The Cell
... composition than the rest of the cell. • Much of the nucleoplasm consists of chromatin, various proteins bound to DNA. • Usually the chromatin appears as long, thin threads called chromosomes. ...
... composition than the rest of the cell. • Much of the nucleoplasm consists of chromatin, various proteins bound to DNA. • Usually the chromatin appears as long, thin threads called chromosomes. ...
Cells - Cloudfront.net
... 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? 2. What was Anton van Leeuwenhoek the first to see in the 1600s? 3. What did a thin slice of cork seem like to Robert Hooke when he observed it through a microscope? 4. What did the German botanist Matthias Schleiden conclude? 5. What did th ...
... 1. What is the structure that makes up every living thing? 2. What was Anton van Leeuwenhoek the first to see in the 1600s? 3. What did a thin slice of cork seem like to Robert Hooke when he observed it through a microscope? 4. What did the German botanist Matthias Schleiden conclude? 5. What did th ...
BIOL241StudyGuideExp1JUL2012
... Describe the location, structure, and function of each of the following organelles/structures: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum (rough and smooth), Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, centrioles, cilia, flagella, and microvilli. Identify the 3 major cytoskeletal fibers. Be ...
... Describe the location, structure, and function of each of the following organelles/structures: nucleus, nucleolus, endoplasmic reticulum (rough and smooth), Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, centrioles, cilia, flagella, and microvilli. Identify the 3 major cytoskeletal fibers. Be ...
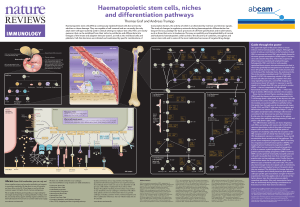
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... attrition or tissue damage. They are capable of self-renewal and are currently the only adult stem-cell type routinely used in clinical settings to replace lost cells. HSCs are mostly quiescent but can be mobilized from their niche to proliferate and differentiate into lineages of the innate and ada ...
... attrition or tissue damage. They are capable of self-renewal and are currently the only adult stem-cell type routinely used in clinical settings to replace lost cells. HSCs are mostly quiescent but can be mobilized from their niche to proliferate and differentiate into lineages of the innate and ada ...
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells
... For energy these bacteria use sulfer oxidation rather than oxidation from sugars made through photosynthesis!! SO cool!!!!! •Record held by a type of thermophile known as a hyperthermophile: 235°F. ...
... For energy these bacteria use sulfer oxidation rather than oxidation from sugars made through photosynthesis!! SO cool!!!!! •Record held by a type of thermophile known as a hyperthermophile: 235°F. ...
A1982PK03800001
... chance observation made with fresh sections of pea stems stained for peroxidase activity that there seemed to be a lot more activity associated with cell walls after ethylene treatment. Ethylene did, it turned out, increase markedly the levels of both lonically and covalently bound isozymes of perox ...
... chance observation made with fresh sections of pea stems stained for peroxidase activity that there seemed to be a lot more activity associated with cell walls after ethylene treatment. Ethylene did, it turned out, increase markedly the levels of both lonically and covalently bound isozymes of perox ...
The Cell - Ernst Klett
... The Cell – A Microscopic Factory Cell organelles and their functions All cells have a cell membrane which is a thin skin surrounding the cytoplasm. It acts like a boundary and stops the cell’s content from escaping. It also controls which substances like water, food, oxygen are allowed to enter the ...
... The Cell – A Microscopic Factory Cell organelles and their functions All cells have a cell membrane which is a thin skin surrounding the cytoplasm. It acts like a boundary and stops the cell’s content from escaping. It also controls which substances like water, food, oxygen are allowed to enter the ...
Cell Processes Notes - Mr. Coski`s Homepage
... of a large particle out of the cell by first surrounding it with a vesicle and then moving it to the cell membrane where it is expelled. ...
... of a large particle out of the cell by first surrounding it with a vesicle and then moving it to the cell membrane where it is expelled. ...
Biology 11 C
... bioremediation, bacteriophage, antibodies, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, symbiotic relationship Unit 3 – Genetics (In Grade 11 University Biology Textbook) Define: heredity, gene, DNA, genetics, chromosomes Asexual vs. sexual reproduction: definition, advantage, disadvantage Cloning: ap ...
... bioremediation, bacteriophage, antibodies, parasitism, commensalism, mutualism, symbiotic relationship Unit 3 – Genetics (In Grade 11 University Biology Textbook) Define: heredity, gene, DNA, genetics, chromosomes Asexual vs. sexual reproduction: definition, advantage, disadvantage Cloning: ap ...
File
... A. bone cell, bone tissue, femur (thigh bone), skeleton, dog B. dog, skeleton, femur, bone tissue, bone cell C. skeleton, bone tissue, bone cell, dog, femur D. bone tissue, bone cell, femur, skeleton, dog ...
... A. bone cell, bone tissue, femur (thigh bone), skeleton, dog B. dog, skeleton, femur, bone tissue, bone cell C. skeleton, bone tissue, bone cell, dog, femur D. bone tissue, bone cell, femur, skeleton, dog ...
Diffusion Through a Membrane Lab
... http://ccollege.hccs.edu/instru/Biology/Wagle/Plasmolysis.swf plant cell ...
... http://ccollege.hccs.edu/instru/Biology/Wagle/Plasmolysis.swf plant cell ...
Topic 1 Cells Powerpoint
... • G1 major event is growth of the new cells. • S major event is replication of the DNA • G2 major events are further growth as well as preparing for Mitosis (M phase). DNA starts to condense, organelles are copied, microtubules begin to form. ...
... • G1 major event is growth of the new cells. • S major event is replication of the DNA • G2 major events are further growth as well as preparing for Mitosis (M phase). DNA starts to condense, organelles are copied, microtubules begin to form. ...
PTEN Regulation
... global formation of myosin II filaments and also activates myosin light chain kinase, which enhances traction on actin filaments. This drives retraction of pseudopods and retraction of the uropod tail. However, it does not explain why myosin II is excluded from the anterior region of the cell. ...
... global formation of myosin II filaments and also activates myosin light chain kinase, which enhances traction on actin filaments. This drives retraction of pseudopods and retraction of the uropod tail. However, it does not explain why myosin II is excluded from the anterior region of the cell. ...
Chapter 11 Practice Questions
... 15) ________ are found in the CNS and act as the glue that binds axons and blood vessels ...
... 15) ________ are found in the CNS and act as the glue that binds axons and blood vessels ...
Functions of Life Content
... meats/sugaring fruits helps preserve them – it raises the ionic content.) -Salt: Ionic strength is needed for proton transfer, etc. -pH (both high and low pH can act as barrier to life): Mary’s explanation was that a cell runs its energy metabolism like a battery, where the proton quantity must be c ...
... meats/sugaring fruits helps preserve them – it raises the ionic content.) -Salt: Ionic strength is needed for proton transfer, etc. -pH (both high and low pH can act as barrier to life): Mary’s explanation was that a cell runs its energy metabolism like a battery, where the proton quantity must be c ...
Slide 1
... cell parts and attach them to your floor plan over the factory part that performs a similar task. When you have finished you will have created a model of a typical eukaryotic animal cell. ...
... cell parts and attach them to your floor plan over the factory part that performs a similar task. When you have finished you will have created a model of a typical eukaryotic animal cell. ...
Conclusion Transmission electron microscopy Aim Materials
... bioavailability and potency when compared to 2ME2. 2-MeOE2bisMATE is a derivative of oestrone-3-O-sulphamate (EMATE) and can be regarded as a potent inhibitor of steroid sulphatase (STS) activity. STS takes part in hydrolysis of oestrone sulphate to oestrone. This possibly contributes to the oestrad ...
... bioavailability and potency when compared to 2ME2. 2-MeOE2bisMATE is a derivative of oestrone-3-O-sulphamate (EMATE) and can be regarded as a potent inhibitor of steroid sulphatase (STS) activity. STS takes part in hydrolysis of oestrone sulphate to oestrone. This possibly contributes to the oestrad ...
The Basic Unit of Life
... 2. a) are onion cells produced by plants or animals?______________________________ b) Is a cell wall present?__________________________________________________ 3. a) Describe the shape of the nucleus of an onion cell.___________________________ b) Within what cell part already studied does the nucle ...
... 2. a) are onion cells produced by plants or animals?______________________________ b) Is a cell wall present?__________________________________________________ 3. a) Describe the shape of the nucleus of an onion cell.___________________________ b) Within what cell part already studied does the nucle ...
ch_03 - HCC Learning Web
... Some bacteria have structures responsible for cell motility that include flagella, long extensions beyond the cell surface and glycocalyx that propel a cell through its environment. Bacterial flagella are composed of a filament, a hook, and a basal body. Flagella covering the cell are termed peritri ...
... Some bacteria have structures responsible for cell motility that include flagella, long extensions beyond the cell surface and glycocalyx that propel a cell through its environment. Bacterial flagella are composed of a filament, a hook, and a basal body. Flagella covering the cell are termed peritri ...
Class IX Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life Science
... How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss. Answer: Thecell membrane is selectively permeable and regulates themovement of substances in and out of the cell. Movement of CO2: CO2 is produced during cellular respiration. Therefore, it is present in high concentrations i ...
... How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss. Answer: Thecell membrane is selectively permeable and regulates themovement of substances in and out of the cell. Movement of CO2: CO2 is produced during cellular respiration. Therefore, it is present in high concentrations i ...
Diffusion & Osmosis
... Lesser concentration to greater concentration Use of energy (against concentration gradient) Example: Sodium-Potassium pump; Endo- & Exocytosis ...
... Lesser concentration to greater concentration Use of energy (against concentration gradient) Example: Sodium-Potassium pump; Endo- & Exocytosis ...
Mitochondria Coloring
... cell. This releases energy (ATP) for the cell. The more active a cell (such as a muscle cell), the more mitochondria it will have. The mitochondria are about the size of a bacterial cell and are often peanut-shaped. Mitochondria have their own DNA and a double membrane like the nucleus and chloropla ...
... cell. This releases energy (ATP) for the cell. The more active a cell (such as a muscle cell), the more mitochondria it will have. The mitochondria are about the size of a bacterial cell and are often peanut-shaped. Mitochondria have their own DNA and a double membrane like the nucleus and chloropla ...