Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
... Organisms are either: Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. OR Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. ...
... Organisms are either: Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. OR Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. ...
Organelle Notes
... Essential Question: What organelles are found in Eukaryotic Cells? Notes: Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
... Essential Question: What organelles are found in Eukaryotic Cells? Notes: Questions/Main Ideas: Nucleus Contains the cell’s DNA Control center of cell, the cell’s brain Ribosomes ...
Major Cell Organelles.wpd
... ! typically rounder structure surrounded by a nuclear membrane (lipid bilayer) ! has pores ! contains nucleoplasm which houses DNA ! may contain one or more nucleoli ...
... ! typically rounder structure surrounded by a nuclear membrane (lipid bilayer) ! has pores ! contains nucleoplasm which houses DNA ! may contain one or more nucleoli ...
Ultrafast Solvation: Investigating Molecular Forces in Protein Folding November 12, 2010
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
Endosymbiotic Theory
... National Institutes of Health There are many theories as to how the first life on Earth came to be, including the hydrothermal vents and Panspermia theories. While those explain how the most primitive types of cells came into existence, another theory is needed to describe how those primitive cells ...
... National Institutes of Health There are many theories as to how the first life on Earth came to be, including the hydrothermal vents and Panspermia theories. While those explain how the most primitive types of cells came into existence, another theory is needed to describe how those primitive cells ...
BIOL108 LECTURE NOTES
... o To be stable – must have 8 electrons on the outer ring - A small number of elements make up living things - Molecules: two or more atoms joined - Compound: two or more elements joined together o DNA: complex compound - Covalent Reactions e.g. Oxygen + 2Hydrogen = H-O-H (H2O water) o Molecules of w ...
... o To be stable – must have 8 electrons on the outer ring - A small number of elements make up living things - Molecules: two or more atoms joined - Compound: two or more elements joined together o DNA: complex compound - Covalent Reactions e.g. Oxygen + 2Hydrogen = H-O-H (H2O water) o Molecules of w ...
logcsscibap_2_1_2_d_..
... Animal cells have some of the same structures and organelles that plant cells have, but not all of them. a ...
... Animal cells have some of the same structures and organelles that plant cells have, but not all of them. a ...
Cell organelle powerpoint
... Is square due to rigid square wall Have chlorophyll (which makes it green) Have one large central vacuole ...
... Is square due to rigid square wall Have chlorophyll (which makes it green) Have one large central vacuole ...
Slide 1
... • The overall research goal is to further elucidate the cancer stem cell hypothesis in brain tumours and to characterize the Brain Tumour Initiating Cell (BTIC) • Our work includes tissue culture, molecular biology experiments and in vivo animal work ...
... • The overall research goal is to further elucidate the cancer stem cell hypothesis in brain tumours and to characterize the Brain Tumour Initiating Cell (BTIC) • Our work includes tissue culture, molecular biology experiments and in vivo animal work ...
Ch 4 quiz - TESADVBiology
... ____ 14.The nucleus of a cell contains all of the following EXCEPT a.chromosomes. b. mitochondria. c. DNA. d. RNA. ____ 15.Which type of molecule is found in the plasma membrane? a. carbohydrate b. protein c. phospholipid d. All of the above ____ 16.The lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane a.provide ...
... ____ 14.The nucleus of a cell contains all of the following EXCEPT a.chromosomes. b. mitochondria. c. DNA. d. RNA. ____ 15.Which type of molecule is found in the plasma membrane? a. carbohydrate b. protein c. phospholipid d. All of the above ____ 16.The lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane a.provide ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Objectives: The objective of this course is to
... Objectives: The objective of this course is to explain and give examples of how ionic, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonding interactions determine the structure of nucleic acids and proteins and modulate the specificity of binding between them; to distinguish between different molecular biology techniq ...
... Objectives: The objective of this course is to explain and give examples of how ionic, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonding interactions determine the structure of nucleic acids and proteins and modulate the specificity of binding between them; to distinguish between different molecular biology techniq ...
Name: Date: Block: Science 8 Chapter 1 Review Answer the
... 14. Muscle cells have a greater number of mitochondria than other animal cells. Using the function of the mitochondria, explain why this is. 15. What is cellular respiration? 16. Explain the roles of the following organelles in the production of proteins: ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi ...
... 14. Muscle cells have a greater number of mitochondria than other animal cells. Using the function of the mitochondria, explain why this is. 15. What is cellular respiration? 16. Explain the roles of the following organelles in the production of proteins: ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi ...
Cell Structures
... More rigid than the plasma membrane Helps the cell maintain its shape and provides protection Restricts the cells ability to change shape ...
... More rigid than the plasma membrane Helps the cell maintain its shape and provides protection Restricts the cells ability to change shape ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell - Foothill Technology High School
... system? • System of membrane-bound organelles in euk. cells that work cooperatively together to create secretory proteins, membrane-bound proteins, or plasma membrane proteins ...
... system? • System of membrane-bound organelles in euk. cells that work cooperatively together to create secretory proteins, membrane-bound proteins, or plasma membrane proteins ...
Cell Review!!
... 3. What happens to protein synthesis without the nucleolus? 4. In terms of evolution, which one do you think came first? The prokaryote or the eukaryote? Why? 5. How do cells maintain homeostasis? 6. Where is the cytoplasm in the cell? Describe it. 7. What happens to the cells without flagellum or c ...
... 3. What happens to protein synthesis without the nucleolus? 4. In terms of evolution, which one do you think came first? The prokaryote or the eukaryote? Why? 5. How do cells maintain homeostasis? 6. Where is the cytoplasm in the cell? Describe it. 7. What happens to the cells without flagellum or c ...
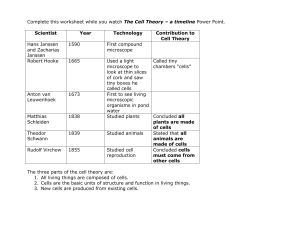
THE CELL HANDOUTS
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
THE CELL HANDOUTS - Wildcat Chemistry
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
... All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced from existing cells. a. ...
7.3 From Cell To Organism
... a. ex- muscle tissue B. Organs 1. A specialized structure with a specific function made up of many different tissues a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood througho ...
... a. ex- muscle tissue B. Organs 1. A specialized structure with a specific function made up of many different tissues a. ex – the heart - made up of muscle, nerve, & other tissues C. Organ System 1. Various organs that carry out a major body function a. ex- circulatory system – carries blood througho ...