4-1 outline answers
... 2. Body cells are diploid; they have pairs of chromosomes. 3. If a zygote has too many or too few chromosomes, it will not develop properly. 4. Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. 5. Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged i ...
... 2. Body cells are diploid; they have pairs of chromosomes. 3. If a zygote has too many or too few chromosomes, it will not develop properly. 4. Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. 5. Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have genes for the same traits arranged i ...
Cellular respiration
... respiration occurs. The electron transport chain. • In this 2nd step, the most number of ATP is produced. About 36 molecules of ATP is made. More or less can be made depending on the type of cell. A fat cell will make less ATP than a muscle cell. • In addition to making ATP water is also produced. • ...
... respiration occurs. The electron transport chain. • In this 2nd step, the most number of ATP is produced. About 36 molecules of ATP is made. More or less can be made depending on the type of cell. A fat cell will make less ATP than a muscle cell. • In addition to making ATP water is also produced. • ...
Business Strategy
... Cast PDMS replica of master Lay down SU-8 on silicon wafer, expose using mask, and develop upper region for pneumatic control of cell insertion channels. Cast PDMS replica of master and then lay over top of lower region ...
... Cast PDMS replica of master Lay down SU-8 on silicon wafer, expose using mask, and develop upper region for pneumatic control of cell insertion channels. Cast PDMS replica of master and then lay over top of lower region ...
Name_____________________ Date_______________ Unit 4
... An internal signal involves the cell sensing the presence of chemicals, called enzymes, which are produced inside the cell An external signal involves the cell sensing the presence of a chemical (such as a growth factor) which was produced in other specialized cells. Cells can also respond to ...
... An internal signal involves the cell sensing the presence of chemicals, called enzymes, which are produced inside the cell An external signal involves the cell sensing the presence of a chemical (such as a growth factor) which was produced in other specialized cells. Cells can also respond to ...
10-3 Notes
... Experiments show that normal cells will reproduce until they come into contact with other cells: •When cells come into contact with other cells, they stop growing. •cell growth and division can be turned on and off. ...
... Experiments show that normal cells will reproduce until they come into contact with other cells: •When cells come into contact with other cells, they stop growing. •cell growth and division can be turned on and off. ...
REVIEW
... 2. Why did it take 150 years for the cell theory to be developed after microscopes were invented? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ __________ ...
... 2. Why did it take 150 years for the cell theory to be developed after microscopes were invented? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ __________ ...
Ch 8 Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
... 1. The discovery of _______________ -structures that contain DNA 2. The structure of _______________ chromosomes a). ____________– long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins C. The _______________ _______________ – the sequence of growth and division of a cell a). _______________ – the majority of ...
... 1. The discovery of _______________ -structures that contain DNA 2. The structure of _______________ chromosomes a). ____________– long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins C. The _______________ _______________ – the sequence of growth and division of a cell a). _______________ – the majority of ...
Cell Division by Mitosis
... Cell Division by Mitosis Label each phase of cell division below. Then and match each statement with each phase ...
... Cell Division by Mitosis Label each phase of cell division below. Then and match each statement with each phase ...
Cells
... In eukaryotic cells, selective entry and exit of other molecules occurs through proteins embedded in the _______________________________________ of the cell membrane. Also Called the ________________________________ Phospholipids bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipids so that their nonpo ...
... In eukaryotic cells, selective entry and exit of other molecules occurs through proteins embedded in the _______________________________________ of the cell membrane. Also Called the ________________________________ Phospholipids bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipids so that their nonpo ...
No Slide Title
... 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... 1. All living things are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Enhanced cell lysis
... Prior to the investigation of intracellular proteins and organelles cells need to be disrupted or lysed to release these components for study. Sonication is one method commonly used by researchers to disrupt cell architecture. We have developed a novel cell lysis apparatus and methodology which enha ...
... Prior to the investigation of intracellular proteins and organelles cells need to be disrupted or lysed to release these components for study. Sonication is one method commonly used by researchers to disrupt cell architecture. We have developed a novel cell lysis apparatus and methodology which enha ...
How Cells Obtain and Use Glucose Modeled with AgentSheets
... • Students will work with agent sheets to create a functioning model of how molecules related to respiration move into and out of the cell. ...
... • Students will work with agent sheets to create a functioning model of how molecules related to respiration move into and out of the cell. ...
Skill Builder _6B homeostasis
... be made continuously to stay at or near the set point (the normal level or range). Homeostasis can be thought of as a dynamic equilibrium rather than a constant, unchanging state. Feedback Regulation Loops The endocrine system plays an important role in homeostasis because hormones regulate the acti ...
... be made continuously to stay at or near the set point (the normal level or range). Homeostasis can be thought of as a dynamic equilibrium rather than a constant, unchanging state. Feedback Regulation Loops The endocrine system plays an important role in homeostasis because hormones regulate the acti ...
Cell Cycle Overview
... The use of fixatives allows the storage of samples before their analysis. Cells could be collecting at different time points, stored in fixative for extended periods and then stained and analyzed ...
... The use of fixatives allows the storage of samples before their analysis. Cells could be collecting at different time points, stored in fixative for extended periods and then stained and analyzed ...
Cell
... which is the site of ribosome production. Chromosomes hold the DNA which is the genetic material of the cell. The nuclear membrane protects the nucleus and allow materials to pass in and out, except for DNA ...
... which is the site of ribosome production. Chromosomes hold the DNA which is the genetic material of the cell. The nuclear membrane protects the nucleus and allow materials to pass in and out, except for DNA ...
Document
... Organelle- a specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell. Vacuole- the cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. ...
... Organelle- a specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell. Vacuole- the cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. ...
Lecture 7: the cytoskeleton and cell movement
... the cell towards the periphery, where myosins take over moving organelles near the plasma membrane. ...
... the cell towards the periphery, where myosins take over moving organelles near the plasma membrane. ...
Cell Pats and Movement Across Memebranes
... Cell Nucleus Nucleus: houses genetic material, DNA Enclosed in double-layered nuclear envelope Nuclear Pores: protein channels for transport Nucleolus: small, dense body inside the nucleus Form ribosomes Chromatin: loosely coiled DNA ...
... Cell Nucleus Nucleus: houses genetic material, DNA Enclosed in double-layered nuclear envelope Nuclear Pores: protein channels for transport Nucleolus: small, dense body inside the nucleus Form ribosomes Chromatin: loosely coiled DNA ...
Cell Membrane
... 1. Contains all the DNA within a cell, which it is referred to as the control center of the cell 2. Surrounded by the “Nuclear Envelope.” - - Membrane that protects the inside contents and also allows for the passage of materials in and out of the nucleus such as RNA and ...
... 1. Contains all the DNA within a cell, which it is referred to as the control center of the cell 2. Surrounded by the “Nuclear Envelope.” - - Membrane that protects the inside contents and also allows for the passage of materials in and out of the nucleus such as RNA and ...
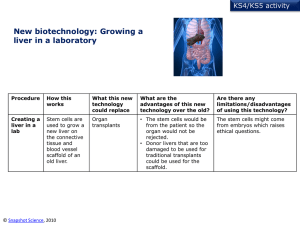
new biotechnology PowerPoint
... animals to create the antibodies so less ethical dilemmas. • Antibodies can be ‘tailor made’ to lock onto a massive range of different antigens like pathogens and proteins that cause allergic reactions. ...
... animals to create the antibodies so less ethical dilemmas. • Antibodies can be ‘tailor made’ to lock onto a massive range of different antigens like pathogens and proteins that cause allergic reactions. ...
MICROSCOPES
... SHAPES OF CELLS Cells are all three-dimensional and can vary in shape and size (nearly all are microscopic). Being microscopic ensures that a cell has a high surface area (cell membrane) to volume ratio. This results in the cell being efficient at exchanging substances. When viewing cells with a mic ...
... SHAPES OF CELLS Cells are all three-dimensional and can vary in shape and size (nearly all are microscopic). Being microscopic ensures that a cell has a high surface area (cell membrane) to volume ratio. This results in the cell being efficient at exchanging substances. When viewing cells with a mic ...
Cell Structure & Function
... http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/biology/chloroplast.html ...
... http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/biology/chloroplast.html ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.