Study Guide for Exam 1 Dr. Osborne
... DNA directs all cellular activities and makes up the genes of the organism d. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) comes in three forms and is involved in protein synthesis ...
... DNA directs all cellular activities and makes up the genes of the organism d. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) comes in three forms and is involved in protein synthesis ...
Organs - Images
... Connective Tissue • Binds the cells and organs of the body together and consist of two basic components: cells and extracellular fibers. • Connective tissue is used for support, storage or transport • The body contains three types of specialized connective ...
... Connective Tissue • Binds the cells and organs of the body together and consist of two basic components: cells and extracellular fibers. • Connective tissue is used for support, storage or transport • The body contains three types of specialized connective ...
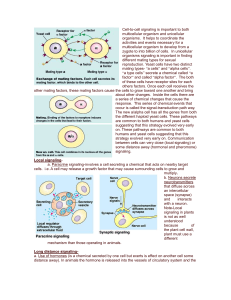
Long distance signaling
... Note-Local signaling in plants is not as well understood because of the plant cell wall, plant must use a different mechanism than those operating in animals. Long distance signalinga. Use of hormones (is a chemical secreted by one cell but exerts is effect on another cell some distance away). In an ...
... Note-Local signaling in plants is not as well understood because of the plant cell wall, plant must use a different mechanism than those operating in animals. Long distance signalinga. Use of hormones (is a chemical secreted by one cell but exerts is effect on another cell some distance away). In an ...
Cell Processes and energy
... •Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus •Contain instructions for cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material, directs all cell functions; found in chromatin RNA (ribonucleic acid)- role in production of proteins; found in cytoplasm and nucleus ...
... •Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus •Contain instructions for cell DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material, directs all cell functions; found in chromatin RNA (ribonucleic acid)- role in production of proteins; found in cytoplasm and nucleus ...
Types of Blood Cells All our blood cells have jobs to do. Red cells
... Bits of red sweets represent our platelets. Platelets are fragments of cells. Each one is about a fifth of the size of a red blood cell. Crush three red sweets into smaller pieces. ...
... Bits of red sweets represent our platelets. Platelets are fragments of cells. Each one is about a fifth of the size of a red blood cell. Crush three red sweets into smaller pieces. ...
1st 9 weeks Review KEY LIVING THINGS
... c. Way(s) they get energy: CONSUME, DECOMPOSE, OR PRODUCE 27. List 3 characteristics of animals: a. Amount of cells: MANY b. Types of cells: EUKARYOTIC c. Way(s) they get energy: CONSUME (EAT) 28. List 3 characteristics of most plants: a. Amount of cells: MANY b. Types of cells: EUKARYOTIC c. Way(s) ...
... c. Way(s) they get energy: CONSUME, DECOMPOSE, OR PRODUCE 27. List 3 characteristics of animals: a. Amount of cells: MANY b. Types of cells: EUKARYOTIC c. Way(s) they get energy: CONSUME (EAT) 28. List 3 characteristics of most plants: a. Amount of cells: MANY b. Types of cells: EUKARYOTIC c. Way(s) ...
TEACHER NOTES
... Teachers should make sure that students have been taught a. b. c. d. e. f. g. ...
... Teachers should make sure that students have been taught a. b. c. d. e. f. g. ...
Krok-Cytology
... D. Granular endoplasmic reticulum. E. Mytochondrions. 14. Labeled aminoacid alanine and tryptophane were inroducted to a mouse in order to study localization of protein biosynthesis in its cells. Around what organellas will the accumulation of labeled aminoacids be observed? A. Ribosomes. B. Cell c ...
... D. Granular endoplasmic reticulum. E. Mytochondrions. 14. Labeled aminoacid alanine and tryptophane were inroducted to a mouse in order to study localization of protein biosynthesis in its cells. Around what organellas will the accumulation of labeled aminoacids be observed? A. Ribosomes. B. Cell c ...
Cells BINGO PPT
... This structure packages and transports proteins made by the ribosomes attached to it and provides surface area for reactions. ...
... This structure packages and transports proteins made by the ribosomes attached to it and provides surface area for reactions. ...
Ch 4b Study Guide
... Compare the structures and functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria. Describe the evidence that suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. Internal and External Support: The Cytoskeleton and Cell Surfaces Compare the structures and functions of microfilaments, intermedia ...
... Compare the structures and functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria. Describe the evidence that suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. Internal and External Support: The Cytoskeleton and Cell Surfaces Compare the structures and functions of microfilaments, intermedia ...
Roles and Instructions for Cell Role Play
... functions in less then 60 seconds. Mastery Level Teacher gives cell a simple command. Cell has 30 seconds to complete the task. Cell may only pass notes from one organelle to the next. Teacher gives another command 15 seconds after first command. Teacher continues giving commands until cell cannot p ...
... functions in less then 60 seconds. Mastery Level Teacher gives cell a simple command. Cell has 30 seconds to complete the task. Cell may only pass notes from one organelle to the next. Teacher gives another command 15 seconds after first command. Teacher continues giving commands until cell cannot p ...
cell-transport-g9
... region of their higher concentration (dilute solution) to a region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ ...
... region of their higher concentration (dilute solution) to a region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane’ ...
WJCBR Ryabin J 2016 Living Architecture
... for many organelles and even cytosolic enzyme molecules. It is also involved with several types of cell motility (Campbell, 2002). Free ribosomes reside in the cytosol and carry out protein synthesis by the process of translation. Mitochondria generate ATP by the catabolic process of cellular respir ...
... for many organelles and even cytosolic enzyme molecules. It is also involved with several types of cell motility (Campbell, 2002). Free ribosomes reside in the cytosol and carry out protein synthesis by the process of translation. Mitochondria generate ATP by the catabolic process of cellular respir ...
Levels of Organization
... Nervous Tissue conducts signals Human Hair follicle. Wellcome Library ...
... Nervous Tissue conducts signals Human Hair follicle. Wellcome Library ...
The cell - Emilangues
... You can think of the lysosomes as the recyclers of the cell. They take proteins and break them up into amino acids so they can be used again. Mitochondria are like the cell’s power plant. They perform the function of cellular respiration, which we will discuss in more details later on in the video. ...
... You can think of the lysosomes as the recyclers of the cell. They take proteins and break them up into amino acids so they can be used again. Mitochondria are like the cell’s power plant. They perform the function of cellular respiration, which we will discuss in more details later on in the video. ...
File chapter 7
... http://peer.tamu.edu/curriculum_modules/Cell_Biology/module_1/levels%20of%20organization.jpg ...
... http://peer.tamu.edu/curriculum_modules/Cell_Biology/module_1/levels%20of%20organization.jpg ...
File
... “daughter” cells in a process called cell division. Before cell division, the cell copies all of its DNA. It then divides into two “daughter” cells. Each daughter cell receives a complete set of DNA. ...
... “daughter” cells in a process called cell division. Before cell division, the cell copies all of its DNA. It then divides into two “daughter” cells. Each daughter cell receives a complete set of DNA. ...
Characteristics of living things
... use energy to carry out life’s activities. Metabolism – is the total of all chemical ...
... use energy to carry out life’s activities. Metabolism – is the total of all chemical ...
1 Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -so: carries food produced in leaves to other parts of the plant -3 things systems are needed for: 1. a division of labor (aka levels of organization) 2. many individual cells can’t work together without regulation and coordination 3. cells aren’t in direct contact with the outside environment -orga ...
... -so: carries food produced in leaves to other parts of the plant -3 things systems are needed for: 1. a division of labor (aka levels of organization) 2. many individual cells can’t work together without regulation and coordination 3. cells aren’t in direct contact with the outside environment -orga ...
Cells Cells -Cells are the building blocks of living things
... -help move chromosomes during cell division -bundles of microtubules -usually found near the nucleus -found in animals can’t see them in plant cells -cilia are short flagella cells that have cilia are often covered with hundreds of them can move cells along with an oar-like motion can move materi ...
... -help move chromosomes during cell division -bundles of microtubules -usually found near the nucleus -found in animals can’t see them in plant cells -cilia are short flagella cells that have cilia are often covered with hundreds of them can move cells along with an oar-like motion can move materi ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.