Cell structure teacher notes PreAP 14-15
... b. protein channel – allows larger molecules needed by the cell to pass through the cell membrane c. receptor protein – allows cell to communicate with outside environment d. LDL cholesterol – helps keep membrane fluid and stable ...
... b. protein channel – allows larger molecules needed by the cell to pass through the cell membrane c. receptor protein – allows cell to communicate with outside environment d. LDL cholesterol – helps keep membrane fluid and stable ...
Lecture 22: Cancer II and Cell Junctions
... Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes ...
... Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes ...
Protozoans - DoralBio8
... There are four type of protozoans and they are distinguished by the way they move Types of protozoans - Zooflagellates ...
... There are four type of protozoans and they are distinguished by the way they move Types of protozoans - Zooflagellates ...
Section 7.2 Notes Name: Cell Structure A cell is like a . CELL
... 52. What are the functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria? A. ___________________capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into food that contains ___________________ energy in a process called photosynthesis. 53. ________________convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that ...
... 52. What are the functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria? A. ___________________capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into food that contains ___________________ energy in a process called photosynthesis. 53. ________________convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that ...
Section 3 - HCABIOLOGY
... 5. The process in which a cell membrane engulfs large particles through vesicles is called ________________________. 6. The process in which a cell membrane expels substances out of a cell through vesicles is called ___________________. ...
... 5. The process in which a cell membrane engulfs large particles through vesicles is called ________________________. 6. The process in which a cell membrane expels substances out of a cell through vesicles is called ___________________. ...
Unit 5 review sheet
... recall that all of the cells of a particular organism contain all of the genetic code for the organism; summarize the unique characteristics of embryonic and adult stem cells; compare the results of cell division and cell differentiation. ...
... recall that all of the cells of a particular organism contain all of the genetic code for the organism; summarize the unique characteristics of embryonic and adult stem cells; compare the results of cell division and cell differentiation. ...
Gastrulation
... Does the bit modify the development of its new neighbour tissue. Tests induction Recombine different bits in tissue culture: Do they modify each others development? Molecular Techniques •What molecules/genes are expressed around the time and position of interesting developmental events: random or di ...
... Does the bit modify the development of its new neighbour tissue. Tests induction Recombine different bits in tissue culture: Do they modify each others development? Molecular Techniques •What molecules/genes are expressed around the time and position of interesting developmental events: random or di ...
1.2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
... Key Point #1: The function of a cell (what it does) is determined by its structure (what it is made of) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic code that instructs the cell how to run (it’s what makes you “you”) Organelle: Part of a cell ...
... Key Point #1: The function of a cell (what it does) is determined by its structure (what it is made of) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic code that instructs the cell how to run (it’s what makes you “you”) Organelle: Part of a cell ...
Cellular Transport
... • Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. • Movement of water – from “less salty” to “more salty” side of membrane – from low solute concentration to high solute concentration. – from high water concentration to low water concentration. ...
... • Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. • Movement of water – from “less salty” to “more salty” side of membrane – from low solute concentration to high solute concentration. – from high water concentration to low water concentration. ...
Cell Structure Get ready for a little friendly competition….
... ● Cells that have a high energy requirement, such as muscle cells, may have thousands of mitochondria. ● Outer membrane is smooth ● Inner membrane is folded = MAX SURFACE AREA ...
... ● Cells that have a high energy requirement, such as muscle cells, may have thousands of mitochondria. ● Outer membrane is smooth ● Inner membrane is folded = MAX SURFACE AREA ...
cell-intro-powerpoint-for-notes
... • These cells have other organelles that each have a specific job • Most Eukaryotes are multicellular • Plants, animals, including humans are ...
... • These cells have other organelles that each have a specific job • Most Eukaryotes are multicellular • Plants, animals, including humans are ...
kvdw - mmmig
... Pneumococcal cell wall PAMPs in disease progression. The cell wall of pneumococci is a major determinant of the course of disease. The interaction of PCho on the cell wall teichoic acid binds to PAFr and enables bacterial invasion of cells and transmigration across barriers. It also enables the cell ...
... Pneumococcal cell wall PAMPs in disease progression. The cell wall of pneumococci is a major determinant of the course of disease. The interaction of PCho on the cell wall teichoic acid binds to PAFr and enables bacterial invasion of cells and transmigration across barriers. It also enables the cell ...
Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell - Downey Unified School District
... • Microtubules- large hollow tubes that help during mitosis ...
... • Microtubules- large hollow tubes that help during mitosis ...
(1.2) Cell Division (p22-27)
... coiled threads called chromatin. • To reproduce the chromatin packs together to form chromosomes. • Chromosomes pass on hereditary information when a cell divides. ...
... coiled threads called chromatin. • To reproduce the chromatin packs together to form chromosomes. • Chromosomes pass on hereditary information when a cell divides. ...
PGS: 124 – 138 - Lincoln County Schools
... of DNA or a cell membrane.) Further, The natural world is complex; it is too complicated to comprehend all at once. Scientists and students learn to define small portions for the convenience of investigation. ...
... of DNA or a cell membrane.) Further, The natural world is complex; it is too complicated to comprehend all at once. Scientists and students learn to define small portions for the convenience of investigation. ...
Biology
... are made of very long double helix molecules called ______________________ and protein. When a cell divides these structures coil up tightly and become visible especially if they have been stained. When a cell is not dividing, the DNA is loosely coiled and appear as dense granular patches called chr ...
... are made of very long double helix molecules called ______________________ and protein. When a cell divides these structures coil up tightly and become visible especially if they have been stained. When a cell is not dividing, the DNA is loosely coiled and appear as dense granular patches called chr ...
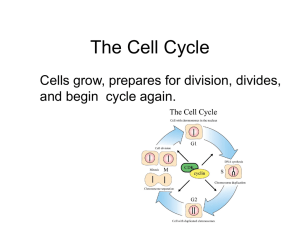
Stages of the cell cycle
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
What could have caused this?
... • Normal cells lose their ability to limit and direct their growth. They divide too rapidly and grow without any order. ...
... • Normal cells lose their ability to limit and direct their growth. They divide too rapidly and grow without any order. ...
Two types of cells
... • They can be single celled (just one cell) or can make up more complex multi-cellular organisms. • All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells. ...
... • They can be single celled (just one cell) or can make up more complex multi-cellular organisms. • All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotic cells. ...
Orflo Application Protocol 12/2016 Propidium Iodide (PI)
... 1. Remove old media and replace with serum free media (NOTE: Some cell lines respond poorly to serum-free media. These lines might require a gradual introduction to serum-free (24hrs in 1% FBS, 24hrs in 0 FBS) 2. To release cells, passage as appropriate and add 10% FBS. For cell cycle arrest ...
... 1. Remove old media and replace with serum free media (NOTE: Some cell lines respond poorly to serum-free media. These lines might require a gradual introduction to serum-free (24hrs in 1% FBS, 24hrs in 0 FBS) 2. To release cells, passage as appropriate and add 10% FBS. For cell cycle arrest ...
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic
... The last part of the chapter provides a brief presentation of the important mechanisms that move substances across cell membranes. An understanding of these mechanisms is essential to an understanding of how the cell functions. Both passive and active processes are presented, with the emphasis place ...
... The last part of the chapter provides a brief presentation of the important mechanisms that move substances across cell membranes. An understanding of these mechanisms is essential to an understanding of how the cell functions. Both passive and active processes are presented, with the emphasis place ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.