2014 Quiz IA Answers
... Boundaries separating the internal environment from the outside world Mechanisms that permit cells to ingest food Biochemical pathways that permit energy stored in complex molecules to be released The capacity to reproduce Ability to respond to stimuli in the natural world ...
... Boundaries separating the internal environment from the outside world Mechanisms that permit cells to ingest food Biochemical pathways that permit energy stored in complex molecules to be released The capacity to reproduce Ability to respond to stimuli in the natural world ...
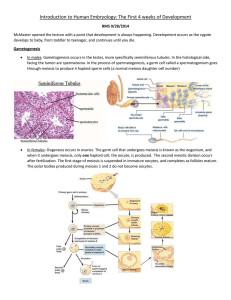
Introduction to Human Embryology: The First 4 weeks of Development
... egg to be released from a mature follicle in the ovaries and travels down the oviduct in hopes of being fertilized. Lastly, the luteal phase involves the corpus luteum, the ruptured follicle from which the ovum emerged, begins secreting progesterone to continue to keep the uterus in good shape for i ...
... egg to be released from a mature follicle in the ovaries and travels down the oviduct in hopes of being fertilized. Lastly, the luteal phase involves the corpus luteum, the ruptured follicle from which the ovum emerged, begins secreting progesterone to continue to keep the uterus in good shape for i ...
Lesson 2 - Leon County Schools
... What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements and see if you have changed your mind. ...
... What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements and see if you have changed your mind. ...
CELL ORGANELLE ANALOGY PROJECT RUBERIC
... CELL ORGANELLE ANALOGY PROJECT Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your ...
... CELL ORGANELLE ANALOGY PROJECT Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your ...
Cells, Tissues and Organs
... All organisms are made of small building blocks called cells. Your body contains over 3 billion of them. Most cells are very small and can be seen only with a microscope. However some cells, such as birds’ eggs, are large enough to be seen with your eye. The emu egg is the largest single cell of all ...
... All organisms are made of small building blocks called cells. Your body contains over 3 billion of them. Most cells are very small and can be seen only with a microscope. However some cells, such as birds’ eggs, are large enough to be seen with your eye. The emu egg is the largest single cell of all ...
From a Cell to an Organism Levels of Organization
... What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements and see if you have changed your mind. ...
... What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements and see if you have changed your mind. ...
word version
... ____ 13. Cells in a living thing undergo division at different rates based on a. the amount of ATP present. c. their particular function. b. the size of the nucleus. d. their size. ____ 14. Why must a cell replicate its DNA prior to mitosis? a. each cell needs 2 copies of DNA b. each cell formed in ...
... ____ 13. Cells in a living thing undergo division at different rates based on a. the amount of ATP present. c. their particular function. b. the size of the nucleus. d. their size. ____ 14. Why must a cell replicate its DNA prior to mitosis? a. each cell needs 2 copies of DNA b. each cell formed in ...
Ch 7 - Cell Parts
... transports materials throughout the cytoplasm? 5. What part of the cell has a cis and a trans face? ...
... transports materials throughout the cytoplasm? 5. What part of the cell has a cis and a trans face? ...
PLANKTON
... • Reproduction is asexual, no sexual reproduction, in contrast to other algae • Wide-spread distribution - freshwater, marine, terrestrial and symbiotic relationships • No flagellated cells, two main groupings based on filamentous nature, which is further divided by the presence or absence of akinet ...
... • Reproduction is asexual, no sexual reproduction, in contrast to other algae • Wide-spread distribution - freshwater, marine, terrestrial and symbiotic relationships • No flagellated cells, two main groupings based on filamentous nature, which is further divided by the presence or absence of akinet ...
6CO2 + 6H2O ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ C6H12O6 + 6O2
... • Reproduction is asexual, no sexual reproduction, in contrast to other algae • Wide-spread distribution - freshwater, marine, terrestrial and symbiotic relationships • No flagellated cells, two main groupings based on filamentous nature, which is further divided by the presence or absence of akinet ...
... • Reproduction is asexual, no sexual reproduction, in contrast to other algae • Wide-spread distribution - freshwater, marine, terrestrial and symbiotic relationships • No flagellated cells, two main groupings based on filamentous nature, which is further divided by the presence or absence of akinet ...
Comparing plant and animal cells
... Comparing plant and animal cells 5 minutes Students start by looking at a mongoose in a natural setting, so both an animal and a plant are visible. They are prompted to think about how animals and plants differ in their behaviour. It would be good to get students to brainstorm their ideas about all ...
... Comparing plant and animal cells 5 minutes Students start by looking at a mongoose in a natural setting, so both an animal and a plant are visible. They are prompted to think about how animals and plants differ in their behaviour. It would be good to get students to brainstorm their ideas about all ...
- Google Sites
... as much information as you can remember. (What cell types use each process? What organelle? When does each occur? Reactants? Products? Etc.) ...
... as much information as you can remember. (What cell types use each process? What organelle? When does each occur? Reactants? Products? Etc.) ...
Overview - Hadley School for the Blind
... Science is very much a part of your everyday life. Whether you consider the basic electrical bulb or cutting-edge developments in agriculture and medicine, you soon realize that science is all around you. This course discusses the various areas of science, such as life science, physical science, and ...
... Science is very much a part of your everyday life. Whether you consider the basic electrical bulb or cutting-edge developments in agriculture and medicine, you soon realize that science is all around you. This course discusses the various areas of science, such as life science, physical science, and ...
Overview - Hadley School for the Blind
... 21. Imagine an animal cell as a city. Consider the parts of a city: the land on which it is built, the city’s border, and government offices or a city hall. Other components are the various stores, gas stations, and places of business, and the people who live and work in the city. Compare five part ...
... 21. Imagine an animal cell as a city. Consider the parts of a city: the land on which it is built, the city’s border, and government offices or a city hall. Other components are the various stores, gas stations, and places of business, and the people who live and work in the city. Compare five part ...
Active Transport
... supply of metabolic energy may be spent maintaining these processes. Because active transport mechanisms depend on cellular metabolism for energy, they are sensitive to many metabolic poisons that interfere with the supply of ATP. Two mechanisms exist for the transport of small-molecular weight mate ...
... supply of metabolic energy may be spent maintaining these processes. Because active transport mechanisms depend on cellular metabolism for energy, they are sensitive to many metabolic poisons that interfere with the supply of ATP. Two mechanisms exist for the transport of small-molecular weight mate ...
You Know You`re a Plant if You
... The large vacuole is where plant cells stores water, waste, and food. The vacuole can take up more than one-third of the whole cell, but there are other important parts as well. Think about the cell as a building again. Each one needs a place to make power so it will be warm in the winter and cool i ...
... The large vacuole is where plant cells stores water, waste, and food. The vacuole can take up more than one-third of the whole cell, but there are other important parts as well. Think about the cell as a building again. Each one needs a place to make power so it will be warm in the winter and cool i ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • The continuity of life from one cell to another is based on the reproduction of cells via cell division. • This division process occurs as part of the cell cycle, the life of a cell from its origin in the division of a parent cell until its own division into two. ...
... • The continuity of life from one cell to another is based on the reproduction of cells via cell division. • This division process occurs as part of the cell cycle, the life of a cell from its origin in the division of a parent cell until its own division into two. ...
chapter 2-6: Active Transport and Endocytosis
... third view, the membrane has pinched off from the surface membrane and is now a vesicle (K). The structure of the vesicle is identical to that of the plasma membrane, and as you can see, it contains the particles. The materials in this vesicle will soon be broken down by enzymes that are derived fro ...
... third view, the membrane has pinched off from the surface membrane and is now a vesicle (K). The structure of the vesicle is identical to that of the plasma membrane, and as you can see, it contains the particles. The materials in this vesicle will soon be broken down by enzymes that are derived fro ...
Stem cells
... • While this unit will be a bit more of the biological side of things, it’s also good to know that we’ve got a solid background from those previous ...
... • While this unit will be a bit more of the biological side of things, it’s also good to know that we’ve got a solid background from those previous ...
Section 10-2 Cell Division 3 reasons why cells divide instead of
... Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside the cell. External Regulators Proteins that respond to events outside the cell are called external regulators. External regulators direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. Growth factors ...
... Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside the cell. External Regulators Proteins that respond to events outside the cell are called external regulators. External regulators direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. Growth factors ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.