•Eukaryotic cells are about 1000 times larger than bacteria cells and
... DNA. Viruses have evolved a way of encapsulating and delivering their genes to human cells in a pathogenic manner. Scientists have tried to take advantage of this capability and manipulate the virus genome to remove disease-causing genes and insert therapeutic genes. Target cells such as the patient ...
... DNA. Viruses have evolved a way of encapsulating and delivering their genes to human cells in a pathogenic manner. Scientists have tried to take advantage of this capability and manipulate the virus genome to remove disease-causing genes and insert therapeutic genes. Target cells such as the patient ...
What is a Cell
... For ease of study, we divide the cell into three main parts: 1. plasma membrane 2. cytoplasm 3. nucleus ...
... For ease of study, we divide the cell into three main parts: 1. plasma membrane 2. cytoplasm 3. nucleus ...
A View of the Cell - OCVTS.org | Ocean County Vocational
... • Structure: Center of the Cell • Function : Control center of the cell; Contains the direction to make proteins and other important molecules (DNA). • Prokaryotes: DNA in cytoplasm • Plant and animal cells ...
... • Structure: Center of the Cell • Function : Control center of the cell; Contains the direction to make proteins and other important molecules (DNA). • Prokaryotes: DNA in cytoplasm • Plant and animal cells ...
File
... at which the DNA can bind with spindle proteins c) the array of vesicles that will form between two dividing nuclei and give rise to the metaphase plate d) the ring of actin microfilaments that will cause the appearance of the cleavage furrow ...
... at which the DNA can bind with spindle proteins c) the array of vesicles that will form between two dividing nuclei and give rise to the metaphase plate d) the ring of actin microfilaments that will cause the appearance of the cleavage furrow ...
What is a stem cell?
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Neurons
... An action potential occurs when there is a reversal of the normal resting potential (goes from negative to positive). Also called depolarization. Depolarization occurs due to the opening of voltage gated Na channel allowing the influx of Na. Repolarization of the cell is due to Potassium efflux. I ...
... An action potential occurs when there is a reversal of the normal resting potential (goes from negative to positive). Also called depolarization. Depolarization occurs due to the opening of voltage gated Na channel allowing the influx of Na. Repolarization of the cell is due to Potassium efflux. I ...
Cell Test 2.1-2.3 IB SL 2013 VA KEY - IB-Biology
... have cholesterol in the cell membrane, plant cells do not; plant cells generally have a fixed shape / more regular whereas animal cells are more rounded; ...
... have cholesterol in the cell membrane, plant cells do not; plant cells generally have a fixed shape / more regular whereas animal cells are more rounded; ...
Cell division
... If you would like more information on factors that can lead to cancer read the article “How Cancer Arises” posted under assignments on blackboard. This is optional. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... If you would like more information on factors that can lead to cancer read the article “How Cancer Arises” posted under assignments on blackboard. This is optional. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
CELL DIVISION Mitosis
... – Proto-oncogenes – produce proteins that turn on cell division – Mutations in proto-oncogenes (now called oncogenes) may cause these genes to stay turned on and produce excess growth stimulating proteins resulting in uncontrolled cell division ...
... – Proto-oncogenes – produce proteins that turn on cell division – Mutations in proto-oncogenes (now called oncogenes) may cause these genes to stay turned on and produce excess growth stimulating proteins resulting in uncontrolled cell division ...
Cell Boundaries
... cell surrounds and takes in material from environment. Material does not pass through the membrane; instead, it is engulfed and closed by a portion of membrane and cytoplasm. ...
... cell surrounds and takes in material from environment. Material does not pass through the membrane; instead, it is engulfed and closed by a portion of membrane and cytoplasm. ...
Cells - Madison County Schools
... There are 11 main organ systems. • The organs in the organ system depend on each other. If any part of the system fails, the whole system is affected. And failure of one organ system can affect other organ systems. • Main organ systems : integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, nervo ...
... There are 11 main organ systems. • The organs in the organ system depend on each other. If any part of the system fails, the whole system is affected. And failure of one organ system can affect other organ systems. • Main organ systems : integumentary system, skeletal system, muscular system, nervo ...
student Presentation
... covering which separates the contents of the cell from its external environment & gives separate identity to the cell this covering is called plasma membrane. It is a living, extremely delicate elastic membrane of about ...
... covering which separates the contents of the cell from its external environment & gives separate identity to the cell this covering is called plasma membrane. It is a living, extremely delicate elastic membrane of about ...
Chapter 5-3
... • “Gate-keeper”- helps regulate what enters and leaves the cell • __________ process by which a stable internal environment is kept ...
... • “Gate-keeper”- helps regulate what enters and leaves the cell • __________ process by which a stable internal environment is kept ...
3.1 Cell Theory
... • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
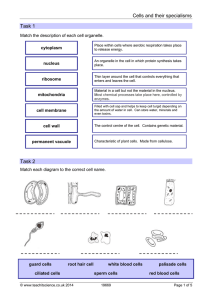
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
down the concentration gradient
... concentration gradient is referred to as Diffusion. • The movement of H20 across a selectively permeable membrane with the concentration gradient is referred to as Osmosis. ...
... concentration gradient is referred to as Diffusion. • The movement of H20 across a selectively permeable membrane with the concentration gradient is referred to as Osmosis. ...
Cell boundaries
... 2 of the ways this energy is used are: 1 – Small molecules are “pumped” across a membrane by transport proteins 2 – Larger molecules are moved across the membrane using endocytosis and exocytosis ...
... 2 of the ways this energy is used are: 1 – Small molecules are “pumped” across a membrane by transport proteins 2 – Larger molecules are moved across the membrane using endocytosis and exocytosis ...
Class Notes
... across cell membranes does not require the cell to use energy. A special name for diffusion of water! Water molecules (fast and small) pass through the cell’s selectively permeable membrane The solute molecule is too large to pass -- only the water diffuses until equilibrium is reached. Large molecu ...
... across cell membranes does not require the cell to use energy. A special name for diffusion of water! Water molecules (fast and small) pass through the cell’s selectively permeable membrane The solute molecule is too large to pass -- only the water diffuses until equilibrium is reached. Large molecu ...
midterm exam review
... Draw the stages of mitosis and tell what occurs during each stage. Draw the stages of meiosis (I and II) and tell what occurs in each stage. When does crossing over occur? Why is it important? Define gametogenesis. How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ? Where do each occur? What do eac ...
... Draw the stages of mitosis and tell what occurs during each stage. Draw the stages of meiosis (I and II) and tell what occurs in each stage. When does crossing over occur? Why is it important? Define gametogenesis. How do spermatogenesis and oogenesis differ? Where do each occur? What do eac ...
Diffusion and Osmosis Cells need a way to move water molecule
... A. molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration B. When the molecules are spread out evenly, diffusion stops because there is no longer a concentration gradient concentration gradient: the difference between the concentration of a particular molecule in one area ...
... A. molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration B. When the molecules are spread out evenly, diffusion stops because there is no longer a concentration gradient concentration gradient: the difference between the concentration of a particular molecule in one area ...
Slide 1 - Simpson
... the double-layered membrane enclosing the nucleus of a cell. Contains pores which allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus (such as RNA) ...
... the double-layered membrane enclosing the nucleus of a cell. Contains pores which allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus (such as RNA) ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.