Growth
... Plate counts - spread plates & pour plates used to do viable cell counts Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) since it is not absolutely certain that each colony arose from an individual cell Viable cell counts very sensitive: Any viable cell colony ...
... Plate counts - spread plates & pour plates used to do viable cell counts Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) since it is not absolutely certain that each colony arose from an individual cell Viable cell counts very sensitive: Any viable cell colony ...
3_Cell_Project
... to get a job Cletus, and help pay your college tuition. Your sister cells have cleaned out the savings account.” Cletus was not expecting this and was totally unprepared to start working. However, as a dutiful son, Cletus agreed to begin looking for a job right away. Cletus began looking in the want ...
... to get a job Cletus, and help pay your college tuition. Your sister cells have cleaned out the savings account.” Cletus was not expecting this and was totally unprepared to start working. However, as a dutiful son, Cletus agreed to begin looking for a job right away. Cletus began looking in the want ...
the cell – project - Southington Public Schools
... 2. The cell must include the following structures: Plant Cell: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi complex, mitochondria Animal Cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, nucleus, lysosome, vacuole, rough endoplasmic r ...
... 2. The cell must include the following structures: Plant Cell: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi complex, mitochondria Animal Cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, nucleus, lysosome, vacuole, rough endoplasmic r ...
H - Midland ISD
... has two parts. Mitosis is the process of cell division and Interphase is the process of growing and functioning. • During mitosis the cell separates into two new identical sister cells. ...
... has two parts. Mitosis is the process of cell division and Interphase is the process of growing and functioning. • During mitosis the cell separates into two new identical sister cells. ...
the cell – project - Southington Public Schools
... 2. The cell must include the following structures: Plant Cell: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi complex, mitochondria Animal Cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, nucleus, lysosome, vacuole, rough endoplasmic r ...
... 2. The cell must include the following structures: Plant Cell: cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi complex, mitochondria Animal Cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, nucleus, lysosome, vacuole, rough endoplasmic r ...
Parts of a Cell
... Cells are alive and the basic living units of organization in all organisms All cells come from other cells ...
... Cells are alive and the basic living units of organization in all organisms All cells come from other cells ...
MCA Review Part I - Learn District 196
... -the root grows downward into the soil, (+) -the shoot grows upward, (-) ...
... -the root grows downward into the soil, (+) -the shoot grows upward, (-) ...
File
... Golgi Bodies • Protein “packaging plant” or “shippers” • Coats proteins and other materials so they can move different location inside/outside of cell ...
... Golgi Bodies • Protein “packaging plant” or “shippers” • Coats proteins and other materials so they can move different location inside/outside of cell ...
Document
... has two parts. Mitosis is the process of cell division and Interphase is the process of growing and functioning. • During mitosis the cell separates into two new identical sister cells. ...
... has two parts. Mitosis is the process of cell division and Interphase is the process of growing and functioning. • During mitosis the cell separates into two new identical sister cells. ...
Ch3CellStructurewphysio
... • Structure that carries out a specialized metabolic function inside a cell ...
... • Structure that carries out a specialized metabolic function inside a cell ...
The Cell - Education Service Center, Region 2
... function – used to store water, food or waste. In plant cells, they help keep the plant from wilting. ...
... function – used to store water, food or waste. In plant cells, they help keep the plant from wilting. ...
THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT VOCABULARY
... The maintenance of stable internal conditions despite the changes in an organism’s surroundings. An animal that does not have a backbone. Strong connective tissue that holds together the bones in a movable joint. A small round cell structure that contains chemicals that break down large food particl ...
... The maintenance of stable internal conditions despite the changes in an organism’s surroundings. An animal that does not have a backbone. Strong connective tissue that holds together the bones in a movable joint. A small round cell structure that contains chemicals that break down large food particl ...
Name - Humble ISD
... ___________________ the concentration of the sucrose solution. After the cells shrivel, their solute concentration is ___________________ the concentration of the sucrose solution. 16. Watering a houseplant with too concentrated a solution of fertilizer can result in wilting because the fertilizer c ...
... ___________________ the concentration of the sucrose solution. After the cells shrivel, their solute concentration is ___________________ the concentration of the sucrose solution. 16. Watering a houseplant with too concentrated a solution of fertilizer can result in wilting because the fertilizer c ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... B. Individual cells in the organism grow larger. C. The organism gains new cells from other organisms. D. Cells in the organism divide, increasing the total number of cells. 15. Describe the process of cell division that is associated with sexual reproduction. • description of meiosis (e.g., Meiosis ...
... B. Individual cells in the organism grow larger. C. The organism gains new cells from other organisms. D. Cells in the organism divide, increasing the total number of cells. 15. Describe the process of cell division that is associated with sexual reproduction. • description of meiosis (e.g., Meiosis ...
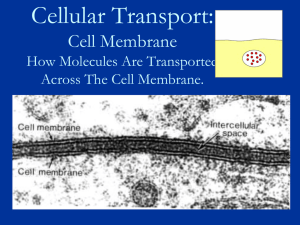
Cellular Transport
... o Engulfing – cell membrane surrounds a particle, engulfs it, and a vacuole forms o Transport protein – ‘picks up’ molecules from outside the cell Concentration – the amount of molecules in a specified area Concentration gradient – a difference in amount of molecules between two areas Equilibr ...
... o Engulfing – cell membrane surrounds a particle, engulfs it, and a vacuole forms o Transport protein – ‘picks up’ molecules from outside the cell Concentration – the amount of molecules in a specified area Concentration gradient – a difference in amount of molecules between two areas Equilibr ...
Mitosis Foldable
... o Draw picture of what is happening and label with the following: 2 daughter cells, nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleus for each cell o On inside of flap write name of phase, cytokinesis o On white paper write what is happening during cytokinesis: Cytokinesis starts at about the same time as telo ...
... o Draw picture of what is happening and label with the following: 2 daughter cells, nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleus for each cell o On inside of flap write name of phase, cytokinesis o On white paper write what is happening during cytokinesis: Cytokinesis starts at about the same time as telo ...
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell The Cell Theory • All living organisms
... o Has most of cell’s genes & usually most visible organelle o Nuclear envelope – double membrane enclosing nucleus Separates it from cytoplasm Nuclear Pores – regulate what enters & leaves nucleus o Nuclear Lamina – structural protein that maintains shape of nucleus o Chromatin – DNA + histones ...
... o Has most of cell’s genes & usually most visible organelle o Nuclear envelope – double membrane enclosing nucleus Separates it from cytoplasm Nuclear Pores – regulate what enters & leaves nucleus o Nuclear Lamina – structural protein that maintains shape of nucleus o Chromatin – DNA + histones ...
4.1 Answer packet for quiz
... Passive Transport – The diffusion of particles through proteins in the cell membrane from areas where the concentration of particles is high to areas where the concentration of particles is low ...
... Passive Transport – The diffusion of particles through proteins in the cell membrane from areas where the concentration of particles is high to areas where the concentration of particles is low ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... mitochondrion makes the cell’s energy the more energy the cell needs, the more mitochondria it has ...
... mitochondrion makes the cell’s energy the more energy the cell needs, the more mitochondria it has ...
Cells - Quia
... observed organisms that were unicellular and multicellular. observed common cell structures such as membranes and nuclei. made comparisons of various animal and plant tissues. ...
... observed organisms that were unicellular and multicellular. observed common cell structures such as membranes and nuclei. made comparisons of various animal and plant tissues. ...
cell membrane
... • How do cells maintain homeostasis? • How are cell membranes (plasma membranes) selectively permeable (semi-permeable)? • Why is it important that cells are able to transport molecules with (active transport) and without (passive transport) energy? ...
... • How do cells maintain homeostasis? • How are cell membranes (plasma membranes) selectively permeable (semi-permeable)? • Why is it important that cells are able to transport molecules with (active transport) and without (passive transport) energy? ...