considerable amount of studying, memorizing, and analyzing the structure and function of living organisms. The rigor of the course is equivalent to ...
Class: Protein functional Annotation and Family Classification
... II. Computational Analysis Beyond Homology ...
... II. Computational Analysis Beyond Homology ...
Wing-beat mechanism of insect revealed by ultrafast X - SPring-8
... the two major contractile proteins in muscle. Their attachment and a subsequent structural change in myosin are believed to cause force generation. The bottom row is related to the most crucial finding in this study, and shows the intensities of two reflections, 111 and 201. A strengthening of 111 a ...
... the two major contractile proteins in muscle. Their attachment and a subsequent structural change in myosin are believed to cause force generation. The bottom row is related to the most crucial finding in this study, and shows the intensities of two reflections, 111 and 201. A strengthening of 111 a ...
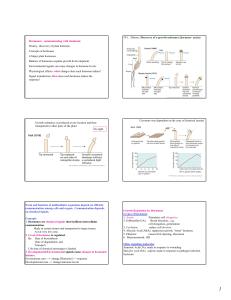
Hormones: communicating with chemicals History
... History- discovery of plant hormone Concepts of hormones 6 Major plant hormones Balance of hormones regulate growth & development. Environmental signals can cause changes in hormone levels. Physiological effects- what changes does each hormone induce? Signal transduction- How does each hormone induc ...
... History- discovery of plant hormone Concepts of hormones 6 Major plant hormones Balance of hormones regulate growth & development. Environmental signals can cause changes in hormone levels. Physiological effects- what changes does each hormone induce? Signal transduction- How does each hormone induc ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.