Endocytosis and Exocytosis
... non-dissolved solid particles into its cytoplasm. In phagocytosis, the cell extends finger-like projections of its cell membrane, called pseudopods, around a piece of solid material outside of the cell. The pseudopods that surround the solid object eventually join to form a vacuole within the cell’s ...
... non-dissolved solid particles into its cytoplasm. In phagocytosis, the cell extends finger-like projections of its cell membrane, called pseudopods, around a piece of solid material outside of the cell. The pseudopods that surround the solid object eventually join to form a vacuole within the cell’s ...
Pathophysiology - mwsu-wiki
... The word patho is derived from Greek word Pathos which means suffering and logos means disclosure or more commonly system of formal study and physio means function of organism. Definition of pathophysiology: It is the systemic study of functional changes in the cell, tissues, and organs altered by t ...
... The word patho is derived from Greek word Pathos which means suffering and logos means disclosure or more commonly system of formal study and physio means function of organism. Definition of pathophysiology: It is the systemic study of functional changes in the cell, tissues, and organs altered by t ...
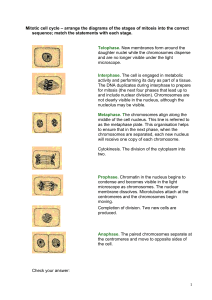
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
answer key
... 6. According to Dang & Semenza, both p53 and MYC have been linked to changes in glycolysis in tumor cells. In your view, which is stronger: the evidence implicating p53 in this, or the evidence implicating MYC? Please cite specific evidence mentioned in the article. [4-5 sentences; 7 points] You cou ...
... 6. According to Dang & Semenza, both p53 and MYC have been linked to changes in glycolysis in tumor cells. In your view, which is stronger: the evidence implicating p53 in this, or the evidence implicating MYC? Please cite specific evidence mentioned in the article. [4-5 sentences; 7 points] You cou ...
The Cell - CoconinoHighSchool
... Cells differ in size, shape, and function The female egg cell is the largest cell in the body & can be seen without a ...
... Cells differ in size, shape, and function The female egg cell is the largest cell in the body & can be seen without a ...
Topic: Types of Cells and Membranes
... between cells and allows for recognition between cells Assists in the transport of molecules across the membrane (like water & sugars) ...
... between cells and allows for recognition between cells Assists in the transport of molecules across the membrane (like water & sugars) ...
TISSUE INJURY
... Surgery – Certain anaesthetic agents cause vasodilatation that restricts the skin’s natural ability to alter the diameter of peripheral blood vessels thus controlling thermoregulation. As a consequence, excess amounts of body heat can evaporate. Post operatively these clients can go into a phase ...
... Surgery – Certain anaesthetic agents cause vasodilatation that restricts the skin’s natural ability to alter the diameter of peripheral blood vessels thus controlling thermoregulation. As a consequence, excess amounts of body heat can evaporate. Post operatively these clients can go into a phase ...
Cell Reproduction
... Cell Division in Eukaryotes • A cell typically goes through stages during its life, growing and developing before it divides into new cells. • The cell cycle is the repeating events that make up the life of a cell ...
... Cell Division in Eukaryotes • A cell typically goes through stages during its life, growing and developing before it divides into new cells. • The cell cycle is the repeating events that make up the life of a cell ...
Cell Division
... cell increases in size, it keeps the same amount of DNA. Eventually the cell will grow too much for the DNA to control all its activities Memory Trick: Think of DNA like a library of books. If a town (cell) is too big, people may have to wait for books! ...
... cell increases in size, it keeps the same amount of DNA. Eventually the cell will grow too much for the DNA to control all its activities Memory Trick: Think of DNA like a library of books. If a town (cell) is too big, people may have to wait for books! ...
DIFFERENTIATION OF T CELLS INDUCED BY
... :~ Figures in this column represent percent of starting cell population induced to express TL and Thy-1 antigens in vitro (for details see Komuro and Boyse, reference 4). The starting population was the " B " layer of mouse spleen cells fractionated on BSA density gradients as before (4) but at the ...
... :~ Figures in this column represent percent of starting cell population induced to express TL and Thy-1 antigens in vitro (for details see Komuro and Boyse, reference 4). The starting population was the " B " layer of mouse spleen cells fractionated on BSA density gradients as before (4) but at the ...
PRKimmel - Revised-EK
... caused. Up until now, it was not known where the bubbles seen during high intensity ultrasound operation are produced in the body. We found the source of the bubbles. Where there are cells that are not entirely enclosed by dense tissue, there will be bubbles. If bubbles are seen in the blood vessels ...
... caused. Up until now, it was not known where the bubbles seen during high intensity ultrasound operation are produced in the body. We found the source of the bubbles. Where there are cells that are not entirely enclosed by dense tissue, there will be bubbles. If bubbles are seen in the blood vessels ...
Chapter 4
... osmosis. • For any cell to survive, it must be in osmotic balance with its environment. • Osmotic balance occurs when movement of water in and out of the cell is equal. ...
... osmosis. • For any cell to survive, it must be in osmotic balance with its environment. • Osmotic balance occurs when movement of water in and out of the cell is equal. ...
Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane
... • Organisms are grouped according to what type of cell they have • Prokaryotes – have cells that do not have a membrane surrounding the nucleus and lack most organelles (unicellular or simple multicellular organisms - Bacteria, cyanobacteria) (pic pg 23) • Eukaryotes- have cells that are usually muc ...
... • Organisms are grouped according to what type of cell they have • Prokaryotes – have cells that do not have a membrane surrounding the nucleus and lack most organelles (unicellular or simple multicellular organisms - Bacteria, cyanobacteria) (pic pg 23) • Eukaryotes- have cells that are usually muc ...
Biology: Assignment #4 Cell Membrane
... Unfortunately, this kind of transport requires the cell to work against the natural direction of diffusion. This causes the cell use energy. One example of this is how nerve cells work. They pump sodium out and pull potassium in. Although they must expend energy in this process, doing so allows them ...
... Unfortunately, this kind of transport requires the cell to work against the natural direction of diffusion. This causes the cell use energy. One example of this is how nerve cells work. They pump sodium out and pull potassium in. Although they must expend energy in this process, doing so allows them ...
Biology of Cancer
... IGF-1, IGF-2, etc. All of the heterotypic interactions needed to maintain normal tissue function may continue to operate within carcinomas. Figure 13.4 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) ...
... IGF-1, IGF-2, etc. All of the heterotypic interactions needed to maintain normal tissue function may continue to operate within carcinomas. Figure 13.4 The Biology of Cancer (© Garland Science 2007) ...
Reprogramming somatic cells without fusion or ethical confusion
... induction of pluripotency translated to a gain in drug resistance. This was established by inserting a bifunctional (selection-reporter) cassette into the mouse Fbx15 gene, which is expressed specifically in mouse ESCs. Thus, growth of drug-resistant colonies with an ESC-like morphology implied repr ...
... induction of pluripotency translated to a gain in drug resistance. This was established by inserting a bifunctional (selection-reporter) cassette into the mouse Fbx15 gene, which is expressed specifically in mouse ESCs. Thus, growth of drug-resistant colonies with an ESC-like morphology implied repr ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... This technique was the gold standard for the treatment of immature necrotic teeth for a long time. In 1993, Torabinejad and his colleagues published first articles about the new bioactive material, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) (2, 3). At the turn of the millennium, the first case reports of apic ...
... This technique was the gold standard for the treatment of immature necrotic teeth for a long time. In 1993, Torabinejad and his colleagues published first articles about the new bioactive material, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) (2, 3). At the turn of the millennium, the first case reports of apic ...
Cytoskeleton 14
... Cilia act as antenna to receive signals for the cell. Usually one/cell. Membrane proteins on cilia transmit molecular signals from the environment of the cell to the interior. Flagella and cilia are similar in ultrastructure. Nine doublets of microtubules make a ring having two single microtuble ...
... Cilia act as antenna to receive signals for the cell. Usually one/cell. Membrane proteins on cilia transmit molecular signals from the environment of the cell to the interior. Flagella and cilia are similar in ultrastructure. Nine doublets of microtubules make a ring having two single microtuble ...
Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate
... media (MSC-CM (exo-)) containing 2% horse serum to induce myogenic differentiation. To examine myogenesis, quantitative real time-PCR assays were performed for the MyoD, myogenin and Myh4. We performed immunocytochemistry for myosin heavy chain using mouse anti F59. Total nuclear numbers were counte ...
... media (MSC-CM (exo-)) containing 2% horse serum to induce myogenic differentiation. To examine myogenesis, quantitative real time-PCR assays were performed for the MyoD, myogenin and Myh4. We performed immunocytochemistry for myosin heavy chain using mouse anti F59. Total nuclear numbers were counte ...
Bio 11 – Test 1 Characteristics of Living Things The Cell
... Be able to label both the plant and animal cell diagrams as on pg.13 in your textbook Review your cell structure/function chart for all the cell parts and organelles Go over your cell questions 1-11 as well as your text ques. From pg.28 ...
... Be able to label both the plant and animal cell diagrams as on pg.13 in your textbook Review your cell structure/function chart for all the cell parts and organelles Go over your cell questions 1-11 as well as your text ques. From pg.28 ...
Name
... 4. What two general classes are cells divided into and what is the classification based upon? 2pts Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic 5. Give a brief description of eukaryotic cell. 2pts They are highly structural and has a nucleus 6. Give a brief description of prokaryotic cells They are simply structural ...
... 4. What two general classes are cells divided into and what is the classification based upon? 2pts Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic 5. Give a brief description of eukaryotic cell. 2pts They are highly structural and has a nucleus 6. Give a brief description of prokaryotic cells They are simply structural ...
ppt4
... To determine if the production of cells in the dentate gyrus are affected by NMDA receptor activation. Animals were injected with a specific noncompetitive NMDA receptor ...
... To determine if the production of cells in the dentate gyrus are affected by NMDA receptor activation. Animals were injected with a specific noncompetitive NMDA receptor ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.