Overview - Hadley School for the Blind
... Science is very much a part of your everyday life. Whether you consider the basic electrical bulb or cutting-edge developments in agriculture and medicine, you soon realize that science is all around you. This course discusses the various areas of science, such as life science, physical science, and ...
... Science is very much a part of your everyday life. Whether you consider the basic electrical bulb or cutting-edge developments in agriculture and medicine, you soon realize that science is all around you. This course discusses the various areas of science, such as life science, physical science, and ...
You Know You`re a Plant if You
... The large vacuole is where plant cells stores water, waste, and food. The vacuole can take up more than one-third of the whole cell, but there are other important parts as well. Think about the cell as a building again. Each one needs a place to make power so it will be warm in the winter and cool i ...
... The large vacuole is where plant cells stores water, waste, and food. The vacuole can take up more than one-third of the whole cell, but there are other important parts as well. Think about the cell as a building again. Each one needs a place to make power so it will be warm in the winter and cool i ...
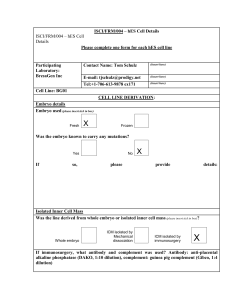
ISCI/FRM/004 – hES Cell Details
... BG01 hESC were originally isolated on C57/BL6 MEFs. Subsequently they have been passaged on ICR or FVB strain MEFs. Within the timepoints of the ISCI work, only FVB MEFs were used ...
... BG01 hESC were originally isolated on C57/BL6 MEFs. Subsequently they have been passaged on ICR or FVB strain MEFs. Within the timepoints of the ISCI work, only FVB MEFs were used ...
Active Transport
... supply of metabolic energy may be spent maintaining these processes. Because active transport mechanisms depend on cellular metabolism for energy, they are sensitive to many metabolic poisons that interfere with the supply of ATP. Two mechanisms exist for the transport of small-molecular weight mate ...
... supply of metabolic energy may be spent maintaining these processes. Because active transport mechanisms depend on cellular metabolism for energy, they are sensitive to many metabolic poisons that interfere with the supply of ATP. Two mechanisms exist for the transport of small-molecular weight mate ...
Section 10-2 Cell Division 3 reasons why cells divide instead of
... Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside the cell. External Regulators Proteins that respond to events outside the cell are called external regulators. External regulators direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. Growth factors ...
... Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside the cell. External Regulators Proteins that respond to events outside the cell are called external regulators. External regulators direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. Growth factors ...
Cell Cycle Notes
... two identical sister chromatids. When the cell divides, the chromatids separate from each other. One chromatid goes to each of the two new cells. Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the centromere. ...
... two identical sister chromatids. When the cell divides, the chromatids separate from each other. One chromatid goes to each of the two new cells. Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the centromere. ...
Cell Membranes and Transport
... a.Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.Structure is related to its function! Outside of cell Proteins ...
... a.Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.Structure is related to its function! Outside of cell Proteins ...
Cell Transport
... How do cells get what they need and get rid of what they need to get rid of? Objective: - We will be able to describe the different processes that allow movement across the cell membrane, including: diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. ...
... How do cells get what they need and get rid of what they need to get rid of? Objective: - We will be able to describe the different processes that allow movement across the cell membrane, including: diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. ...
Two Kinds of Cells Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea
... describing its physical environment, and explaining how it survives in its environment. ...
... describing its physical environment, and explaining how it survives in its environment. ...
Plant Cell Anatomy
... starchy plants like tubers and fruits. ATP - ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate; it is a high-energy molecule used for energy storage by organisms. In plant cells, ATP is produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts. cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds t ...
... starchy plants like tubers and fruits. ATP - ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate; it is a high-energy molecule used for energy storage by organisms. In plant cells, ATP is produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts. cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds t ...
Idioblastic mucilage - Modern Phytomorphology
... Idioblastic cells are individual cells which prominently differ from their neighbouring cells in size, content, ontogeny and metabolism. They are considered as secretory structures composed of one cell only. This fact stresses their functional complexity compared to the multicellular glands. Idiobla ...
... Idioblastic cells are individual cells which prominently differ from their neighbouring cells in size, content, ontogeny and metabolism. They are considered as secretory structures composed of one cell only. This fact stresses their functional complexity compared to the multicellular glands. Idiobla ...
Cells!!!!
... retaining moisture, and helps the cell adhere to surfaces and nutrients. • Cell Wall - Outer covering of most cells that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. • Cytosol - A gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic m ...
... retaining moisture, and helps the cell adhere to surfaces and nutrients. • Cell Wall - Outer covering of most cells that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. • Cytosol - A gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic m ...
Microbiology – Alcamp Lecture: Bacterial Structures
... • Examples: – __________ _________ – __________ – __________ ...
... • Examples: – __________ _________ – __________ – __________ ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... B(4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells. The student is expected to: B.4A compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells B(10) Science con ...
... B(4) Science concepts. The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are different from cells. The student is expected to: B.4A compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells B(10) Science con ...
Cell Transport and Division
... from phase to phase during the cell cycle • Some enzymes work to replicate DNA, some begin cell division, and others control the rest of the cell cycle ...
... from phase to phase during the cell cycle • Some enzymes work to replicate DNA, some begin cell division, and others control the rest of the cell cycle ...
An Interactive Lecture Guide to help you understand THE
... PASSIVE TRANSPORT involves diffusion without any input of energy. It moves substances down their concentration gradients. Three types: DIFFUSION-The natural movement of small molecules from high to low concentration OSMOSIS- The diffusion of water FACILITATED DIFFUSION requires the help of trans ...
... PASSIVE TRANSPORT involves diffusion without any input of energy. It moves substances down their concentration gradients. Three types: DIFFUSION-The natural movement of small molecules from high to low concentration OSMOSIS- The diffusion of water FACILITATED DIFFUSION requires the help of trans ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Move your mouse around on the diagram of the cell diagram and the organelle name will appear in the window. When you are done with an organelle, click on “Return to Cell Diagram” (bottom of pict ...
... Move your mouse around on the diagram of the cell diagram and the organelle name will appear in the window. When you are done with an organelle, click on “Return to Cell Diagram” (bottom of pict ...
General Biology Notes 9 The Cell Membrane (pages 204, 205, 208
... 3. Helps maintain the cell size and _____________ C. In order to fulfill its functions, the cell membrane must be _________________ in water (so it doesn’t dissolve) but it must be willing to __________________ with water, (so it doesn’t separate from water like _________ does) D. The membrane is ab ...
... 3. Helps maintain the cell size and _____________ C. In order to fulfill its functions, the cell membrane must be _________________ in water (so it doesn’t dissolve) but it must be willing to __________________ with water, (so it doesn’t separate from water like _________ does) D. The membrane is ab ...
Export To Word
... Engage: What object, event, or questions will the teacher use to trigger the students' curiosity and engage them in the concepts? Students should be given the pre-test at the beginning of class. The teacher can show pictures of different organisms, including koalas, dandelions, and spirillum, and as ...
... Engage: What object, event, or questions will the teacher use to trigger the students' curiosity and engage them in the concepts? Students should be given the pre-test at the beginning of class. The teacher can show pictures of different organisms, including koalas, dandelions, and spirillum, and as ...
Lab #2 – Skin Cells - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Human Biology 11 – Dalesandro Lab #2 – Skin Cells ...
... Human Biology 11 – Dalesandro Lab #2 – Skin Cells ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.