CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... 8. Video-enhanced contrast microscopy accentuates the light and dark regions and may use a computer to contrast regions with false colors. 9. Bright-field, phase contrast, differential interference and darkfield are different types of light microscopy that improve our ability to see various features ...
... 8. Video-enhanced contrast microscopy accentuates the light and dark regions and may use a computer to contrast regions with false colors. 9. Bright-field, phase contrast, differential interference and darkfield are different types of light microscopy that improve our ability to see various features ...
cell division
... Chromosomes (stained purple) are visible within the nucleus of this cell from an African blood lily. The thinner red threads in the surrounding cytoplasm are the cytoskeleton. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Chromosomes (stained purple) are visible within the nucleus of this cell from an African blood lily. The thinner red threads in the surrounding cytoplasm are the cytoskeleton. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Slide 1 - Solon City Schools
... Based on the chart, which cell is most likely lacking organelles ...
... Based on the chart, which cell is most likely lacking organelles ...
Cancer
... • Not all mutations that lead to cancerous cells result in the cells reproducing at a faster, more uncontrolled rate. For example, a mutation may simply cause a cell to keep from self-destructing. All normal cells have surveillance mechanisms that look for damage or for problems with their own contr ...
... • Not all mutations that lead to cancerous cells result in the cells reproducing at a faster, more uncontrolled rate. For example, a mutation may simply cause a cell to keep from self-destructing. All normal cells have surveillance mechanisms that look for damage or for problems with their own contr ...
Jim`s talk
... Java and an Internet connection (it runs over the web) It is free but you must register ...
... Java and an Internet connection (it runs over the web) It is free but you must register ...
Why do cancer cells have too many centrosomes?
... Cell division is the biological basis of life, allowing a single fertilised egg cell to become a multicellular organism containing trillions of cells. This process is strictly regulated as uncontrolled cell division results in cancer. A cell must duplicate its contents exactly and separate evenl ...
... Cell division is the biological basis of life, allowing a single fertilised egg cell to become a multicellular organism containing trillions of cells. This process is strictly regulated as uncontrolled cell division results in cancer. A cell must duplicate its contents exactly and separate evenl ...
Term1 Cell Analogy Portfolio Product
... of your analogy, made with materials of your choosing that you must obtain yourself. You may build a physical model, draw by hand, or create a computer model or presentation. 2. 8 labels that adequately introduce each part of your analogy, its function within your analogy, and how it compares to a ...
... of your analogy, made with materials of your choosing that you must obtain yourself. You may build a physical model, draw by hand, or create a computer model or presentation. 2. 8 labels that adequately introduce each part of your analogy, its function within your analogy, and how it compares to a ...
Ask the Doctor - Lyme Disease Association of Australia
... Flexibility of the membranes dictates how well that cell and the proteins spanning its cell membrane are going to function. These membrane proteins are responsible for many specialized functions; some act as receptors that allow the cell to respond to external signals, some are responsible for the s ...
... Flexibility of the membranes dictates how well that cell and the proteins spanning its cell membrane are going to function. These membrane proteins are responsible for many specialized functions; some act as receptors that allow the cell to respond to external signals, some are responsible for the s ...
Cell Observation Exercise - Mr. Hill`s Science Website
... 2. What is the general location of the nucleus in the plant cell? ...
... 2. What is the general location of the nucleus in the plant cell? ...
High Current Density Operation at Los Bronces Electrowinning Plant
... built to treat around 700 million tons of marginal ROM ore averaging 0.45 % total copper. The mineralogy of this material is estimated to be 70% chalcopyrite, 20% chalcocite/covellite and the balance oxides. The original electrowinning plant design capacity for copper production was nominal 19,500 t ...
... built to treat around 700 million tons of marginal ROM ore averaging 0.45 % total copper. The mineralogy of this material is estimated to be 70% chalcopyrite, 20% chalcocite/covellite and the balance oxides. The original electrowinning plant design capacity for copper production was nominal 19,500 t ...
Document
... Looking at Table A, determine which type of milk, per serving, will theoretically yield a greater amount of ATP in the human body, and what is the reason for this? a. soymilk, because it contains no cholesterol ...
... Looking at Table A, determine which type of milk, per serving, will theoretically yield a greater amount of ATP in the human body, and what is the reason for this? a. soymilk, because it contains no cholesterol ...
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Cells
... • Contains 1 single, long, circular ds DNA (called ccDNA) ccDNA) *Function*Function-carries all info required for cell structure & function *plasmids also in nucleoid ...
... • Contains 1 single, long, circular ds DNA (called ccDNA) ccDNA) *Function*Function-carries all info required for cell structure & function *plasmids also in nucleoid ...
Name
... materials that enter and leave. Without this ability, the cell cannot maintain (2) __HOMEOSTASIS___________and will die. The cell must regulate internal concentrations of water, (3) __GLUCOSE____________________, and other nutrients and must eliminate waste products. Homeostasis in a cell is maintai ...
... materials that enter and leave. Without this ability, the cell cannot maintain (2) __HOMEOSTASIS___________and will die. The cell must regulate internal concentrations of water, (3) __GLUCOSE____________________, and other nutrients and must eliminate waste products. Homeostasis in a cell is maintai ...
cell cycle staging from fluorecence dapi images
... subpopulations of cells. Several methods have been developed and used to quantify DNA content in biological samples. DNA content analysis progressed from highly laborious and time-consuming methods to faster and highly quantitative techniques [1]. The accessibility to DNA fluorophores that bind stoi ...
... subpopulations of cells. Several methods have been developed and used to quantify DNA content in biological samples. DNA content analysis progressed from highly laborious and time-consuming methods to faster and highly quantitative techniques [1]. The accessibility to DNA fluorophores that bind stoi ...
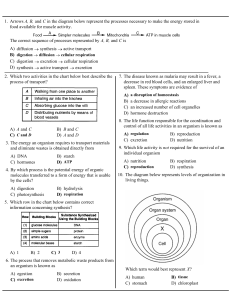
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
Micro-worlds
... He created the word “cell” for the rows of little empty boxes he saw through the microscope. ...
... He created the word “cell” for the rows of little empty boxes he saw through the microscope. ...
File - Biology
... Meiosis Review 1. In human cells: a. What does diploid and haploid mean with regard to chromosomes? b. What are the diploid and haploid numbers for cells? c. Which types of cells have diploid chromosomes, and which have haploid chromosomes? 2. What are homologous chromosomes? How are they related an ...
... Meiosis Review 1. In human cells: a. What does diploid and haploid mean with regard to chromosomes? b. What are the diploid and haploid numbers for cells? c. Which types of cells have diploid chromosomes, and which have haploid chromosomes? 2. What are homologous chromosomes? How are they related an ...
the cell - Learning Central
... understand this process and this is a part of your study to be discussed during Module 2 ...
... understand this process and this is a part of your study to be discussed during Module 2 ...
Benchmark SC.F.1.2.4: The student knows that similar cells
... Parts of Plant Cells (hyperlinked) Parts of Animal Cells (hyperlinked) Parts of a Cell Applet 2/ Worksheet 2 Brain Pop Video 1: Cell Structure Hands-On Activity 2: Build Model of Animal Cell and Plant Cell using Play-doh and Candy/Pasta Brain Pop Video 2: Cell Specialization Nutrient Transport into ...
... Parts of Plant Cells (hyperlinked) Parts of Animal Cells (hyperlinked) Parts of a Cell Applet 2/ Worksheet 2 Brain Pop Video 1: Cell Structure Hands-On Activity 2: Build Model of Animal Cell and Plant Cell using Play-doh and Candy/Pasta Brain Pop Video 2: Cell Specialization Nutrient Transport into ...
cellular transport regent
... Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Three Types of Solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic ...
... Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane Three Types of Solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic ...
Cell Practice Test
... B. transport lipids and proteins throughout the cell C. regulate what passes in and out of the cell ...
... B. transport lipids and proteins throughout the cell C. regulate what passes in and out of the cell ...