... Metabolites in glycolysis pathway reached isotopic steady state for [1,2-(13)C]glucose within 1.5h, and metabolites in the TCA cycle reached isotopic steady state for [U-(13)C]glutamine within 3h. Combined analysis of multiple data sets produced detailed flux maps at two key metabolic phases, expone ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis? It contains the directions for making protiens What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell? Ribosomes How does the membrane of the cell differ from the nu ...
... How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis? It contains the directions for making protiens What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell? Ribosomes How does the membrane of the cell differ from the nu ...
Plant Cell - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... • Your poem, rap, or song should include information about all the cell organelles and structures and what they do in a cell. • You will turn your rap/poem/ or song in on a piece of paper and will have the option to either perform your piece before or after school for your teacher or in front of the ...
... • Your poem, rap, or song should include information about all the cell organelles and structures and what they do in a cell. • You will turn your rap/poem/ or song in on a piece of paper and will have the option to either perform your piece before or after school for your teacher or in front of the ...
Life is Cellular - Pasadena High School
... *MULTICELLULAR means many-celled! *Remember: MULTI = many. *Plants, fungi, and animals are MULTICELLULAR. *Multicellular cells have many specialized parts & that have specific roles that they are in charge of. *These parts and organs are called organelles. ...
... *MULTICELLULAR means many-celled! *Remember: MULTI = many. *Plants, fungi, and animals are MULTICELLULAR. *Multicellular cells have many specialized parts & that have specific roles that they are in charge of. *These parts and organs are called organelles. ...
Ch7-2CellStructure - Saint Joseph High School
... • Houses most of the DNA, which controls the cell’s functions • Surrounded by a double membrane, called the nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane • The nuclear envelope is made of two lipid bilayers • Why do you think that there are 2? ...
... • Houses most of the DNA, which controls the cell’s functions • Surrounded by a double membrane, called the nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane • The nuclear envelope is made of two lipid bilayers • Why do you think that there are 2? ...
APOPTOSIS AND NECROSIS APOPTOSIS All the cells in our body
... All the cells in our body are highly regulated and not only control the rate of cell division, but also by the rate of cell death. When cells are no longer needed and they become a threat to the organism, they undergo a suicidal programmed cell death or APOPTOSIS. This process involves a specific pr ...
... All the cells in our body are highly regulated and not only control the rate of cell division, but also by the rate of cell death. When cells are no longer needed and they become a threat to the organism, they undergo a suicidal programmed cell death or APOPTOSIS. This process involves a specific pr ...
Name
... Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match. ...
... Directions: Choose a color for each of the parts below and fill in the square with the color of your choice. Color the cell part to match. ...
Link to Lecture 1
... Bacteria versus mitochondria and chloroplasts 1. Similar size as bacteria 2. Reproduction by division into two like bacteria 3. Own DNA that encodes some of their components in the same manner 4. Divide each time the organelle divides 5. Use their organelle’s inner structure and ribosome to transcr ...
... Bacteria versus mitochondria and chloroplasts 1. Similar size as bacteria 2. Reproduction by division into two like bacteria 3. Own DNA that encodes some of their components in the same manner 4. Divide each time the organelle divides 5. Use their organelle’s inner structure and ribosome to transcr ...
Tour Of The Cell
... that has pores for molecular transport. • Chromatin = DNA + protein complex of threadlike fibers that make up the eukaryotic chromosome. • Chromosome = Chromatin fibers condense into visible chromosomes during cell division. • Nucleolus = rRNA synthesized and formed into ribosomes ...
... that has pores for molecular transport. • Chromatin = DNA + protein complex of threadlike fibers that make up the eukaryotic chromosome. • Chromosome = Chromatin fibers condense into visible chromosomes during cell division. • Nucleolus = rRNA synthesized and formed into ribosomes ...
Learning objectives
... transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advanta ...
... transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advanta ...
Chapter 6 learning objectives
... transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advanta ...
... transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advanta ...
Chapter Six
... transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advanta ...
... transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are both upper and lower limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advanta ...
Identify each eukaryotic organelle and describe its function.
... converts food energy into energy the cell can use (ATP); the ...
... converts food energy into energy the cell can use (ATP); the ...
File
... are the cells. The dark line surrounding each rectangle is an organelle called the cell wall. Function: Cell walls offer structural support. They let each cell fill up with more water without bursting. This keeps the cells “full” and upright. Since plants have no skeleton, they use turgor pressure ( ...
... are the cells. The dark line surrounding each rectangle is an organelle called the cell wall. Function: Cell walls offer structural support. They let each cell fill up with more water without bursting. This keeps the cells “full” and upright. Since plants have no skeleton, they use turgor pressure ( ...
BIO208 Bacterial Genetics Worksheet 1 1. Using standard bacterial
... 2. Is strain "a" in question #1 prototroph or an auxotroph? Strain "b"? (Assume the strains are wild type for all genes but the one in question). 3. Describe 5 steps involved in the lytic life cycle of bacteriophages. 4. Fill in Transformation Transduction Conjugation _______________a. naked DNA is ...
... 2. Is strain "a" in question #1 prototroph or an auxotroph? Strain "b"? (Assume the strains are wild type for all genes but the one in question). 3. Describe 5 steps involved in the lytic life cycle of bacteriophages. 4. Fill in Transformation Transduction Conjugation _______________a. naked DNA is ...
cell - Nozha Language Schools
... 3- A gelatinous liquid that Surrounds the nucleus of the living cell and contain some structures. ( cytoplasm ) 4- A vacuole in the plant cell. ( sap vacuole ) 5- A group of organs that work together. ( systems ) 6- A unicellular organism used in making bread and alcohol.( yeast fungus ) 7- Small or ...
... 3- A gelatinous liquid that Surrounds the nucleus of the living cell and contain some structures. ( cytoplasm ) 4- A vacuole in the plant cell. ( sap vacuole ) 5- A group of organs that work together. ( systems ) 6- A unicellular organism used in making bread and alcohol.( yeast fungus ) 7- Small or ...
Appendix B6 Lyticase-based cell lysis protocol of assay for 96 well plates
... After incubation with lyticase, 100 µl of 0.01% triton X100 solution in H2O is added in each well and incubated for 15 min at room temperature. This hypo-osmotic shock is sufficient for a complete lysis of yeast cells but a freezing/thaw cycle at –80°C can be performed to obtain complete cell lysis ...
... After incubation with lyticase, 100 µl of 0.01% triton X100 solution in H2O is added in each well and incubated for 15 min at room temperature. This hypo-osmotic shock is sufficient for a complete lysis of yeast cells but a freezing/thaw cycle at –80°C can be performed to obtain complete cell lysis ...
The Cell - Structure - Jefferson County School Board
... meet the criteria for science). Cognitive Complexity: High ...
... meet the criteria for science). Cognitive Complexity: High ...
Commercial uses of cells
... respiration in yeast. • Describe the role of carbon dioxide in bread making • Write a simple word equation to summarise the process of malting in barley grains about to be used in the brewing of beer. • Copy the following sentences choosing the correct answer from each choice in brackets: – During t ...
... respiration in yeast. • Describe the role of carbon dioxide in bread making • Write a simple word equation to summarise the process of malting in barley grains about to be used in the brewing of beer. • Copy the following sentences choosing the correct answer from each choice in brackets: – During t ...
Maurie Perl 212-365-7443 [email protected] Joint Research
... for NYSCF,” NYSCF CEO and co-founder, Susan L. Solomon noted. “This is a pioneering opportunity to use blood, the most accessible way to look at patients’ cells, on a large scale to generate personalized stem cell lines in the laboratory.” “Q-State’s mission is to harness advances in stem cell and o ...
... for NYSCF,” NYSCF CEO and co-founder, Susan L. Solomon noted. “This is a pioneering opportunity to use blood, the most accessible way to look at patients’ cells, on a large scale to generate personalized stem cell lines in the laboratory.” “Q-State’s mission is to harness advances in stem cell and o ...
Quick Review
... 1. What is DNA replication? During which stage of the cell cycle does it occur? 2. During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell? 3. What occurs during cytokinesis? ...
... 1. What is DNA replication? During which stage of the cell cycle does it occur? 2. During which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell? 3. What occurs during cytokinesis? ...
Carcinogenesis
... • Characteristic double allelic activity: – both alleles must be damaged for malignant activity – retinoblastoma follows “two hit” model ...
... • Characteristic double allelic activity: – both alleles must be damaged for malignant activity – retinoblastoma follows “two hit” model ...
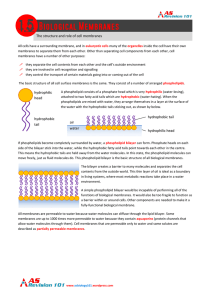
The structure and role of cell membranes hydrophilic head
... side of the bilayer stick into the water, while the hydrophobic fatty acid tails point towards each other in the centre. This means the hydrophobic tails are held away from the water molecules. In this state, the phospholipid molecules can move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid b ...
... side of the bilayer stick into the water, while the hydrophobic fatty acid tails point towards each other in the centre. This means the hydrophobic tails are held away from the water molecules. In this state, the phospholipid molecules can move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid b ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.