TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.1
... 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at different rates Rates of cell division vary widely and are linked to the body’s need. The length of gap 1 varies most widely among cell types. Some cells, such as neurons, enter a stage called G0, where cells are unlikely to divide again. Cell size is limit ...
... 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at different rates Rates of cell division vary widely and are linked to the body’s need. The length of gap 1 varies most widely among cell types. Some cells, such as neurons, enter a stage called G0, where cells are unlikely to divide again. Cell size is limit ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
... 6. During ______________ the contents inside the cell divide. 7. Why is mitosis important when you are injured? 8. What is a malignant tumor? 9. Why do some cells like skin and stomach lining divide faster than others? 10. What do cells have at the end of the S phase of interphase? 11. What is a sub ...
Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of
... Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; (D) differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mi ...
... Cells and Organelles Test Review C) recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; (D) differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mi ...
lesson_10
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
Cell Power Point Questions
... 2) ___________ came up with the term cells. 3) ___________ was the first to record observations of what we know as bacteria from the plaque of teeth and he called these ____________. 4) The three scientists that contributed to cell theory are: - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 5) ...
... 2) ___________ came up with the term cells. 3) ___________ was the first to record observations of what we know as bacteria from the plaque of teeth and he called these ____________. 4) The three scientists that contributed to cell theory are: - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 5) ...
Matching Cell Parts WS File
... ____4. Bags of enzymes used to digest particles/bacteria; “garbage men” of the cell; work with vacuoles. ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane breaking loose; stores substances ____8 ...
... ____4. Bags of enzymes used to digest particles/bacteria; “garbage men” of the cell; work with vacuoles. ____5. Control center of the cell; contains nucleolus and DNA ____6. External surface is studded with ribosomes ____7. Formed from a piece of cell membrane breaking loose; stores substances ____8 ...
Science Chapter 1 Test Notes
... 7. The system that directs activities of all other body systems is called the nervous system. 8. A group of cells that work together to perform a certain function is a tissue. 9. The basic unit of structure and function of all living things is a cell. 10. The nucleus directs a cell’s activities. 11. ...
... 7. The system that directs activities of all other body systems is called the nervous system. 8. A group of cells that work together to perform a certain function is a tissue. 9. The basic unit of structure and function of all living things is a cell. 10. The nucleus directs a cell’s activities. 11. ...
The wacky history of cell theory
... 1. Scientists can only make discoveries in a laboratory with white lab coats and science gizmos that go beep. True or False 2. Why do you think there were so many heated debates around the development of the cell theory? ...
... 1. Scientists can only make discoveries in a laboratory with white lab coats and science gizmos that go beep. True or False 2. Why do you think there were so many heated debates around the development of the cell theory? ...
PPoint Lec 18
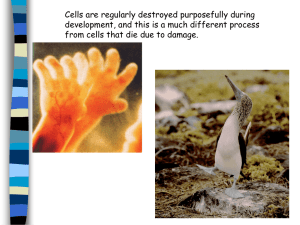
... of cells-1090 in this case, 131 of which undergo programmed cell death) Also-now whole genome is sequenced Because the fate of each cell can be traced, mutant strains of worms have been identified where those 131 cells don’t die. The genes responsible for this have been identified and are called ...
... of cells-1090 in this case, 131 of which undergo programmed cell death) Also-now whole genome is sequenced Because the fate of each cell can be traced, mutant strains of worms have been identified where those 131 cells don’t die. The genes responsible for this have been identified and are called ...
Name - St. Rose of Lima School
... Which organelles are common to both plant and animal cells? Why is the vacuole larger in the plant cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... Which organelles are common to both plant and animal cells? Why is the vacuole larger in the plant cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Document
... 2. Which part of the cell is selectively permeable, allowing only certain things in and out, in order to maintain this balance? 3. Give a creative example of diffusion. ...
... 2. Which part of the cell is selectively permeable, allowing only certain things in and out, in order to maintain this balance? 3. Give a creative example of diffusion. ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... M - Pre-existing cells make cells. L - All living organisms are made of cells B - Basic structure and function of life. ...
... M - Pre-existing cells make cells. L - All living organisms are made of cells B - Basic structure and function of life. ...
Name______________________________________
... 10) The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are thesechannels and pumps made of? ...
... 10) The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are thesechannels and pumps made of? ...
Name School Class Date Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells
... Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells 3. Looking at Onion Cells ...
... Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells 3. Looking at Onion Cells ...
CELL ORGANELLE PRACTCE matching
... A. This is the liquid within living cells. It is important because it helps materials to spread through the cell B. This is the Packaging center in the cell. This cell-part will package-up proteins C. Found only in Plant cells. Supports and Protects the cell D. Found in Plant Cells and Animal Cells ...
... A. This is the liquid within living cells. It is important because it helps materials to spread through the cell B. This is the Packaging center in the cell. This cell-part will package-up proteins C. Found only in Plant cells. Supports and Protects the cell D. Found in Plant Cells and Animal Cells ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about external regulators. a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. They prevent e ...
... 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about external regulators. a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. They prevent e ...
Common Parts of the Cell Practice
... 2.1 Common Parts of the Cell Practice 1. Why are there so many different types of cells in a multicellular organism? ...
... 2.1 Common Parts of the Cell Practice 1. Why are there so many different types of cells in a multicellular organism? ...
Cell Cycle and DNA Power Point Notes
... 4. In G2 phase, the cell prepares for __________________________________________. 5. Cell Division is made up of ___________________________ and _______________________________. 6. In mitosis, the nucleus of the cell divides. There is still only one cell. The four phases of mitosis are _____________ ...
... 4. In G2 phase, the cell prepares for __________________________________________. 5. Cell Division is made up of ___________________________ and _______________________________. 6. In mitosis, the nucleus of the cell divides. There is still only one cell. The four phases of mitosis are _____________ ...
Cells “The Building Blocks of Life”
... – Based on limited information or knowledge – Verified of falsified through experimentation ...
... – Based on limited information or knowledge – Verified of falsified through experimentation ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Cells in the intestine for example live only three days and must be constantly replaced, whereas cells of the liver live for more than a year. Brain cells on the other hand may never reproduce. ...
... Cells in the intestine for example live only three days and must be constantly replaced, whereas cells of the liver live for more than a year. Brain cells on the other hand may never reproduce. ...
vocab flip chart - Effingham County Schools
... found in all the cells of all living things, the blueprint for life, is the instructions for proteins ...
... found in all the cells of all living things, the blueprint for life, is the instructions for proteins ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.