Chapter 2
... themselves for long periods of time by cell division • in contrast, specialized cells (liver cells, muscle cells, etc..) have a shorter life span • May be transformed into a specialized cell (ex. Pancreatic cell that is capable of producing insulin) Adult Stem Cells – undifferentiated, and can poten ...
... themselves for long periods of time by cell division • in contrast, specialized cells (liver cells, muscle cells, etc..) have a shorter life span • May be transformed into a specialized cell (ex. Pancreatic cell that is capable of producing insulin) Adult Stem Cells – undifferentiated, and can poten ...
Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Human Reproduction
... Diploid (somatic cell) – A cell consisting of homologous chromosomes . In humans, this cell has 46 chromosomes. One chromosome of a pair came from the mother and one from the father. All cells in the human body are diploid except sex cells. Haploid (gamete) – A cell that does not contain chromosom ...
... Diploid (somatic cell) – A cell consisting of homologous chromosomes . In humans, this cell has 46 chromosomes. One chromosome of a pair came from the mother and one from the father. All cells in the human body are diploid except sex cells. Haploid (gamete) – A cell that does not contain chromosom ...
Cells
... There are two main types of cells. Eukaryotic cells are cells with organelles that have a membrane around them. You will find out more about organelles below. Plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have organelles with membranes around them. Bacter ...
... There are two main types of cells. Eukaryotic cells are cells with organelles that have a membrane around them. You will find out more about organelles below. Plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have organelles with membranes around them. Bacter ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... and enjoy myself in the local pubs at night. As a young man I loved science! I had lots of questions about science, but without any proof, nobody would pay me for my ideas. Due to my passion to discover and create… not that I am bragging or anything… I left behind many contributions to science from ...
... and enjoy myself in the local pubs at night. As a young man I loved science! I had lots of questions about science, but without any proof, nobody would pay me for my ideas. Due to my passion to discover and create… not that I am bragging or anything… I left behind many contributions to science from ...
Cells - Avon Community School Corporation
... › Cell/plasma membrane a membrane which encloses to cell Serves to protect cell from pathogens and permit molecules to pass into cell ...
... › Cell/plasma membrane a membrane which encloses to cell Serves to protect cell from pathogens and permit molecules to pass into cell ...
April 22, 2009
... Will derived cells be histocompatible with each individual? ✤ short term: immune suppression or tolerance induction ✤ solution: ✤ therapeutic cloning: isolate somatic nucleus from patient and grow in oocyte. embryo is genetically identical to patient ✤ stem cell line modified by homologous recombina ...
... Will derived cells be histocompatible with each individual? ✤ short term: immune suppression or tolerance induction ✤ solution: ✤ therapeutic cloning: isolate somatic nucleus from patient and grow in oocyte. embryo is genetically identical to patient ✤ stem cell line modified by homologous recombina ...
B4 Diffusion and osmosis
... Animal cells react in the same way as plant cells do towards water loss and water intake. When too much water is lost, animal cells will shrink and collapse. When too much water enters an animal cell, the cell will also swell up. Unlike plant cells, animal cells (like red blood cells) do not have a ...
... Animal cells react in the same way as plant cells do towards water loss and water intake. When too much water is lost, animal cells will shrink and collapse. When too much water enters an animal cell, the cell will also swell up. Unlike plant cells, animal cells (like red blood cells) do not have a ...
The Cell - myndrs.com
... Put carbohydrate chains (labels) on the packages of proteins so that specific cells recognize them once they are released in the blood. Makes lysosomes ...
... Put carbohydrate chains (labels) on the packages of proteins so that specific cells recognize them once they are released in the blood. Makes lysosomes ...
S3 Biology Revision
... Base pairing rules: Adenine always pairs with Thymine. Guanine always pairs with Cytosine. ...
... Base pairing rules: Adenine always pairs with Thymine. Guanine always pairs with Cytosine. ...
The Immune System Concept 43.1- In innate immunity, recognition
... Peptides and proteins work to fight and destroy ...
... Peptides and proteins work to fight and destroy ...
1901 Plant Cell Model GUD
... oxygen and nutrients into energy for the cell to use. I. Ribosome – Some ribosomes are attached to the rough ER and are composed of RNA. J. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) – The smooth ER transports materials throughout the cell, produces membrane proteins and digests lipids. K. Rough Endop ...
... oxygen and nutrients into energy for the cell to use. I. Ribosome – Some ribosomes are attached to the rough ER and are composed of RNA. J. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) – The smooth ER transports materials throughout the cell, produces membrane proteins and digests lipids. K. Rough Endop ...
Plants and animals are made up of millions of tiny parts called cells
... out all the processes of life. 2. Cell membrane: a covering that surrounds and protects a cell. It controls what enters and leaves the cell. 3. Cytoplasm: a thick fluid that fills most of the space inside a cell. 4. Nucleus: the “brain” of the cell. Directs the cell’s ...
... out all the processes of life. 2. Cell membrane: a covering that surrounds and protects a cell. It controls what enters and leaves the cell. 3. Cytoplasm: a thick fluid that fills most of the space inside a cell. 4. Nucleus: the “brain” of the cell. Directs the cell’s ...
Microorganism Study Guide
... out all the processes of life. 2. Cell membrane: a covering that surrounds and protects a cell. It controls what enters and leaves the cell. 3. Cytoplasm: a thick fluid that fills most of the space inside a cell. 4. Nucleus: the “brain” of the cell. Directs the cell’s ...
... out all the processes of life. 2. Cell membrane: a covering that surrounds and protects a cell. It controls what enters and leaves the cell. 3. Cytoplasm: a thick fluid that fills most of the space inside a cell. 4. Nucleus: the “brain” of the cell. Directs the cell’s ...
Critical roles of RNA helicase DDX3 and its interactions with eIF4E
... post-transfection, cells were left untreated or stressed with 1 M sorbitol for 1 h. After recovery in normal medium for 24 h, cell viability was assessed by cell counting and normalized to that of the untreated control plasmid transfectants. *** P < 0.001. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydroge ...
... post-transfection, cells were left untreated or stressed with 1 M sorbitol for 1 h. After recovery in normal medium for 24 h, cell viability was assessed by cell counting and normalized to that of the untreated control plasmid transfectants. *** P < 0.001. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydroge ...
Types of cells and organelles
... • Microfilaments are threadlike & made of ACTIN • Microtubules are tubelike & made of TUBULIN ...
... • Microfilaments are threadlike & made of ACTIN • Microtubules are tubelike & made of TUBULIN ...
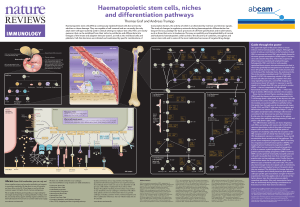
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... (TSPs) seed the thymus and become committed to the T-cell lineage (lower right panel). In the thymus, the cells travel from the cortex through the subcapsular zone to the medulla, encountering different epithelial niches that guide them through several developmental stages. Finally, CD4+ and CD8+ T ...
... (TSPs) seed the thymus and become committed to the T-cell lineage (lower right panel). In the thymus, the cells travel from the cortex through the subcapsular zone to the medulla, encountering different epithelial niches that guide them through several developmental stages. Finally, CD4+ and CD8+ T ...
Learning Targets
... Structure Cell Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure ...
... Structure Cell Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure ...
CH 2.1 Cell Transportation PowerPoint
... Water flows to side of the membrane where water has low concentration. (High to Low) Water diffuses until it has equal concentration on both sides of the membrane Therefore, an unequal distribution of particles is called a concentration gradient ...
... Water flows to side of the membrane where water has low concentration. (High to Low) Water diffuses until it has equal concentration on both sides of the membrane Therefore, an unequal distribution of particles is called a concentration gradient ...
thyroid gland
... that lengthen with increased activity of the cells with well developed RER & Golgi which are necessary for the production and secretion of protein material. Stimulation by pituitary TSH increases synthesis and secretion.During an active secretory phase the thyroid follicular cells show: more promi ...
... that lengthen with increased activity of the cells with well developed RER & Golgi which are necessary for the production and secretion of protein material. Stimulation by pituitary TSH increases synthesis and secretion.During an active secretory phase the thyroid follicular cells show: more promi ...
chpt6(H)syllabus
... Objectives 6-1: The student will be able to explain the main ideas of the cell theory. describe how microscopes aid the study of cells. compare and contrast plant and animal cells. distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Objectives 6-2: The student will be able to describe th ...
... Objectives 6-1: The student will be able to explain the main ideas of the cell theory. describe how microscopes aid the study of cells. compare and contrast plant and animal cells. distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Objectives 6-2: The student will be able to describe th ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... making ATP using the chemical energy found in glucose and other nutrients. In mitochondria, this process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In fact, the carbon dioxide that you exhale with every breath comes from the cellular reactions that produce carbon dioxide as a byprod ...
... making ATP using the chemical energy found in glucose and other nutrients. In mitochondria, this process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In fact, the carbon dioxide that you exhale with every breath comes from the cellular reactions that produce carbon dioxide as a byprod ...
Pathophysiology - mwsu-wiki
... Plasma membrane: Surround a cell or enclose an intracellular organelle. Functions: Protection Transport Cell to cell recognition Cellular motility Maintaining cellular shape Membrane composition: The major chemical components of all membranes are Lipids Proteins Intracellular membranes have higher p ...
... Plasma membrane: Surround a cell or enclose an intracellular organelle. Functions: Protection Transport Cell to cell recognition Cellular motility Maintaining cellular shape Membrane composition: The major chemical components of all membranes are Lipids Proteins Intracellular membranes have higher p ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.