Cells: Microscopes, Cell Structure, Function, and Organelles Study
... 1. What invention made it possible for people to discover and learn about cells? 2. A microscope makes distant or small objects look bigger? Pick one 3. What are the three parts of the cell theory? Make sure you know all of them! 4. What is magnification? (when using microscopes) 5. What is resoluti ...
... 1. What invention made it possible for people to discover and learn about cells? 2. A microscope makes distant or small objects look bigger? Pick one 3. What are the three parts of the cell theory? Make sure you know all of them! 4. What is magnification? (when using microscopes) 5. What is resoluti ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
... A: The type of memory cell that will produce antibodies quickly in response to a pathogen the body has “seen” before; responsible for immunity. ...
HW 5 Producing New Cells
... (c) During cell division the chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. State the term biologists use to describe that region of the cell. ...
... (c) During cell division the chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. State the term biologists use to describe that region of the cell. ...
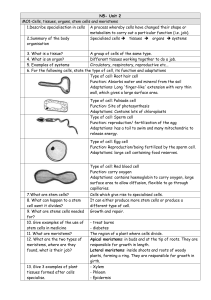
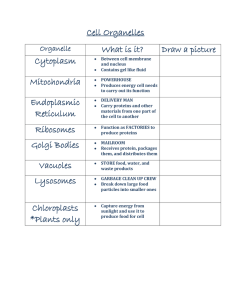
ws: Oodles of Organelles
... with the DESCRIPTIONS OF THE FUNCTIONS of the following organelles; NUMBER AND LETTER YOUR PAPER JUST AS THE LIST SHOWS BELOW. The numbers locate the organelles in an animal cell; the letters locate the organelles in a plant cell. ...
... with the DESCRIPTIONS OF THE FUNCTIONS of the following organelles; NUMBER AND LETTER YOUR PAPER JUST AS THE LIST SHOWS BELOW. The numbers locate the organelles in an animal cell; the letters locate the organelles in a plant cell. ...
Biology_Semester_2_Learning_Targets
... a. Describe properties of water that makes it important to life. b. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important to living organisms. c. Describe the composition and role of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. d. Identify biomolecules with the use of indicators. e. ...
... a. Describe properties of water that makes it important to life. b. Explain what chemical compounds are and why they are important to living organisms. c. Describe the composition and role of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. d. Identify biomolecules with the use of indicators. e. ...
CELL TYPES EPITHELIA CONNECTIVE TISSUE NERVOUS TISSUE
... Epithelial cells form coherent cell sheets called epithelia, which line the inner and outer surfaces of the body. There are many specialized types of epithelia. Absorptive cells have numerous hairlike projections called microvilli on their free surface to increase the area for absorption. ...
... Epithelial cells form coherent cell sheets called epithelia, which line the inner and outer surfaces of the body. There are many specialized types of epithelia. Absorptive cells have numerous hairlike projections called microvilli on their free surface to increase the area for absorption. ...
Cell Theory, Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Cells
... Prokaryotic Cells – They are cells that have a cell membrane and cytoplasm, but do not contain a nucleus. (bacteria) ...
... Prokaryotic Cells – They are cells that have a cell membrane and cytoplasm, but do not contain a nucleus. (bacteria) ...
“Cells Structure and Transport Practice Quiz” Cells Types 1. List the
... a. if they are found in plant or animal cells (or both) b. what they look like (in your own words) c. their function (what it does/is used for) d. How the organelles work in systems to achieve common goals Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosome Chloroplast Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Lysoso ...
... a. if they are found in plant or animal cells (or both) b. what they look like (in your own words) c. their function (what it does/is used for) d. How the organelles work in systems to achieve common goals Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosome Chloroplast Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Lysoso ...
Cell/Microscope Review - Union Beach School District
... Cells carry out the functions needed to support life ...
... Cells carry out the functions needed to support life ...
Cytoplasm is where all the chemical reactions take
... CELLS 1. All living things are made of cells which are either unicellular eg bacteria and yeast or multicellular organisms. 2. Microscopes are used to study cells, light microscopes can magnify about 1500 times and an electron microscope magnifies 40,000 to 500,000 times. ...
... CELLS 1. All living things are made of cells which are either unicellular eg bacteria and yeast or multicellular organisms. 2. Microscopes are used to study cells, light microscopes can magnify about 1500 times and an electron microscope magnifies 40,000 to 500,000 times. ...
N5- Unit 2 MO1-Cells, tissues, organs, stem cells and meristems 1
... Adaptations: contains haemoglobin to carry oxygen, large surface area to allow diffusion, flexible to go through capillaries. 7.What are stem cells? 8. What can happen to a stem cell went it divides? 9. What are stems cells needed for? 10. Give examples of the use of stem cells in medicine 11. What ...
... Adaptations: contains haemoglobin to carry oxygen, large surface area to allow diffusion, flexible to go through capillaries. 7.What are stem cells? 8. What can happen to a stem cell went it divides? 9. What are stems cells needed for? 10. Give examples of the use of stem cells in medicine 11. What ...
File - Timber Wolves
... ***If it does not have these characteristics, then it is _____________ What are the three things 1) ____________ (all energy used by life comes from the _______) every organism needs in 2) ____________ order to live? (C 10) 3) ____________ to live What is a cell? (C 11) The _______________ unit of a ...
... ***If it does not have these characteristics, then it is _____________ What are the three things 1) ____________ (all energy used by life comes from the _______) every organism needs in 2) ____________ order to live? (C 10) 3) ____________ to live What is a cell? (C 11) The _______________ unit of a ...
I am a sperm cell
... Muscle cells are long and flat to allow them to relax and contract. When muscle is being used it is contracting and when a muscle is not being used it is relaxing. ...
... Muscle cells are long and flat to allow them to relax and contract. When muscle is being used it is contracting and when a muscle is not being used it is relaxing. ...
Chapter 3/Lesson 1 Part 2 Notes
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
Lab Activity-Stages of Cell Cycle
... 4. Graph the number vs stage. Use a Pie Chart. This should give you an approximate cell cycle. Since you are looking at a “snapshot” of an area of active cell division, stages that take longer will have more visible in that stage. Since stages that are short will not be likely to be caught in that s ...
... 4. Graph the number vs stage. Use a Pie Chart. This should give you an approximate cell cycle. Since you are looking at a “snapshot” of an area of active cell division, stages that take longer will have more visible in that stage. Since stages that are short will not be likely to be caught in that s ...
1. Name 4 bases (subunits) of DNA. 2. Write series of bases will
... theory states that all cells are produced by a) preexisting cells b) free-‐cell formation c) endocytosis d) prokaryotic cells ...
... theory states that all cells are produced by a) preexisting cells b) free-‐cell formation c) endocytosis d) prokaryotic cells ...
Name: Date: Class Period: Video questions: Video 1: Gene
... What is a regulatory gene? What is an example of a regulatory sequence? What is lactose? What does it mean when a gene is expressed? What is the function of the TATA box? What is the function of an operator sequence? Why would bacteria want to make enzymes (proteins) that break down lactose only whe ...
... What is a regulatory gene? What is an example of a regulatory sequence? What is lactose? What does it mean when a gene is expressed? What is the function of the TATA box? What is the function of an operator sequence? Why would bacteria want to make enzymes (proteins) that break down lactose only whe ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.