Cells
... of cells which are organised into tissues, organs and systems to carry out life processes. There are many types of cell. Each has a different structure or feature so it can do a specific job. ...
... of cells which are organised into tissues, organs and systems to carry out life processes. There are many types of cell. Each has a different structure or feature so it can do a specific job. ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... fluid within the body • IgA predominates in secretions across epithelial including breast milk. The fetus received IgG from the mother by transplacental transport. IgE is found mainly with mast cells (specially of respiratory tract, GIT & skin) • The brain is normally devoid of immunoglobulins ...
... fluid within the body • IgA predominates in secretions across epithelial including breast milk. The fetus received IgG from the mother by transplacental transport. IgE is found mainly with mast cells (specially of respiratory tract, GIT & skin) • The brain is normally devoid of immunoglobulins ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... 8. To recap, the botanist _______________, the zoologist _______________, and the medical doctor ________________ all co-founded the cell theory. 9. What must be used to view most cells? 10. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? ...
... 8. To recap, the botanist _______________, the zoologist _______________, and the medical doctor ________________ all co-founded the cell theory. 9. What must be used to view most cells? 10. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? ...
Cell Theory/Cell Basics Notes Page
... 8. To recap, the botanist _______________, the zoologist _______________, and the medical doctor ________________ all co-founded the cell theory. 9. What must be used to view most cells? 10. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? ...
... 8. To recap, the botanist _______________, the zoologist _______________, and the medical doctor ________________ all co-founded the cell theory. 9. What must be used to view most cells? 10. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? ...
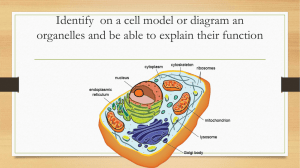
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... contain more hemoglobin and, therefore, carry more oxygen molecules. It also allows the cell to have its distinctive bi-concave shape which aids diffusion. This shape would not be possible if the cell had a nucleus in the ...
... contain more hemoglobin and, therefore, carry more oxygen molecules. It also allows the cell to have its distinctive bi-concave shape which aids diffusion. This shape would not be possible if the cell had a nucleus in the ...
cells review sheet two
... 1. Who first noticed cells when looking at cork using a compound microscope? A. Robert Hooke B. Anton von Leewenhoek C. Rudolf Virchow 2. Which organelle is found inside the nucleus of a cell? A. centrioles B. nucleolus C. chloroplast ...
... 1. Who first noticed cells when looking at cork using a compound microscope? A. Robert Hooke B. Anton von Leewenhoek C. Rudolf Virchow 2. Which organelle is found inside the nucleus of a cell? A. centrioles B. nucleolus C. chloroplast ...
Agreement form for MoFlo XDP Cell Sorter
... UMMC Cancer Institute Flow Cytometry Core - MoFlo Cell Sorter Name of investigator:……………………………………………………………………………. email:……………………………………………………………………………………………………. Phone:…………………………………………………………………………………………………… Type of samples to be analyzed (please indicate cell type(s) and size, and fluorescent dyes use ...
... UMMC Cancer Institute Flow Cytometry Core - MoFlo Cell Sorter Name of investigator:……………………………………………………………………………. email:……………………………………………………………………………………………………. Phone:…………………………………………………………………………………………………… Type of samples to be analyzed (please indicate cell type(s) and size, and fluorescent dyes use ...
The Basic Unit - missmbrougham
... The functions of living things are performed by the cells they are made of ...
... The functions of living things are performed by the cells they are made of ...
The Cell Cycle
... Why must cells divide? MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS GROW BY MAKING MORE CELLS WHEN CELLS GET TOO BIG, THEIR MEMBRANES CANNOT EXCHANGE WASTE AND NUTRIENTS FAST ENOUGH TO KEEP THEM ALIVE • DIVISION IS NEEDED FOR GROWTH (INCREASE IN SIZE), HEALING, AND DEVELOPMENT (CHANGES IN BODY STRUCTURE) SOME ORGANISMS ...
... Why must cells divide? MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS GROW BY MAKING MORE CELLS WHEN CELLS GET TOO BIG, THEIR MEMBRANES CANNOT EXCHANGE WASTE AND NUTRIENTS FAST ENOUGH TO KEEP THEM ALIVE • DIVISION IS NEEDED FOR GROWTH (INCREASE IN SIZE), HEALING, AND DEVELOPMENT (CHANGES IN BODY STRUCTURE) SOME ORGANISMS ...
Cell Review!!
... Stores enzymes & waste: __________________________ Cleans up cells: ___________________________ Photosynthesis (location): ________________________ Protein synthesis: ___________________________ Ribosome synthesis: ___________________________ ...
... Stores enzymes & waste: __________________________ Cleans up cells: ___________________________ Photosynthesis (location): ________________________ Protein synthesis: ___________________________ Ribosome synthesis: ___________________________ ...
Communication & cell signalling
... components Outside the cell between cells Different molecules send different signals ...
... components Outside the cell between cells Different molecules send different signals ...
Quiz- Cells/ Photosynthesis/ Respiration
... Which of the following statementsis NOT part of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. b. All cells are producedfrom other cells' c. Only animalsare composedof cells' d. All living things are composedof cells' What is the function of a cell membrane? ...
... Which of the following statementsis NOT part of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. b. All cells are producedfrom other cells' c. Only animalsare composedof cells' d. All living things are composedof cells' What is the function of a cell membrane? ...
Cell Structure
... How are cells organized to perform the work they do? How do cells differentiate into different types? How do cells work together to maintain homeostasis? ...
... How are cells organized to perform the work they do? How do cells differentiate into different types? How do cells work together to maintain homeostasis? ...
ch 3 section 1 notes student copy
... - ________________________ was the first person to see cells. - Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to see ______________, which he called animalcules, and _______________. - Matthias ________________ concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that ________________ ...
... - ________________________ was the first person to see cells. - Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first to see ______________, which he called animalcules, and _______________. - Matthias ________________ concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that ________________ ...
CELLS AND TISSUES WORKSHEET ANATOMY AND
... 1. Forms the lining of the small intestine______________________________ 2. A single layer of flattened cells___________________________________3. Lines the esophagus__________________________ 4. A single layer of hexagonal cells_________________________ 5. A single layer of square-like cells_______ ...
... 1. Forms the lining of the small intestine______________________________ 2. A single layer of flattened cells___________________________________3. Lines the esophagus__________________________ 4. A single layer of hexagonal cells_________________________ 5. A single layer of square-like cells_______ ...
Marine Turtle Expeditions
... • Hormone – a chemical compound produced by cells in trace quantities, secreted directly into the blood & then carried via circulation to other cells, the function of which are changed by this chemical • Target cell, tissue or organ – those cells or organs that are affected by a hormone • Endocrine ...
... • Hormone – a chemical compound produced by cells in trace quantities, secreted directly into the blood & then carried via circulation to other cells, the function of which are changed by this chemical • Target cell, tissue or organ – those cells or organs that are affected by a hormone • Endocrine ...
Cell practice problem
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ________________ ...
Document
... The Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. Cell contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
... The Cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. Cell contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
Revision Poster
... 2.1.2 – 2.1.4 + 2.4 Cells & Tissues Cell: the smallest unit of matter that can carry on all the processes of life. They are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. ...
... 2.1.2 – 2.1.4 + 2.4 Cells & Tissues Cell: the smallest unit of matter that can carry on all the processes of life. They are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. ...
eukaryote: cell that has a membrane
... 2.1.2 – 2.1.4 + 2.4 Cells & Tissues Cell: the smallest unit of matter that can carry on all the processes of life. They are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. ...
... 2.1.2 – 2.1.4 + 2.4 Cells & Tissues Cell: the smallest unit of matter that can carry on all the processes of life. They are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. ...
Kingdoms Of Life: Monerans
... In the new cell, chromosomes exchange pieces. New cell divides into two new cells ...
... In the new cell, chromosomes exchange pieces. New cell divides into two new cells ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.