cell theory - Valhalla High School
... Cell Theory Timeline • 1839 - Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann create cell theory. The theory states that all living things are made up of one or more cells. Schleiden publishes his cell theory applying it to plants, while Schwann publishes his applied to animals. ...
... Cell Theory Timeline • 1839 - Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann create cell theory. The theory states that all living things are made up of one or more cells. Schleiden publishes his cell theory applying it to plants, while Schwann publishes his applied to animals. ...
Cell organelles you need to know for unit test
... Cell organelles= parts of the cell 1. Cytoplasm-mostly made up of water, this jelly like organelle found inside the cell that holds all the other cells in place. 2. Cell wall- Found only in plants it is a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape, it also provides support which helps plants grow ...
... Cell organelles= parts of the cell 1. Cytoplasm-mostly made up of water, this jelly like organelle found inside the cell that holds all the other cells in place. 2. Cell wall- Found only in plants it is a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape, it also provides support which helps plants grow ...
Class Test
... 4. State two features visible under a light microscope that indicate that cells are typical plant cells. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the stain that you used when examining an animal cell under the microscope. _____________________ 6. D ...
... 4. State two features visible under a light microscope that indicate that cells are typical plant cells. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the stain that you used when examining an animal cell under the microscope. _____________________ 6. D ...
2-Cells-pro vs euk - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... cells. That’s 100,000,000,000,000 or 1 x 1014 cells. There are about 200 different cell types in mammals (one of us). Cells are teeny, tiny, measuring on average about 0.002 cm (20 um) across. That’s about 1250 cells, “shoulder-to-shoulder” per inch. ...
... cells. That’s 100,000,000,000,000 or 1 x 1014 cells. There are about 200 different cell types in mammals (one of us). Cells are teeny, tiny, measuring on average about 0.002 cm (20 um) across. That’s about 1250 cells, “shoulder-to-shoulder” per inch. ...
Endocytosis - Cloudfront.net
... • Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) – 1) Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs a solid particle – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way ...
... • Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) – 1) Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs a solid particle – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way ...
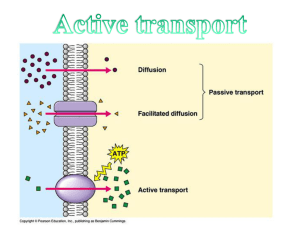
Active Transport
... Active Transport – the movement of materials from a low concentration to a high concentration, which requires energy, or ATP. I. Cell Pumps – special carrier proteins that require energy to pump substances against a concentration gradient (low to high). A. How Cell Pumps Work 1. Carrier Protein (pum ...
... Active Transport – the movement of materials from a low concentration to a high concentration, which requires energy, or ATP. I. Cell Pumps – special carrier proteins that require energy to pump substances against a concentration gradient (low to high). A. How Cell Pumps Work 1. Carrier Protein (pum ...
Section 5-2: Active Transport
... Active Transport – the movement of materials from a low concentration to a high concentration, which requires energy, or ATP. I. Cell Pumps – special carrier proteins that require energy to pump substances against a concentration gradient (low to high). A. How Cell Pumps Work 1. Carrier Protein (pum ...
... Active Transport – the movement of materials from a low concentration to a high concentration, which requires energy, or ATP. I. Cell Pumps – special carrier proteins that require energy to pump substances against a concentration gradient (low to high). A. How Cell Pumps Work 1. Carrier Protein (pum ...
Bill Nye: CELLS
... 3. _____________________ is when more cells are made than die off. 4. Bill says that ALL cells have a nucleus, but we know that some cells, like ________________________cells have NO nucleus. 5. Mitochondria in cells are like a fireplace, they provide _________________. 6. __________________________ ...
... 3. _____________________ is when more cells are made than die off. 4. Bill says that ALL cells have a nucleus, but we know that some cells, like ________________________cells have NO nucleus. 5. Mitochondria in cells are like a fireplace, they provide _________________. 6. __________________________ ...
... degradability of dry matter. Idioblasts with druses of oxalate were observed around the vascular tissues, in the midrib. It works like defense mechanisms of plant against herbivores and can affect the availability of minerals for animals. "Maniçoba" hay, in spite of its advanced maturity stage (earl ...
CELL RESPIRATION: uses GLUCOSE to produce energy (ATP)
... Prokaryotic cells: do not contain a nucleus (DNA is floating in the cytoplasm – Contain ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane – Do not contain membrane-bound organelles Eukaryotic cells: contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Unicellular organisms: one-celled organisms Multicellular o ...
... Prokaryotic cells: do not contain a nucleus (DNA is floating in the cytoplasm – Contain ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane – Do not contain membrane-bound organelles Eukaryotic cells: contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Unicellular organisms: one-celled organisms Multicellular o ...
Part 2 Review - Manhasset Schools
... 1. Basic parts of the cell that are easily seen under the microscope are the cytoplasm, cell membrane, and cell wall (in plants). 2. Molecules tend to move from HIGH TO LOW concentration WITHOUT the use of energy (diffusion). 3. Diffusion of WATER molecules is particularly important and has the spec ...
... 1. Basic parts of the cell that are easily seen under the microscope are the cytoplasm, cell membrane, and cell wall (in plants). 2. Molecules tend to move from HIGH TO LOW concentration WITHOUT the use of energy (diffusion). 3. Diffusion of WATER molecules is particularly important and has the spec ...
II. The Cell - Quakertown Community School District
... The Nucleus Nucleus—control center - enclosed by nuclear envelope - contains most of the genes that control the entire cell - DNA organized with proteins into chromatin - nucleolus-produces ribosomes ...
... The Nucleus Nucleus—control center - enclosed by nuclear envelope - contains most of the genes that control the entire cell - DNA organized with proteins into chromatin - nucleolus-produces ribosomes ...
Chapter 01
... • Beam of x-rays focused on protein crystal – regularly repeating atoms in crystal structure deflect x-rays at certain angles • X-rays produce pattern of exposure spots on photographic film placed behind protein sample ...
... • Beam of x-rays focused on protein crystal – regularly repeating atoms in crystal structure deflect x-rays at certain angles • X-rays produce pattern of exposure spots on photographic film placed behind protein sample ...
Cell Death Process
... in Eukaryotes • Cell death can occur by either of two distinct mechanisms – apoptosis or necrosis. • Apoptosis: originally defined according to a set of characteristic ultrastructural features that include nuclear and cytoplasmic condensation, cell fragmentation and phagocytosis. • Necrosis: cell de ...
... in Eukaryotes • Cell death can occur by either of two distinct mechanisms – apoptosis or necrosis. • Apoptosis: originally defined according to a set of characteristic ultrastructural features that include nuclear and cytoplasmic condensation, cell fragmentation and phagocytosis. • Necrosis: cell de ...
Bacteria and Viruses Notes Review: Archaebacteria • Are
... Do not require light, but instead use energy from chemical reactions using Ammonia, HS, nitrates, S, and Fe. Live in the deep ocean. ...
... Do not require light, but instead use energy from chemical reactions using Ammonia, HS, nitrates, S, and Fe. Live in the deep ocean. ...
DNA THE BASICS AND BEYOND Name Per
... Artificial Embryo Twinning Watch the video to the right of the page 8. Give a way the two are similar. 9. Give a way that they are different Somatic Nuclear Transfer 10. Somatic cell nuclear transfer (_________), also called _________ transfer, uses a different approach than artificial embryo twinni ...
... Artificial Embryo Twinning Watch the video to the right of the page 8. Give a way the two are similar. 9. Give a way that they are different Somatic Nuclear Transfer 10. Somatic cell nuclear transfer (_________), also called _________ transfer, uses a different approach than artificial embryo twinni ...
Study Guide for the LS
... the pigment in vacuoles is what gives some plants their color and makes vegetables crispy if they are full of water cytoplasm: jelly-like fluid inside of the cell nucleolus: stores the materials that will be used later to make ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Be able to identify and label all of the ...
... the pigment in vacuoles is what gives some plants their color and makes vegetables crispy if they are full of water cytoplasm: jelly-like fluid inside of the cell nucleolus: stores the materials that will be used later to make ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Be able to identify and label all of the ...
unit 4 overview
... Central Idea(s): Cells were first observed using very primitive microscopes in the mid 1600s. Advances in technology have allowed greater insights into the intricate structure and function of cells. Today we know that a cell is the basic unit of life and that all cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... Central Idea(s): Cells were first observed using very primitive microscopes in the mid 1600s. Advances in technology have allowed greater insights into the intricate structure and function of cells. Today we know that a cell is the basic unit of life and that all cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Document
... Hexose sugar The structural unit of maltose, starch, glycogen and cellulose Pentose sugar none of above ...
... Hexose sugar The structural unit of maltose, starch, glycogen and cellulose Pentose sugar none of above ...
Micro Notes
... Microbiology 1.2 and 1.3 Most organisms on Earth are single celled (unicellular) 3 Different Categories of Cells/Life: 1. Archaea - prokaryotic, unicellular - have ribosomes and cell wall for protection - live in extreme environments (very hot hydrothermal vent). 2. Bacteria - prokaryotic, unicellul ...
... Microbiology 1.2 and 1.3 Most organisms on Earth are single celled (unicellular) 3 Different Categories of Cells/Life: 1. Archaea - prokaryotic, unicellular - have ribosomes and cell wall for protection - live in extreme environments (very hot hydrothermal vent). 2. Bacteria - prokaryotic, unicellul ...
Section 4.2 - Cells and DNA
... 1. What does DNA stand for? 4. Organelle that sorts and packages proteins for transport. 6. Network of membrane-covered channels within the cell. 7. This organelle is like a manufacturing plant that makes proteins. 8. Organelle that controls all the activities within the cell. 13. X-shaped structure ...
... 1. What does DNA stand for? 4. Organelle that sorts and packages proteins for transport. 6. Network of membrane-covered channels within the cell. 7. This organelle is like a manufacturing plant that makes proteins. 8. Organelle that controls all the activities within the cell. 13. X-shaped structure ...
Cell Model
... would take a picture in front of town hall for the nucleus and a wooden fence of for the cell membrane ...
... would take a picture in front of town hall for the nucleus and a wooden fence of for the cell membrane ...